Intro
Discover the Marine vs Army difference, exploring military branch comparisons, enlisted roles, and combat training, highlighting key distinctions between Marines and Army personnel in uniform.
The difference between the Marine Corps and the Army is a topic of great interest for many, especially for those considering a career in the military. Both branches are vital components of the United States Armed Forces, but they have distinct roles, responsibilities, and cultures. Understanding these differences is essential for making informed decisions about military service.
The Marine Corps and the Army are both ground combat forces, but they operate in different ways and have unique strengths. The Marine Corps is a rapid-response force that specializes in expeditionary operations, meaning they are designed to deploy quickly and operate in a variety of environments. The Army, on the other hand, is a larger and more diverse branch that encompasses a wide range of specialties, from infantry and armor to engineering and logistics.
The history and traditions of the Marine Corps and the Army also set them apart. The Marine Corps was founded in 1775 as a branch of the Navy, with the primary mission of providing security for naval vessels and conducting amphibious assaults. The Army, established in 1775 as well, has a broader range of historical roles, including fighting wars on multiple continents and providing humanitarian aid.
Branch Missions and Responsibilities

The Marine Corps and the Army have distinct missions and responsibilities. The Marine Corps is responsible for conducting expeditionary operations, which involve deploying quickly and operating in a variety of environments. This includes amphibious assaults, urban warfare, and combat operations in remote or austere areas. The Army, on the other hand, has a broader range of responsibilities, including fighting wars on multiple continents, providing humanitarian aid, and conducting peacekeeping operations.
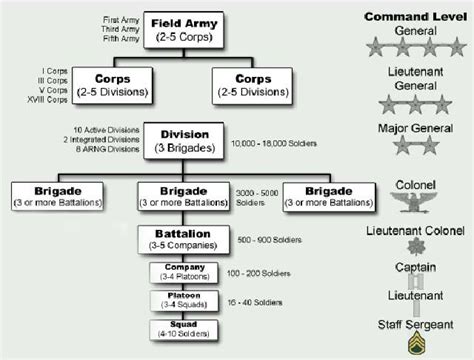
The Marine Corps is organized into several major components, including the Fleet Marine Force, the Force Service Support Group, and the Marine Corps Reserve. The Army is organized into several branches, including the Infantry, Armor, Artillery, and Engineer branches, as well as several specialized branches such as the Special Forces and the Rangers.
Marine Corps Structure
The Marine Corps is a relatively small branch, with approximately 186,000 active-duty personnel. The Marine Corps is organized into several major components, including the Fleet Marine Force, the Force Service Support Group, and the Marine Corps Reserve. The Fleet Marine Force is the largest component of the Marine Corps and is responsible for conducting expeditionary operations.Army Structure
The Army is a larger and more diverse branch, with approximately 475,000 active-duty personnel. The Army is organized into several branches, including the Infantry, Armor, Artillery, and Engineer branches, as well as several specialized branches such as the Special Forces and the Rangers. The Army is also organized into several components, including the Active Component, the Reserve Component, and the National Guard.
The Army's structure is designed to provide a wide range of capabilities, from combat operations to humanitarian aid. The Army's branches are organized into several different types of units, including infantry brigades, armor brigades, and artillery brigades. Each branch has its own unique culture and traditions, and soldiers are often proud to serve in their specific branch.
Enlistment and Commissioning
The process of enlistment and commissioning is also different between the Marine Corps and the Army. To enlist in the Marine Corps, individuals must meet certain eligibility requirements, including being between the ages of 17 and 28, being a U.S. citizen, and meeting certain physical and educational standards. The enlistment process typically involves taking the Armed Services Vocational Aptitude Battery (ASVAB) test, passing a physical fitness test, and completing basic training.To commission as an officer in the Marine Corps, individuals must meet certain eligibility requirements, including having a bachelor's degree, being a U.S. citizen, and meeting certain physical and moral standards. The commissioning process typically involves attending Officer Candidates School (OCS) or the United States Naval Academy.
Training and Education

The training and education programs for the Marine Corps and the Army are also distinct. The Marine Corps is known for its rigorous boot camp, which is designed to test the physical and mental limits of new recruits. The Army's basic training is also challenging, but it is more focused on teaching soldiers specific skills and specialties.
The Marine Corps offers a range of educational programs, including the Marine Corps University, which provides advanced education and training for officers and enlisted personnel. The Army also offers several educational programs, including the United States Military Academy at West Point and the Army University.
Deployment and Operations
The deployment and operations of the Marine Corps and the Army are also different. The Marine Corps is designed to deploy quickly and operate in a variety of environments, including urban and remote areas. The Army is also capable of deploying quickly, but it is often involved in longer-term operations, such as peacekeeping and humanitarian aid.The Marine Corps has a strong tradition of deploying as a cohesive unit, with all elements of the Marine Air-Ground Task Force (MAGTF) working together to achieve a common mission. The Army, on the other hand, often deploys as part of a joint task force, with soldiers from different branches and specialties working together to achieve a common goal.
Culture and Traditions

