Intro
Discover 5 fascinating belt fed machine gun facts, exploring fully automatic firearms, ammunition feeding systems, and military applications, revealing the history and mechanics of these powerful guns.
The world of firearms is vast and fascinating, with various types of guns serving different purposes. Among these, belt-fed machine guns stand out for their distinctive design and functionality. These guns are not just interesting to learn about, but they also play significant roles in military and defense contexts. Here's an introduction to belt-fed machine guns and why they're so intriguing.
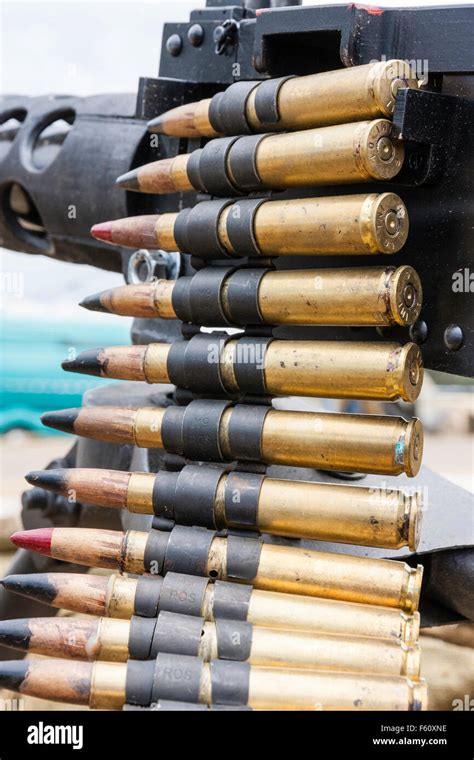
Belt-fed machine guns are designed to fire automatically, using a belt of linked cartridges. This design allows for sustained fire over a long period, making them particularly useful in combat situations where suppressive fire is needed. The history of belt-fed machine guns dates back to the late 19th and early 20th centuries, with continuous development to improve their efficiency, reliability, and firepower.
The significance of belt-fed machine guns extends beyond their military applications. They also represent a pinnacle of firearms engineering, showcasing the ability to design and manufacture weapons that can deliver high volumes of fire accurately and reliably. For enthusiasts and historians alike, studying belt-fed machine guns offers insights into the evolution of weaponry and the technological advancements that have shaped modern combat.
Introduction to Belt Fed Machine Guns

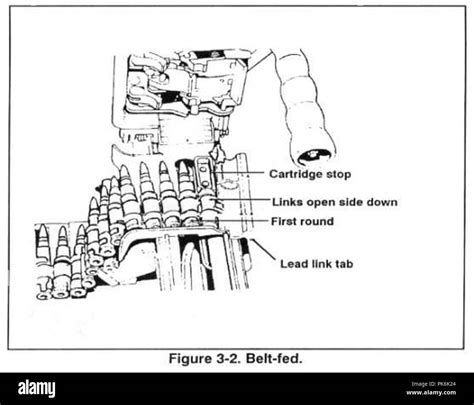
Belt-fed machine guns operate by using a belt that holds the cartridges together in a linked sequence. This belt is fed into the gun, which then strips the cartridges from the belt and chambers them one at a time. The gun fires each cartridge, ejects the spent casing, and then repeats the process with the next cartridge in the belt. This mechanism allows for continuous firing until the belt is exhausted, making belt-fed machine guns highly effective for laying down suppressive fire or engaging multiple targets quickly.
One of the key advantages of belt-fed machine guns is their ability to maintain a high rate of fire over an extended period. This capability is crucial in military contexts, where the goal is often to pin down enemy forces or provide covering fire for advancing troops. Additionally, the use of a belt feed system means that these guns can be loaded with a large quantity of ammunition at once, reducing the need for frequent reloads during combat.
History of Belt Fed Machine Guns

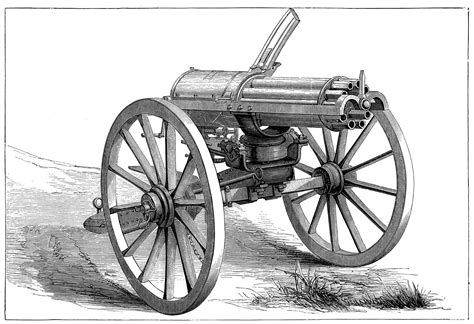
The development of belt-fed machine guns began in the late 19th century, with early models like the Gatling gun. However, these early guns were not truly belt-fed in the modern sense but rather used a drum or hopper to feed the cartridges. The first practical belt-fed machine gun was the Maxim gun, invented by Sir Hiram Maxim in the 1880s. The Maxim gun used a fabric belt to feed the cartridges, and its design influenced the development of subsequent machine guns.
Throughout the 20th century, belt-fed machine guns continued to evolve, with improvements in materials, design, and functionality. The introduction of metal links for the belts increased reliability and durability, while advancements in barrel design and cooling systems allowed for more sustained fire without overheating. Guns like the M1919 Browning machine gun and the MG 42 became iconic in their respective eras, known for their reliability, firepower, and ease of use.
Design and Mechanism

