Intro
Discover the 5 ways Chinas S20 bomber enhances military capabilities, featuring advanced stealth technology, supersonic speeds, and precision-guided munitions, revolutionizing aerial warfare with strategic bomber advancements.
The development of the Xian H-20, also referred to as the China S20 bomber, marks a significant milestone in China's military aviation capabilities. This stealth bomber is designed to provide the People's Liberation Army Air Force (PLAAF) with a long-range, strategic bombing capability, enhancing China's ability to project power beyond its borders. As we delve into the implications and characteristics of the H-20, it's essential to consider the broader strategic context and how this aircraft fits into China's military modernization efforts.
The introduction of the H-20 bomber is part of China's comprehensive military modernization, aimed at transforming the PLAAF into a world-class air force capable of conducting a wide range of missions, from air defense to long-range strikes. The H-20's development reflects China's desire to enhance its deterrence capabilities and to be able to respond to threats at greater distances. This strategic bomber is expected to play a crucial role in China's future military operations, offering a significant improvement over existing capabilities.
Given the secrecy surrounding the H-20's development, much of the information available is speculative or based on official revelations and observations from military parades and exercises. However, several key aspects of the H-20 have become clearer over time, including its stealth design, potential armament, and the roles it is expected to fulfill within the PLAAF.
Introduction to the H-20 Bomber

The Xian H-20 is a subsonic, stealth strategic bomber designed to evade detection by radar. Its flying wing design, similar to the Northrop Grumman B-2 Spirit, is optimized for stealth, reducing its radar cross-section and making it harder to detect and track. This design choice reflects the importance of survivability in modern air warfare, where the ability to penetrate defended airspace is crucial for the success of bombing missions.
Stealth Capabilities
The H-20's stealth capabilities are among its most significant features, allowing it to operate in contested airspace with a higher degree of survivability than non-stealth aircraft. Stealth technology involves the use of materials and designs that absorb or scatter radar waves, reducing the amount of radar energy that is reflected back to the radar antenna. This makes stealth aircraft like the H-20 much harder to detect, especially at long range.Operational Roles of the H-20

The H-20 is expected to fulfill several operational roles within the PLAAF, including strategic bombing, conventional deterrence, and potentially even anti-ship missions. Its long-range capability, coupled with its stealth design, makes it an ideal platform for conducting surprise attacks deep within enemy territory. The bomber's ability to carry a variety of munitions, including precision-guided bombs and possibly hypersonic missiles, further enhances its versatility.
Long-Range Capability
One of the H-20's most significant advantages is its reported long-range capability, which could potentially allow it to strike targets without needing to refuel. This feature is crucial for China, given its vast territory and the distances involved in projecting power across the Asia-Pacific region or even beyond. The ability to conduct long-range missions without reliance on forward bases or aerial refueling enhances the PLAAF's strategic flexibility and response time.Implications for Regional Security

The introduction of the H-20 bomber has significant implications for regional security. The bomber's capabilities will likely influence the strategic calculations of China's neighbors and other regional players, potentially leading to an arms race or increased military cooperation among affected states. The H-20's long-range strike capability also raises concerns about the stability of the nuclear deterrence balance in the region, as it could potentially be used to deliver nuclear weapons.
Deterrence and Stability
The H-20's role in China's nuclear deterrence strategy is a subject of considerable debate. While its primary mission is likely conventional, the bomber's ability to carry nuclear weapons could enhance China's deterrence posture. However, this also introduces complexities related to command and control, strategic stability, and the risk of miscalculation, especially in a crisis scenario.Technological Challenges and Developments

The development of the H-20 bomber presents several technological challenges, including the integration of stealth materials, advanced avionics, and potentially complex mission systems. Overcoming these challenges is crucial not only for the success of the H-20 program but also for China's broader efforts to develop indigenous, high-tech military capabilities.
Engine Technology
One of the critical technological challenges faced by the H-20's developers is the engine. A strategic bomber requires powerful, efficient, and reliable engines to achieve its intended range and payload capabilities. China has been working to develop advanced engine technologies, but the availability of suitable engines for the H-20 has been a subject of speculation and concern.International Reactions and Cooperation

The international community's reaction to the H-20 has been varied, reflecting the complexities of modern geopolitical relations. While some nations have expressed concern over the bomber's implications for regional and global security, others have seen it as an opportunity for cooperation or a symbol of China's rising military prowess.
Cooperation and Deterrence
The H-20's development also highlights the potential for international cooperation on security issues. As nations respond to the bomber's capabilities, there may be increased dialogue on arms control, confidence-building measures, and cooperative security arrangements aimed at reducing the risks associated with advanced military technologies.H-20 Bomber Image Gallery
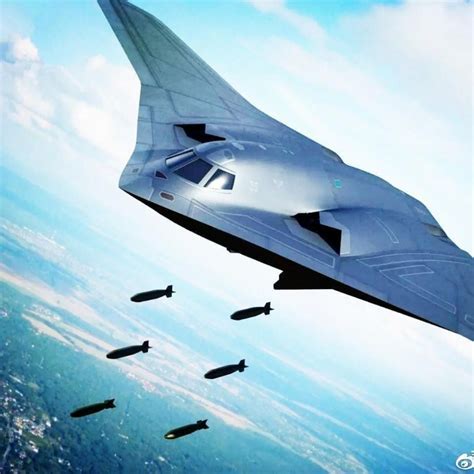







What is the primary role of the H-20 bomber?
+The primary role of the H-20 bomber is strategic bombing, providing the PLAAF with a long-range, stealth capability to conduct missions deep within enemy territory.
What are the implications of the H-20 for regional security?
+The H-20 bomber has significant implications for regional security, potentially altering the strategic balance and prompting responses from neighboring countries and other regional actors.
How does the H-20 reflect China's military modernization efforts?
+The H-20 bomber is a key component of China's military modernization, demonstrating advances in stealth technology, engine design, and strategic capabilities, and underscoring China's commitment to developing a world-class military.
What are the potential challenges in the development and deployment of the H-20?
+Challenges include overcoming technological hurdles, such as engine development and stealth materials, as well as integrating the bomber into existing command and control structures and ensuring its operational effectiveness.
How might the H-20 influence international relations and security dynamics?
+The H-20 could lead to increased tensions and an arms race in the region, prompt re-evaluations of military alliances and security arrangements, and encourage dialogue on arms control and cooperative security measures.
As the world continues to watch the development and deployment of the H-20 bomber, it's clear that this aircraft will play a significant role in shaping the future of military aviation and strategic deterrence. The implications of the H-20 extend far beyond China's borders, influencing regional security dynamics, international relations, and the global balance of power. As such, understanding the H-20's capabilities, limitations, and potential roles is essential for policymakers, strategists, and anyone interested in the evolving landscape of modern warfare. We invite readers to share their thoughts on the H-20 bomber and its implications for global security, and to explore further the complex issues surrounding the development and deployment of advanced military technologies.
