Intro
Discover the 5 key differences, highlighting crucial distinctions, comparisons, and contrasts, to make informed decisions with expert analysis and insights.
The world of technology and innovation is constantly evolving, and with it, the way we live, work, and interact with one another. As we navigate this complex landscape, it's essential to understand the key differences between various concepts, tools, and technologies that shape our daily lives. In this article, we will delve into the 5 key differences between various concepts, exploring their significance, implications, and applications. Whether you're a tech enthusiast, a business professional, or simply someone looking to stay informed, this article aims to provide valuable insights and perspectives on the ever-changing world of technology.
As we embark on this journey, it's crucial to recognize that the distinctions between different concepts are not merely semantic, but rather, they have a profound impact on how we approach problems, design solutions, and interact with one another. By understanding these differences, we can unlock new opportunities, foster innovation, and create a more harmonious and efficient world. So, let's dive into the 5 key differences that will shape the future of technology and beyond.
The importance of recognizing these differences cannot be overstated. In a world where technology is advancing at an unprecedented rate, it's easy to get lost in the noise and confusion. However, by taking the time to understand the nuances and distinctions between various concepts, we can gain a deeper appreciation for the complexities and challenges that lie ahead. Moreover, by acknowledging these differences, we can begin to bridge the gaps between different disciplines, industries, and communities, ultimately leading to a more cohesive and collaborative world.
Introduction to Key Differences
As we explore the 5 key differences, it's essential to recognize that each distinction has its unique characteristics, implications, and applications. Whether it's the difference between artificial intelligence and machine learning, or the distinction between cloud computing and edge computing, each concept has its own strengths, weaknesses, and use cases. By understanding these differences, we can begin to appreciate the complexities and nuances of the technological landscape, ultimately leading to more informed decision-making and innovative solutions.
Key Difference 1: Artificial Intelligence vs Machine Learning
One of the most significant differences in the world of technology is the distinction between artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML). While both concepts are often used interchangeably, they have distinct meanings and applications. AI refers to the broader field of research and development aimed at creating machines that can perform tasks that typically require human intelligence, such as reasoning, problem-solving, and learning. On the other hand, ML is a subset of AI that focuses specifically on the development of algorithms and statistical models that enable machines to learn from data, without being explicitly programmed.
Implications of AI and ML
The implications of AI and ML are far-reaching and profound. As machines become increasingly capable of learning and adapting, we can expect to see significant advancements in areas such as healthcare, finance, and transportation. For instance, AI-powered diagnostic tools can help doctors identify diseases more accurately and quickly, while ML algorithms can optimize financial portfolios and predict market trends. However, as we rely more heavily on AI and ML, we must also address the ethical and societal implications of these technologies, such as job displacement, bias, and privacy concerns.Key Difference 2: Cloud Computing vs Edge Computing
Another significant difference in the world of technology is the distinction between cloud computing and edge computing. Cloud computing refers to the practice of storing, processing, and managing data in remote servers, accessed through the internet. This approach has revolutionized the way we work, collaborate, and store data, enabling greater scalability, flexibility, and cost-effectiveness. On the other hand, edge computing refers to the practice of processing and analyzing data at the edge of the network, closer to the source of the data. This approach is particularly useful for applications that require real-time processing, low latency, and high bandwidth, such as autonomous vehicles, smart homes, and industrial automation.
Applications of Cloud and Edge Computing
The applications of cloud and edge computing are vast and diverse. Cloud computing has enabled the development of software-as-a-service (SaaS) models, platform-as-a-service (PaaS) models, and infrastructure-as-a-service (IaaS) models, which have transformed the way we work, collaborate, and access applications. Edge computing, on the other hand, has enabled the development of smart cities, smart homes, and industrial automation, which require real-time processing and low latency. As we continue to navigate the complexities of cloud and edge computing, we must also address the challenges of security, privacy, and interoperability.Key Difference 3: Blockchain vs Distributed Ledger Technology

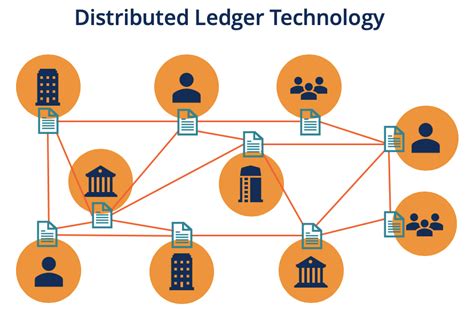
A third significant difference in the world of technology is the distinction between blockchain and distributed ledger technology (DLT). Blockchain refers to a specific type of DLT that uses a decentralized, distributed ledger to record transactions, data, and other information. This approach has enabled the development of cryptocurrencies, such as Bitcoin and Ethereum, which have transformed the way we think about money, value, and trust. On the other hand, DLT refers to a broader category of technologies that enable the creation of decentralized, distributed ledgers, which can be used for a wide range of applications, including supply chain management, identity verification, and voting systems.
