Intro
Discover the 5 key differences, highlighting crucial distinctions, comparisons, and contrasts, to make informed decisions with expert analysis and insights.
The world of technology and innovation is constantly evolving, and with it, the way we approach various aspects of our lives. One such area that has seen significant advancements is the realm of computing and data storage. In this context, understanding the nuances between different types of computing and storage solutions is crucial for making informed decisions. Here, we delve into the realm of computing and explore the 5 key differences between various concepts, highlighting their importance and applications.
In recent years, the terms cloud computing, edge computing, and others have become increasingly popular, but what do they mean, and how do they differ from one another? These questions are not just pertinent for tech enthusiasts but also for businesses and individuals looking to leverage technology to enhance their operations and productivity. The distinctions between these computing paradigms are not just about where data is processed but also about the efficiency, security, and cost-effectiveness they offer.
As we navigate through the complexities of the digital age, it's essential to grasp these differences to make the most out of the technological advancements at our disposal. Whether it's about improving response times, reducing latency, enhancing data security, or optimizing costs, understanding the unique attributes of each computing and storage model is vital. In the following sections, we will explore these differences in detail, providing insights into their working mechanisms, benefits, and practical applications.
Introduction to Computing Paradigms
To begin with, let's introduce the primary computing paradigms we will be discussing: cloud computing, edge computing, fog computing, hybrid computing, and quantum computing. Each of these has its unique characteristics, advantages, and use cases. Cloud computing, for instance, involves delivering computing services over the internet, allowing for on-demand access to a shared pool of configurable computing resources. Edge computing, on the other hand, brings computation closer to the source of the data, reducing latency and improving real-time processing capabilities.
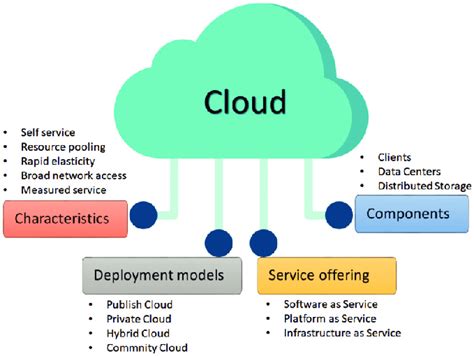
Cloud Computing

Cloud computing has revolutionized the way businesses and individuals approach data storage and processing. By providing scalable, on-demand access to computing services and resources, cloud computing offers a high degree of flexibility and cost savings. The benefits of cloud computing include reduced capital expenditure, enhanced scalability, and improved reliability. However, it also raises concerns about data security and dependence on internet connectivity.
Benefits of Cloud Computing
The advantages of cloud computing can be summarized as follows: - Scalability: Resources can be easily scaled up or down according to needs. - Cost-effectiveness: Reduces the need for upfront capital expenditures. - Reliability: Offers high uptime and redundancy. - Accessibility: Data and applications can be accessed from anywhere.Edge Computing

