Intro
NATOs naval strength combined showcases collective maritime power, featuring allied fleet capabilities, joint naval operations, and cooperative defense strategies.
The North Atlantic Treaty Organization (NATO) is a military alliance established in 1949, comprising 30 North American and European countries. The alliance's primary goal is to provide collective defense against potential security threats. NATO's naval strength is a crucial component of its overall military capabilities, as it enables the alliance to project power, protect sea lines of communication, and conduct a range of maritime operations. In this article, we will explore the combined naval strength of NATO member countries, highlighting their key capabilities, strengths, and weaknesses.
NATO's naval forces are comprised of a diverse range of ships, submarines, and aircraft, operated by its member countries. The alliance's naval strength is based on the collective capabilities of its member nations, which include the United States, the United Kingdom, France, Germany, Italy, and others. Each member country contributes its own unique set of naval capabilities, which are integrated into the overall NATO naval force structure. The combined naval strength of NATO member countries provides a robust and flexible capability, enabling the alliance to respond to a wide range of maritime challenges.
The United States is the largest contributor to NATO's naval strength, with a vast array of ships, submarines, and aircraft. The US Navy is one of the most powerful naval forces in the world, with a global presence and a wide range of capabilities, including aircraft carriers, amphibious assault ships, and ballistic missile submarines. The US Navy's capabilities are complemented by those of other NATO member countries, such as the United Kingdom, France, and Germany, which operate their own fleets of surface ships, submarines, and aircraft.
NATO Naval Capabilities

NATO's naval capabilities are diverse and extensive, encompassing a range of areas, including:
- Anti-submarine warfare (ASW)
- Anti-surface warfare (ASUW)
- Amphibious warfare
- Mine countermeasures (MCM)
- Maritime patrol and reconnaissance
- Naval gunfire support
- Ballistic missile defense (BMD)
These capabilities are provided by a range of platforms, including surface ships, submarines, aircraft, and unmanned systems. NATO's naval forces are also supported by a range of enabling capabilities, such as logistics, communications, and intelligence, surveillance, and reconnaissance (ISR).
NATO Member Country Naval Contributions
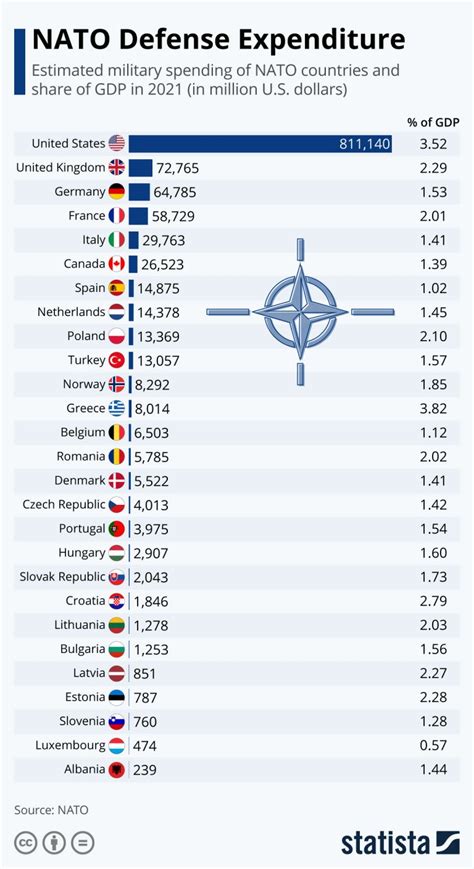
Each NATO member country contributes its own unique set of naval capabilities to the alliance. The United States, for example, provides the majority of NATO's naval capabilities, including its aircraft carriers, amphibious assault ships, and ballistic missile submarines. The United Kingdom, France, and Germany also make significant contributions, operating their own fleets of surface ships, submarines, and aircraft.
Other NATO member countries, such as Italy, Spain, and the Netherlands, also contribute to the alliance's naval capabilities, operating a range of ships, submarines, and aircraft. These contributions are often tailored to specific areas of expertise, such as mine countermeasures or maritime patrol and reconnaissance.
NATO Naval Operations

NATO's naval forces conduct a range of operations, including:
- Maritime security operations
- Counter-piracy operations
- Humanitarian assistance and disaster response
- Maritime interdiction operations
- Amphibious assault operations
These operations are often conducted in conjunction with other NATO forces, such as air and land components, and may involve cooperation with other international organizations, such as the United Nations or the European Union.
NATO Naval Strengths and Weaknesses

