Intro
Discover the 5 Army Branches: Infantry, Armor, Aviation, Engineer, and Signal Corps, exploring their roles, responsibilities, and specialties in modern military operations and defense strategies.
The United States Army is a vast and complex organization, comprising various branches that work together to achieve its mission. Each branch has its unique role, responsibilities, and areas of expertise, contributing to the overall effectiveness of the Army. Understanding the different Army branches is essential for anyone interested in joining the military or learning more about the inner workings of the US Army.
The Army's structure is designed to provide a wide range of capabilities, from combat and support operations to administrative and logistical functions. The five main Army branches are the backbone of the organization, and they work together to ensure the Army's success in various missions and operations. In this article, we will delve into the world of the five Army branches, exploring their roles, responsibilities, and areas of expertise.
The US Army is one of the most powerful and respected military forces in the world, with a long history of bravery, sacrifice, and service. From the Revolutionary War to the present day, the Army has played a vital role in defending the United States and its interests. The five Army branches are an integral part of this tradition, working together to protect the nation and its people.
Introduction to the 5 Army Branches
The five Army branches are Infantry, Armor, Artillery, Engineer, and Signal Corps. Each branch has its unique history, traditions, and culture, shaped by its specific role and responsibilities within the Army. The branches work together to provide a comprehensive range of capabilities, from combat and support operations to administrative and logistical functions.
The Infantry branch is the largest and most deployable branch of the Army, responsible for conducting ground combat operations. The Armor branch operates and maintains tanks and other armored vehicles, providing mobile firepower and shock action on the battlefield. The Artillery branch provides indirect fire support to ground units, using cannons, rockets, and missiles to attack enemy positions.
The Engineer branch is responsible for constructing and maintaining infrastructure, such as roads, bridges, and buildings, as well as conducting demolitions and explosives operations. The Signal Corps branch provides communication and information systems support to the Army, enabling units to communicate and share information effectively.
Infantry Branch

The Infantry branch is the backbone of the Army, responsible for conducting ground combat operations. Infantry soldiers are trained to engage and defeat enemy forces, using a range of weapons and tactics to achieve their objectives. The Infantry branch is divided into several specialties, including rifleman, grenadier, and mortarman, each with its unique role and responsibilities.
Infantry soldiers undergo rigorous training to prepare them for the physical and mental demands of combat. They learn how to use various weapons, such as rifles, machine guns, and grenades, as well as how to navigate and communicate in complex environments. Infantry units are often deployed to remote and hostile areas, where they must be self-sufficient and able to operate independently.
The Infantry branch has a long and proud history, with many notable battles and campaigns throughout American history. From the Revolutionary War to the present day, Infantry soldiers have played a vital role in defending the United States and its interests.
Armor Branch

The Armor branch operates and maintains tanks and other armored vehicles, providing mobile firepower and shock action on the battlefield. Armor soldiers are trained to crew and maintain these vehicles, using them to attack enemy positions and protect friendly forces.
The Armor branch is divided into several specialties, including tank crewman, armored cavalryman, and armor officer. Armor soldiers undergo training to learn how to operate and maintain armored vehicles, as well as how to use them effectively in combat.
The Armor branch has a long history, dating back to World War I. Since then, armor has played a vital role in many conflicts, including World War II, the Korean War, and the Gulf War. Armor soldiers have earned a reputation for their bravery and skill, using their vehicles to break through enemy lines and achieve decisive victories.
Artillery Branch

The Artillery branch provides indirect fire support to ground units, using cannons, rockets, and missiles to attack enemy positions. Artillery soldiers are trained to operate and maintain these systems, using them to provide precise and effective firepower in support of ground operations.
The Artillery branch is divided into several specialties, including cannon crewman, rocket crewman, and missile crewman. Artillery soldiers undergo training to learn how to operate and maintain artillery systems, as well as how to use them effectively in combat.
The Artillery branch has a long history, dating back to the early days of the US Army. Since then, artillery has played a vital role in many conflicts, including the Civil War, World War I, and World War II. Artillery soldiers have earned a reputation for their accuracy and effectiveness, using their systems to provide critical firepower in support of ground operations.
Engineer Branch
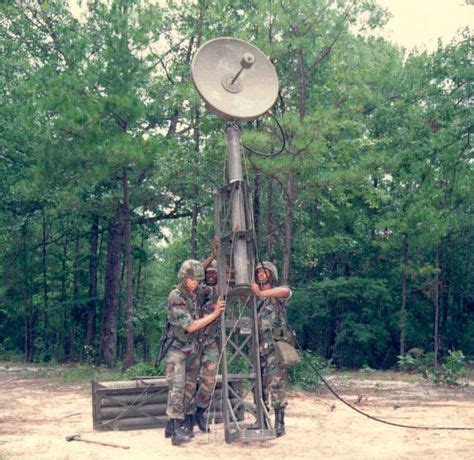
The Engineer branch is responsible for constructing and maintaining infrastructure, such as roads, bridges, and buildings, as well as conducting demolitions and explosives operations. Engineer soldiers are trained to use a range of equipment and techniques to achieve their objectives, including bulldozers, cranes, and explosives.
The Engineer branch is divided into several specialties, including combat engineer, construction engineer, and explosives expert. Engineer soldiers undergo training to learn how to operate and maintain equipment, as well as how to use it effectively in combat and support operations.
The Engineer branch has a long history, dating back to the early days of the US Army. Since then, engineers have played a vital role in many conflicts, including the Civil War, World War I, and World War II. Engineer soldiers have earned a reputation for their skill and versatility, using their expertise to construct and maintain critical infrastructure in support of military operations.
Signal Corps Branch

The Signal Corps branch provides communication and information systems support to the Army, enabling units to communicate and share information effectively. Signal Corps soldiers are trained to operate and maintain a range of communication systems, including radios, satellites, and computer networks.
The Signal Corps branch is divided into several specialties, including signal support systems specialist, network switching systems operator, and satellite communications operator. Signal Corps soldiers undergo training to learn how to operate and maintain communication systems, as well as how to use them effectively in support of military operations.
The Signal Corps branch has a long history, dating back to the early days of the US Army. Since then, signal soldiers have played a vital role in many conflicts, including World War I, World War II, and the Gulf War. Signal Corps soldiers have earned a reputation for their expertise and reliability, using their skills to provide critical communication and information systems support to the Army.
Gallery of Army Branches
Army Branches Image Gallery









What are the five main Army branches?
+The five main Army branches are Infantry, Armor, Artillery, Engineer, and Signal Corps.
What is the role of the Infantry branch?
+The Infantry branch is responsible for conducting ground combat operations, using a range of weapons and tactics to engage and defeat enemy forces.
What is the role of the Armor branch?
+The Armor branch operates and maintains tanks and other armored vehicles, providing mobile firepower and shock action on the battlefield.
What is the role of the Artillery branch?
+The Artillery branch provides indirect fire support to ground units, using cannons, rockets, and missiles to attack enemy positions.
What is the role of the Engineer branch?
+The Engineer branch is responsible for constructing and maintaining infrastructure, such as roads, bridges, and buildings, as well as conducting demolitions and explosives operations.
In conclusion, the five Army branches are the backbone of the US Army, providing a comprehensive range of capabilities and expertise to support military operations. Each branch has its unique role and responsibilities, and they work together to achieve the Army's mission. Whether you're interested in joining the military or simply learning more about the US Army, understanding the five Army branches is essential. We hope this article has provided you with a deeper understanding of the Army branches and their importance in defending the United States and its interests. If you have any questions or comments, please don't hesitate to reach out. Share this article with others who may be interested in learning more about the US Army and its branches.
