Intro
Discover the 5 Army Branches: Infantry, Armor, Aviation, Engineer, and Signal Corps, exploring their roles, responsibilities, and specialties in modern military operations and defense strategies.
The United States Army is one of the most powerful and respected military forces in the world, with a long history of protecting the nation and its interests. The Army is divided into several branches, each with its own unique mission, responsibilities, and areas of expertise. Understanding the different Army branches is essential for anyone interested in joining the military or learning more about the Army's structure and operations. In this article, we will explore the five main Army branches, their roles, and what makes each one unique.
The Army's branches are designed to work together to achieve the military's overall objectives, from combat and peacekeeping to humanitarian aid and disaster relief. Each branch has its own specialized training, equipment, and personnel, allowing the Army to respond to a wide range of situations and challenges. Whether it's fighting on the front lines, providing medical care, or maintaining equipment, every branch plays a vital role in the Army's success.
The Army's branches are also closely tied to the country's national security strategy, with each branch contributing to the overall defense of the nation. From protecting the country's borders to projecting power abroad, the Army's branches work together to deter threats, protect allies, and promote stability around the world. By understanding the different Army branches and their roles, we can gain a deeper appreciation for the complexity and sophistication of the US military.
Introduction to the 5 Army Branches

The five main Army branches are Infantry, Armor, Artillery, Engineer, and Signal Corps. Each branch has its own distinct history, traditions, and culture, shaped by its unique mission and responsibilities. The Infantry branch, for example, is the largest and most combat-oriented branch, with a focus on ground warfare and combat operations. The Armor branch, on the other hand, is responsible for the Army's tank and cavalry units, providing mobile firepower and protection on the battlefield.
Branch 1: Infantry
The Infantry branch is the backbone of the Army, with a long history of bravery and sacrifice. Infantry soldiers are trained to fight on foot, using a range of weapons and tactics to engage and defeat enemy forces. They are the first line of defense, often deploying to the most dangerous and contested areas of the battlefield. Infantry soldiers must be physically fit, mentally tough, and highly adaptable, able to operate in a variety of environments and situations.Infantry Branch Responsibilities

The Infantry branch is responsible for a range of tasks, including combat operations, peacekeeping, and humanitarian aid. Infantry soldiers may be deployed to conduct patrols, raids, and ambushes, or to provide security for key installations and personnel. They may also be involved in training and advising foreign military forces, helping to build capacity and stability in partner nations.
Branch 2: Armor
The Armor branch is responsible for the Army's tank and cavalry units, providing mobile firepower and protection on the battlefield. Armor soldiers operate and maintain a range of armored vehicles, from tanks and infantry fighting vehicles to reconnaissance and scout vehicles. They must be highly trained and skilled, able to operate complex equipment and make quick decisions in high-pressure situations.Armor Branch Equipment

The Armor branch is equipped with some of the most advanced and powerful vehicles in the world, including the M1 Abrams tank and the M2 Bradley infantry fighting vehicle. These vehicles provide a high level of protection and mobility, allowing Armor soldiers to operate in a range of environments and situations. The Armor branch is also responsible for the development and maintenance of armored doctrine, ensuring that the Army's armored forces are always ready to respond to emerging threats and challenges.
Branch 3: Artillery
The Artillery branch is responsible for the Army's firepower, providing indirect fire support to ground units and destroying enemy positions and equipment. Artillery soldiers operate a range of weapons systems, from howitzers and mortars to rocket and missile systems. They must be highly trained and skilled, able to calculate complex firing solutions and adjust their aim in real-time.Artillery Branch Capabilities
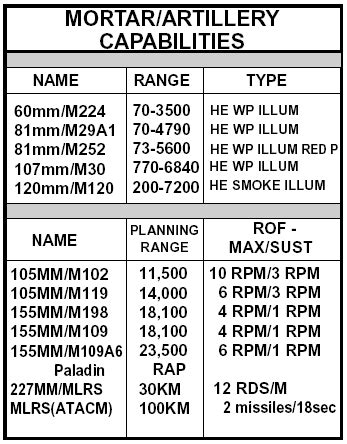
The Artillery branch has a range of capabilities, from providing close support to ground units to conducting deep strikes against enemy command centers and logistics hubs. Artillery soldiers may also be involved in training and advising foreign military forces, helping to build capacity and stability in partner nations. The Artillery branch is constantly evolving, with new technologies and systems being developed to improve its accuracy, range, and lethality.
Branch 4: Engineer
The Engineer branch is responsible for the Army's engineering and construction capabilities, providing critical support to ground units and installations. Engineer soldiers are trained to design, build, and repair a range of infrastructure, from roads and bridges to buildings and fortifications. They must be highly skilled and adaptable, able to operate in a variety of environments and situations.Engineer Branch Projects
The Engineer branch is involved in a range of projects, from building and repairing infrastructure to conducting demolition and explosive ordnance disposal. Engineer soldiers may also be involved in training and advising foreign military forces, helping to build capacity and stability in partner nations. The Engineer branch is constantly evolving, with new technologies and systems being developed to improve its capabilities and effectiveness.
Branch 5: Signal Corps
The Signal Corps branch is responsible for the Army's communications and information systems, providing critical support to ground units and installations. Signal Corps soldiers are trained to design, install, and operate a range of communications systems, from radios and satellites to computer networks and cybersecurity systems. They must be highly skilled and adaptable, able to operate in a variety of environments and situations.Signal Corps Branch Systems

The Signal Corps branch has a range of systems, from tactical radios and satellite communications to strategic networks and cybersecurity systems. Signal Corps soldiers may also be involved in training and advising foreign military forces, helping to build capacity and stability in partner nations. The Signal Corps branch is constantly evolving, with new technologies and systems being developed to improve its capabilities and effectiveness.
Army Branches Image Gallery









What are the 5 main Army branches?
+The 5 main Army branches are Infantry, Armor, Artillery, Engineer, and Signal Corps.
What is the role of the Infantry branch?
+The Infantry branch is the backbone of the Army, with a focus on ground warfare and combat operations.
What is the role of the Armor branch?
+The Armor branch is responsible for the Army's tank and cavalry units, providing mobile firepower and protection on the battlefield.
What is the role of the Artillery branch?
+The Artillery branch is responsible for the Army's firepower, providing indirect fire support to ground units and destroying enemy positions and equipment.
What is the role of the Engineer branch?
+The Engineer branch is responsible for the Army's engineering and construction capabilities, providing critical support to ground units and installations.
In conclusion, the five main Army branches are each unique and play a vital role in the Army's overall mission and success. Whether it's the Infantry branch's focus on ground warfare, the Armor branch's mobile firepower, or the Signal Corps' critical communications systems, every branch contributes to the Army's ability to protect the nation and its interests. By understanding the different Army branches and their roles, we can gain a deeper appreciation for the complexity and sophistication of the US military, and the sacrifices and dedication of the men and women who serve. We invite you to share your thoughts and questions about the Army branches in the comments below, and to explore further the many resources and opportunities available to those interested in joining the military or learning more about the Army's structure and operations.