Edge computing is designed to reduce latency and improve real-time processing by bringing computation closer to the source of the data. This paradigm is particularly useful in applications that require immediate processing and analysis of data, such as IoT devices, autonomous vehicles, and smart homes. Edge computing enhances the efficiency of data processing, reduces bandwidth usage, and improves the overall performance of applications.
Applications of Edge Computing
Edge computing has a wide range of applications, including: - IoT (Internet of Things) - Real-time analytics - Autonomous vehicles - Smart homes and cities - Industrial automationFog Computing
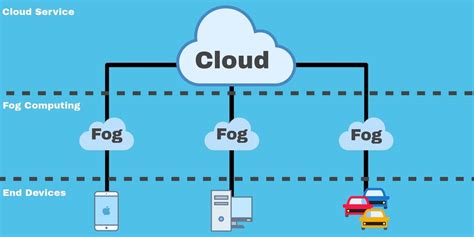
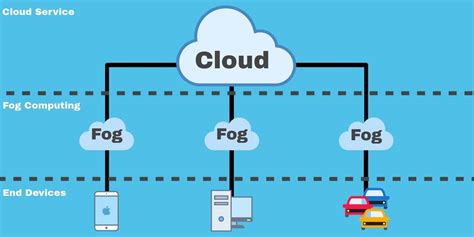
Fog computing can be seen as an extension of cloud computing, where data processing occurs in a fog node or an edge device, rather than in the cloud or a centralized data center. This model is beneficial for applications that require low latency and are geographically distributed. Fog computing supports a wide range of applications, from smart energy management to real-time video processing.
Working Mechanism of Fog Computing
Fog computing works by: - Collecting data from end devices - Processing data in fog nodes - Reducing the amount of data sent to the cloud - Enhancing real-time processing capabilitiesHybrid Computing
Hybrid computing combines different computing models, such as cloud, edge, and on-premises computing, to leverage the strengths of each. This approach allows for flexibility, scalability, and improved security. Hybrid computing is particularly useful for organizations that have diverse computing needs, ranging from public cloud services for web applications to on-premises infrastructure for sensitive data.
Benefits of Hybrid Computing
The benefits of hybrid computing include: - Flexibility: Combines different computing models. - Scalability: Offers scalable resources. - Security: Enhances data security by allowing sensitive data to be stored on-premises.Quantum Computing
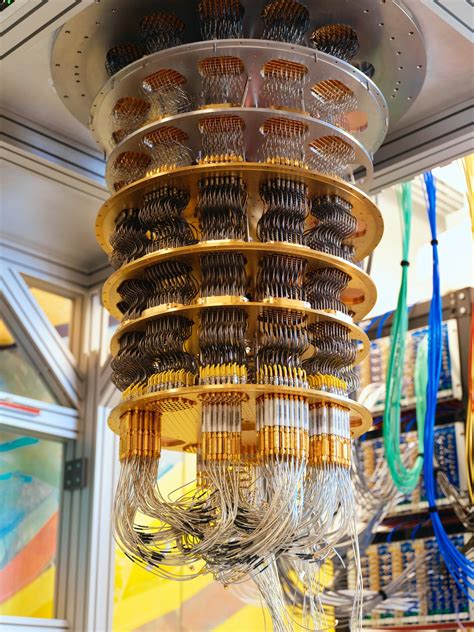

Quantum computing represents a significant leap in computing power, leveraging quantum-mechanical phenomena to perform computations that are beyond the capabilities of classical computers. This technology has the potential to solve complex problems in fields such as cryptography, optimization, and simulation. However, quantum computing is still in its early stages, and significant technical challenges need to be overcome before it becomes widely available.
Applications of Quantum Computing
Quantum computing has potential applications in: - Cryptography: Breaking and making unbreakable codes. - Optimization: Solving complex optimization problems. - Simulation: Simulating complex systems and processes.Computing Paradigms Image Gallery






What is Cloud Computing?
+Cloud computing is a model for delivering computing services over the internet, where resources such as servers, storage, databases, software, and applications are provided as a service to users on-demand.
How Does Edge Computing Work?
+Edge computing works by processing data closer to the source, reducing latency and bandwidth usage. It involves deploying computing resources and services at the edge of the network, near the devices and data sources.
What Are the Benefits of Hybrid Computing?
+The benefits of hybrid computing include flexibility, scalability, and improved security. It allows organizations to leverage the strengths of different computing models, such as cloud, edge, and on-premises computing, to meet their diverse computing needs.
In conclusion, understanding the 5 key differences between various computing paradigms is essential for navigating the complex landscape of modern computing. Each paradigm, from cloud computing to quantum computing, offers unique benefits and is suited for specific applications and use cases. As technology continues to evolve, the ability to differentiate between these computing models will become increasingly important for individuals and organizations looking to harness the power of technology to drive innovation and growth. We invite you to share your thoughts on the future of computing and how these paradigms will shape our digital world. Your insights and experiences are valuable, and we look forward to continuing this conversation in the comments section below.