NATO's naval strength has several key advantages, including:
- Global presence: NATO's naval forces have a global presence, with ships and aircraft operating in all of the world's oceans.
- Diverse capabilities: NATO's naval forces have a wide range of capabilities, including anti-submarine warfare, anti-surface warfare, and amphibious warfare.
- Integrated command structure: NATO's naval forces are integrated into a single command structure, enabling effective coordination and cooperation between different national forces.
However, NATO's naval strength also has some weaknesses, including:
- Aging fleets: Many NATO member countries are operating aging fleets, which can limit their effectiveness and availability.
- Budget constraints: NATO member countries are facing budget constraints, which can limit their ability to invest in new ships, submarines, and aircraft.
- Dependence on US capabilities: NATO's naval strength is heavily dependent on US capabilities, which can create vulnerabilities if the US is unable or unwilling to contribute its forces.
Future of NATO Naval Strength

The future of NATO's naval strength will depend on several factors, including:
- Investment in new technologies: NATO member countries will need to invest in new technologies, such as unmanned systems and cyber capabilities, to remain effective in the maritime domain.
- Cooperation with other international organizations: NATO will need to cooperate with other international organizations, such as the European Union, to address common maritime challenges.
- Development of new operational concepts: NATO will need to develop new operational concepts, such as distributed maritime operations, to take advantage of emerging technologies and capabilities.
NATO Naval Modernization

NATO's naval modernization efforts are focused on several key areas, including:
- Unmanned systems: NATO is investing in unmanned systems, such as unmanned aerial vehicles (UAVs) and unmanned underwater vehicles (UUVs), to enhance its maritime surveillance and reconnaissance capabilities.
- Cyber capabilities: NATO is developing its cyber capabilities to protect its naval forces from cyber threats and to conduct cyber operations against adversaries.
- Distributed maritime operations: NATO is developing new operational concepts, such as distributed maritime operations, to take advantage of emerging technologies and capabilities.
NATO Naval Cooperation

NATO's naval cooperation efforts are focused on several key areas, including:
- Cooperation with other international organizations: NATO is cooperating with other international organizations, such as the European Union, to address common maritime challenges.
- Cooperation with non-NATO countries: NATO is cooperating with non-NATO countries, such as Australia and Japan, to enhance its maritime capabilities and to address common security challenges.
- Development of new partnerships: NATO is developing new partnerships, such as the NATO-Russia Council, to enhance its cooperation with other countries and to address common security challenges.
Gallery of NATO Naval Images
NATO Naval Image Gallery










What is the purpose of NATO's naval strength?
+The purpose of NATO's naval strength is to provide a collective defense against potential security threats, protect sea lines of communication, and conduct a range of maritime operations.
Which countries contribute to NATO's naval strength?
+NATO's naval strength is contributed by its member countries, including the United States, the United Kingdom, France, Germany, Italy, and others.
What are the key capabilities of NATO's naval forces?
+NATO's naval forces have a wide range of capabilities, including anti-submarine warfare, anti-surface warfare, amphibious warfare, mine countermeasures, maritime patrol and reconnaissance, naval gunfire support, and ballistic missile defense.
How does NATO's naval strength contribute to global security?
+NATO's naval strength contributes to global security by providing a collective defense against potential security threats, protecting sea lines of communication, and conducting a range of maritime operations to promote stability and security in the maritime domain.
What are the challenges facing NATO's naval strength?
+NATO's naval strength faces several challenges, including aging fleets, budget constraints, and dependence on US capabilities. These challenges can limit the effectiveness and availability of NATO's naval forces.
In conclusion, NATO's naval strength is a critical component of the alliance's overall military capabilities, providing a collective defense against potential security threats and promoting stability and security in the maritime domain. The combined naval strength of NATO member countries provides a robust and flexible capability, enabling the alliance to respond to a wide range of maritime challenges. However, NATO's naval strength also faces several challenges, including aging fleets, budget constraints, and dependence on US capabilities. To address these challenges, NATO member countries will need to invest in new technologies, develop new operational concepts, and enhance their cooperation with other international organizations. By doing so, NATO can ensure that its naval strength remains a vital component of its overall military capabilities, promoting stability and security in the maritime domain for years to come. We invite you to share your thoughts on the importance of NATO's naval strength and its role in promoting global security. Please leave a comment below or share this article with others to continue the conversation.