The design of belt-fed machine guns centers around the feed system, which includes the belt, the feed tray, and the mechanism that strips the cartridges from the belt and chambers them. The gun also features a firing mechanism, which includes the bolt, firing pin, and extractor, as well as a system for ejecting spent casings. In addition to these core components, modern belt-fed machine guns often include features like quick-change barrels to prevent overheating, bipod or tripod mounts for stability, and sighting systems to aid in aiming.
The mechanism of a belt-fed machine gun involves several stages. First, the belt is loaded into the feed tray, which guides the belt into the gun. As the gun cycles, the feed mechanism pulls the belt forward, positioning the next cartridge to be chambered. The bolt then strips the cartridge from the belt and pushes it into the chamber. After the cartridge is fired, the bolt recoils, extracting the spent casing and ejecting it from the gun. This process continues as long as the gun is firing and there are cartridges in the belt.
Types of Belt Fed Machine Guns

Belt-fed machine guns can be categorized based on their caliber, intended use, and design features. Light machine guns, such as the M249 SAW, are designed to be carried by infantrymen and provide suppressive fire at the squad level. Medium machine guns, like the M240, offer a balance between portability and firepower, often being used in both infantry and vehicle-mounted roles. Heavy machine guns, such as the DShK, are typically mounted on tripods or vehicles and are used for anti-personnel and anti-aircraft roles due to their large caliber and high volume of fire.
In addition to these categories, belt-fed machine guns can also be distinguished by their specific design features. For example, some guns are designed with a gas-operated piston to cycle the action, while others use recoil operation. The choice of materials and the inclusion of features like quick-change barrels, night vision sights, and remote firing capabilities can also vary significantly between different models.
Applications and Usage

The primary application of belt-fed machine guns is in military and defense contexts, where their ability to deliver sustained, high-volume fire is invaluable. They are used by infantry units for suppressive fire, by vehicles for self-defense, and in fixed positions for perimeter defense. Beyond military use, belt-fed machine guns also find applications in law enforcement, particularly in SWAT and counter-terrorism units, where they can be used to breach doors or provide cover during high-risk operations.
In civilian contexts, belt-fed machine guns are less common due to legal restrictions in many countries. However, they can be found in certain niche areas, such as in the film industry for special effects, in historical reenactments, and among collectors who have the necessary licenses and permits. For enthusiasts, understanding the mechanics, history, and applications of belt-fed machine guns can provide a deeper appreciation for firearms technology and the complexities of modern warfare.
Gallery of Belt Fed Machine Guns
Belt Fed Machine Guns Image Gallery








Frequently Asked Questions
What is the primary advantage of belt-fed machine guns?
+The primary advantage of belt-fed machine guns is their ability to deliver sustained, high-volume fire over an extended period without the need for frequent reloads.
How do belt-fed machine guns operate?
+Belt-fed machine guns operate by using a belt that holds linked cartridges. The gun strips the cartridges from the belt, chambers them, fires, and then ejects the spent casing, repeating the process until the belt is exhausted.
What are the main categories of belt-fed machine guns?
+Belt-fed machine guns can be categorized into light, medium, and heavy machine guns based on their caliber, intended use, and design features.
What are the applications of belt-fed machine guns?
+Belt-fed machine guns are primarily used in military and defense contexts for suppressive fire, vehicle defense, and perimeter security. They also have applications in law enforcement and among licensed collectors and enthusiasts.
Are belt-fed machine guns legal for civilian ownership?
+The legality of civilian ownership of belt-fed machine guns varies significantly by country and jurisdiction. In many places, they are heavily regulated or prohibited for civilian use.
In conclusion, belt-fed machine guns represent a fascinating aspect of firearms technology, with a rich history, complex mechanics, and significant applications in military and defense contexts. Understanding these guns not only provides insights into the evolution of weaponry but also highlights the technological advancements and design considerations that have shaped modern combat. Whether you're a historian, an enthusiast, or simply someone interested in learning more about these powerful weapons, there's no denying the intrigue and importance of belt-fed machine guns. We invite readers to share their thoughts, ask questions, and explore further the captivating world of belt-fed machine guns.