Implications of Blockchain and DLT
The implications of blockchain and DLT are far-reaching and profound. As we continue to explore the potential of these technologies, we can expect to see significant advancements in areas such as security, transparency, and accountability. For instance, blockchain-based systems can enable secure, transparent, and tamper-proof voting systems, while DLT-based systems can enable efficient, secure, and transparent supply chain management. However, as we rely more heavily on blockchain and DLT, we must also address the challenges of scalability, interoperability, and regulation.Key Difference 4: Internet of Things (IoT) vs Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT)
A fourth significant difference in the world of technology is the distinction between the Internet of Things (IoT) and the Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT). IoT refers to the network of physical devices, vehicles, home appliances, and other items that are embedded with sensors, software, and connectivity, enabling them to collect and exchange data. This approach has enabled the development of smart homes, smart cities, and wearable devices, which have transformed the way we live, work, and interact with one another. On the other hand, IIoT refers to the use of IoT technologies in industrial settings, such as manufacturing, logistics, and energy management, which require more robust, secure, and reliable connectivity.
Applications of IoT and IIoT
The applications of IoT and IIoT are vast and diverse. IoT has enabled the development of smart homes, smart cities, and wearable devices, which have transformed the way we live, work, and interact with one another. IIoT, on the other hand, has enabled the development of more efficient, productive, and safe industrial processes, which require more robust, secure, and reliable connectivity. As we continue to navigate the complexities of IoT and IIoT, we must also address the challenges of security, privacy, and interoperability.Key Difference 5: Natural Language Processing (NLP) vs Machine Translation
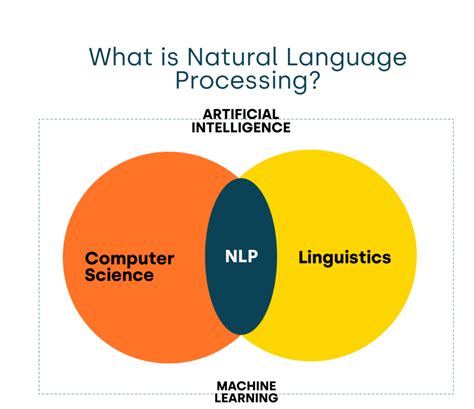
A fifth significant difference in the world of technology is the distinction between Natural Language Processing (NLP) and machine translation. NLP refers to the field of research and development aimed at enabling machines to understand, interpret, and generate human language, which is a fundamental aspect of human communication. This approach has enabled the development of virtual assistants, chatbots, and language translation systems, which have transformed the way we interact with machines and one another. On the other hand, machine translation refers to the specific application of NLP that enables machines to translate text or speech from one language to another, which has enabled more efficient and effective communication across languages and cultures.
Implications of NLP and Machine Translation
The implications of NLP and machine translation are far-reaching and profound. As machines become increasingly capable of understanding and generating human language, we can expect to see significant advancements in areas such as customer service, language education, and cultural exchange. For instance, NLP-powered chatbots can enable more efficient and effective customer service, while machine translation systems can enable more accurate and efficient language translation. However, as we rely more heavily on NLP and machine translation, we must also address the challenges of accuracy, nuance, and cultural sensitivity.5 Key Differences Image Gallery




What is the difference between artificial intelligence and machine learning?
+Artificial intelligence refers to the broader field of research and development aimed at creating machines that can perform tasks that typically require human intelligence, while machine learning is a subset of AI that focuses specifically on the development of algorithms and statistical models that enable machines to learn from data.
What is the difference between cloud computing and edge computing?
+Cloud computing refers to the practice of storing, processing, and managing data in remote servers, accessed through the internet, while edge computing refers to the practice of processing and analyzing data at the edge of the network, closer to the source of the data.
What is the difference between blockchain and distributed ledger technology?
+Blockchain refers to a specific type of distributed ledger technology that uses a decentralized, distributed ledger to record transactions, data, and other information, while distributed ledger technology refers to a broader category of technologies that enable the creation of decentralized, distributed ledgers.
As we conclude our exploration of the 5 key differences, we invite you to share your thoughts, comments, and questions. How do you think these differences will shape the future of technology and beyond? What implications do you see for your industry, community, or personal life? Join the conversation and let's continue to explore the complexities and nuances of the technological landscape. Share this article with your network, and let's work together to create a more informed, innovative, and interconnected world.
