Intro
Compare Buran and Space Shuttle programs, exploring reusable spacecraft, orbital vehicles, and Soviet-era space technology advancements, highlighting key differences and similarities.
The space race between the United States and the Soviet Union was a defining characteristic of the Cold War era. One of the most notable aspects of this competition was the development of reusable spacecraft, with the United States producing the Space Shuttle and the Soviet Union creating the Buran. While both programs were ambitious and groundbreaking, they had distinct differences in design, functionality, and ultimate fate. Understanding these differences provides valuable insights into the engineering, political, and economic contexts of the time.
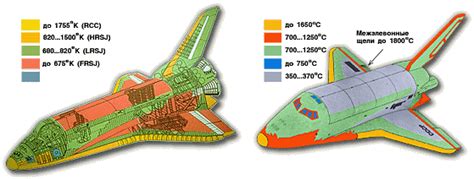
The Space Shuttle, officially called the Space Transportation System (STS), was the first operational orbital spacecraft designed to be reusable. It consisted of a spaceplane, a solid rocket booster, and an external fuel tank. The Space Shuttle was capable of carrying crew and cargo into low Earth orbit, conducting space missions, and returning to Earth like an airplane. Its development began in the 1970s, with the first launch occurring in 1981. Over its operational lifetime, the Space Shuttle program successfully conducted numerous missions, including deploying satellites, building the International Space Station, and servicing the Hubble Space Telescope.
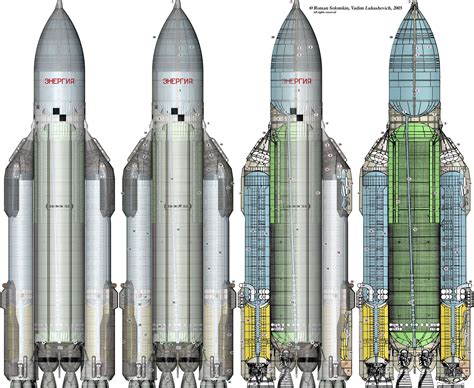
On the other hand, the Buran program was the Soviet response to the Space Shuttle, aiming to create a similar reusable spacecraft. Buran, which means "snowstorm" or "blizzard" in Russian, was designed to be launched into space by the Energia rocket and then return to Earth, landing like a conventional aircraft. Although it shared a similar concept with the Space Shuttle, the Buran had several distinct features, including its lack of main engines (it relied on the Energia rocket for ascent) and a more automated flight control system. The Buran made its first and only unmanned flight in 1988, successfully completing a single orbit of Earth and landing back at the Baikonur Cosmodrome.
Design and Development
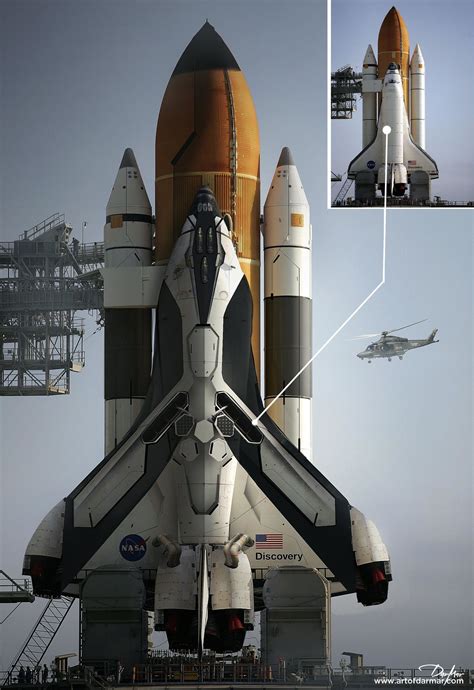

The design and development of the Space Shuttle and Buran were influenced by the technological capabilities and strategic priorities of their respective countries. The Space Shuttle was designed to be a multi-purpose vehicle, capable of carrying out a variety of missions, from satellite deployment to space station construction. Its development involved significant technological advancements, including the creation of thermal protection systems to withstand re-entry and the development of a reliable solid rocket booster.
In contrast, the Buran was designed with a focus on unmanned operations, although it was theoretically capable of carrying a crew. Its development was marked by secrecy and a lack of transparency, which made it difficult for outsiders to assess its capabilities and limitations. The Buran's automated flight control system and its ability to launch and recover in a fully automated mode were among its most notable features, reflecting the Soviet emphasis on unmanned spaceflight capabilities.
Operational History