The culture and traditions of the Marine Corps and the Army are also unique. The Marine Corps has a strong tradition of esprit de corps, with Marines often referring to themselves as a "band of brothers." The Army also has a strong sense of camaraderie, but it is often more focused on the specific branch or unit that a soldier serves in.
The Marine Corps has several unique traditions, including the Marine Corps Birthday, which is celebrated on November 10th, and the Eagle, Globe, and Anchor emblem, which is a symbol of the Marine Corps. The Army also has several unique traditions, including the Army Song and the Army crest.
Uniforms and Insignia
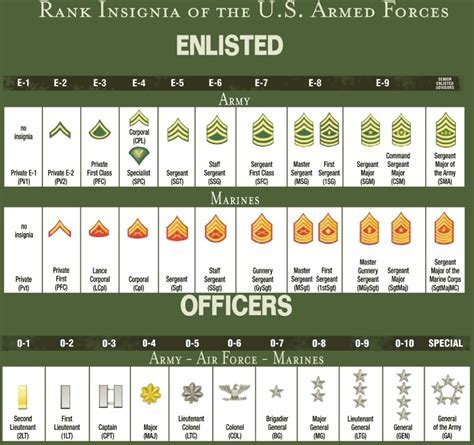
The uniforms and insignia of the Marine Corps and the Army are also distinct. The Marine Corps uniform is known for its distinctive dress blues, which are worn for formal occasions. The Army uniform is also formal, but it is more varied, with different branches and units having their own unique uniforms and insignia.The Marine Corps has several unique insignia, including the Eagle, Globe, and Anchor emblem and the Marine Corps seal. The Army also has several unique insignia, including the Army crest and the branch insignia for different specialties.
Benefits and Drawbacks

The benefits and drawbacks of serving in the Marine Corps and the Army are also different. The Marine Corps is known for its rigorous training and deployment schedule, which can be challenging for some individuals. However, the Marine Corps also offers a strong sense of camaraderie and esprit de corps, which can be a major benefit for those who serve.
The Army also has its benefits and drawbacks. The Army is a larger and more diverse branch, which can provide more opportunities for advancement and specialization. However, the Army's deployment schedule can also be challenging, and the branch's bureaucracy can be frustrating for some individuals.
Conclusion and Final Thoughts
In conclusion, the Marine Corps and the Army are two distinct branches of the United States Armed Forces, each with its own unique culture, traditions, and responsibilities. While both branches are essential to the nation's defense, they offer different experiences and opportunities for those who serve.Ultimately, the decision to join the Marine Corps or the Army depends on an individual's personal preferences and goals. Those who value a strong sense of camaraderie and esprit de corps may prefer the Marine Corps, while those who prefer a more diverse range of specialties and opportunities may prefer the Army.
Marine Vs Army Image Gallery









What is the main difference between the Marine Corps and the Army?
+The main difference between the Marine Corps and the Army is their mission and responsibilities. The Marine Corps is a rapid-response force that specializes in expeditionary operations, while the Army is a larger and more diverse branch that encompasses a wide range of specialties.
What is the culture like in the Marine Corps?
+The culture in the Marine Corps is known for its strong sense of camaraderie and esprit de corps. Marines often refer to themselves as a "band of brothers" and have a strong tradition of loyalty and dedication to their fellow Marines.
What are the benefits of serving in the Army?
+The benefits of serving in the Army include a wide range of opportunities for advancement and specialization, as well as access to education and training programs. The Army also offers a sense of camaraderie and esprit de corps, as well as the opportunity to serve in a variety of different roles and specialties.
How do I decide which branch to join?
+Deciding which branch to join depends on your personal preferences and goals. Consider what you want to achieve in your military career, as well as what type of culture and traditions you prefer. Research the different branches and talk to recruiters and veterans to get a better sense of what each branch has to offer.
What is the deployment schedule like for the Marine Corps and the Army?
+The deployment schedule for the Marine Corps and the Army can vary depending on the specific unit and mission. However, both branches typically deploy for 6-12 months at a time, with some deployments lasting longer or shorter depending on the circumstances.
We hope this article has provided you with a comprehensive understanding of the differences between the Marine Corps and the Army. Whether you're considering a career in the military or simply interested in learning more about these two branches, we encourage you to continue exploring and learning. Share your thoughts and questions in the comments below, and don't forget to share this article with others who may be interested.