The operational history of the Space Shuttle and Buran highlights their differing fates and the challenges they faced. The Space Shuttle program operated for over three decades, with 135 missions conducted between 1981 and 2011. Despite facing significant challenges, including the tragic losses of the Challenger and Columbia, the program achieved numerous successes and played a critical role in the development of the International Space Station.
The Buran, on the other hand, had a very short operational history. After its single unmanned flight in 1988, the program was canceled due to a combination of factors, including the dissolution of the Soviet Union, lack of funding, and shifting priorities within the Russian space program. The Buran spacecraft itself was destroyed in 2002 when the hangar it was stored in collapsed, marking a tragic end to a program that had once held such promise.
Technological Legacy

The technological legacy of the Space Shuttle and Buran programs is significant, with both contributing to advancements in materials science, propulsion systems, and computer technology. The Space Shuttle's thermal protection system, for example, was a crucial innovation that enabled the spacecraft to withstand the extreme temperatures of re-entry. Similarly, the Buran's automated flight control system pushed the boundaries of what was thought possible in terms of autonomous spaceflight.
Both programs also inspired future generations of engineers and scientists, demonstrating the potential for reusable spacecraft to revolutionize access to space. The lessons learned from these programs, including the importance of robust design, rigorous testing, and adaptive management, continue to influence the development of modern spacecraft.
Economic and Political Context

The economic and political context in which the Space Shuttle and Buran programs were developed and operated played a critical role in their outcomes. The Space Shuttle program was a product of the United States' Cold War strategy, aiming to demonstrate technological superiority and maintain a leadership position in space exploration. The program's high cost and the challenges it faced, including the loss of two orbiters, were tolerated due to its strategic importance.
The Buran program, on the other hand, was heavily influenced by the economic and political turmoil of the late Soviet era. The program's cancellation was a direct result of the Soviet Union's dissolution and the subsequent economic crisis that Russia faced. The lack of funding and the shifting priorities of the Russian space program meant that the Buran, despite its technological achievements, was not given the opportunity to fulfill its potential.
Comparison of Key Features

A comparison of the key features of the Space Shuttle and Buran highlights their similarities and differences:
- Reusability: Both spacecraft were designed to be reusable, significantly reducing the cost per launch compared to expendable rockets.
- Payload Capacity: The Space Shuttle had a larger payload capacity than the Buran, making it more versatile for a variety of missions.
- Crew Capacity: The Space Shuttle was designed to carry a crew of up to seven, while the Buran was initially designed for unmanned flights but had the potential for crewed missions.
- Launch System: The Space Shuttle used solid rocket boosters and an external fuel tank, whereas the Buran was launched using the Energia rocket.
- Operational History: The Space Shuttle had a long and storied operational history, while the Buran made only one unmanned flight.
Gallery of Buran and Space Shuttle Images
Buran and Space Shuttle Image Gallery








Frequently Asked Questions
What was the main purpose of the Space Shuttle program?
+The main purpose of the Space Shuttle program was to provide a reusable spacecraft capable of carrying crew and cargo into low Earth orbit, conducting space missions, and returning to Earth.
How many flights did the Buran make?
+The Buran made only one unmanned flight in 1988.
What was the significance of the Energia rocket in the Buran program?
+The Energia rocket was the launch vehicle used for the Buran spacecraft, providing the necessary thrust to reach orbit.
Why was the Buran program canceled?
+The Buran program was canceled due to a combination of factors, including the dissolution of the Soviet Union, lack of funding, and shifting priorities within the Russian space program.
What was the legacy of the Space Shuttle and Buran programs?
+Both programs contributed significantly to the advancement of space technology, inspiring future generations and paving the way for modern reusable spacecraft.
In conclusion, the comparison between the Space Shuttle and Buran offers a fascinating glimpse into the technological, political, and economic complexities of the space race during the Cold War era. While both programs achieved remarkable technological feats, their differing operational histories and ultimate fates reflect the broader strategic and economic contexts in which they were developed. As the world continues to push the boundaries of space exploration, the lessons learned from these pioneering programs will remain invaluable. We invite readers to share their thoughts on the significance of the Space Shuttle and Buran programs and how they have influenced modern space exploration. Your insights and comments are welcome, and we encourage you to explore further the rich history and technological achievements of these iconic spacecraft.
