Intro
Discover the 5 key missile differences, including range, speed, and guidance systems, to understand ballistic, cruise, and hypersonic missiles unique features and capabilities.
The world of missiles is complex and fascinating, with various types designed for specific purposes. Understanding the differences between these missiles is crucial for military strategists, defense analysts, and anyone interested in global security. In this article, we will delve into the key differences between various missiles, exploring their characteristics, capabilities, and applications.
Missiles have been a cornerstone of modern warfare, providing nations with a means to project power, deter adversaries, and defend against threats. The development of missiles has been driven by advancements in technology, leading to a wide range of systems with unique features and capabilities. From ballistic missiles to cruise missiles, each type has its strengths and weaknesses, making them suitable for different roles and scenarios.
The importance of understanding missile differences cannot be overstated. In today's geopolitical landscape, missiles play a critical role in shaping international relations, influencing conflict dynamics, and impacting global stability. By examining the key differences between missiles, we can gain insights into the strategic calculations of nations, the evolution of military technologies, and the potential consequences of missile proliferation.
Introduction to Missile Types

To appreciate the differences between missiles, it's essential to understand the primary categories and their characteristics. Missiles can be broadly classified into several types, including ballistic missiles, cruise missiles, surface-to-air missiles, air-to-air missiles, and anti-ship missiles. Each type is designed for specific missions, with distinct features such as range, speed, guidance systems, and warhead types.
Ballistic Missiles

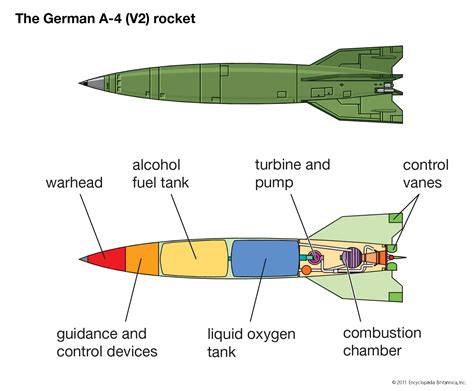
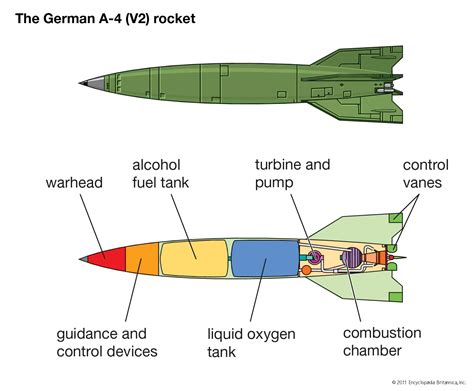
Ballistic missiles are propelled into space and follow a ballistic trajectory to their target. They are typically powered by rocket motors and can carry nuclear or conventional warheads. Ballistic missiles are characterized by their high speed, long range, and ability to evade defenses. They can be further divided into subcategories, including intercontinental ballistic missiles (ICBMs), intermediate-range ballistic missiles (IRBMs), and short-range ballistic missiles (SRBMs).
Characteristics of Ballistic Missiles
Ballistic missiles have several key characteristics that distinguish them from other types: * High speed: Ballistic missiles can reach speeds of over 20,000 km/h, making them difficult to intercept. * Long range: Ballistic missiles can travel thousands of kilometers, allowing them to strike targets across continents. * High altitude: Ballistic missiles reach space, making them less vulnerable to air defenses. * Warhead types: Ballistic missiles can carry nuclear, conventional, or chemical warheads, depending on their design and purpose.Cruise Missiles

Cruise missiles are powered by jet engines and fly at low altitudes, using terrain-following radar to navigate. They are typically used for precision strikes against land or sea targets and can carry conventional or nuclear warheads. Cruise missiles are characterized by their low speed, long range, and ability to evade defenses.
Characteristics of Cruise Missiles
Cruise missiles have several key characteristics that distinguish them from other types: * Low speed: Cruise missiles typically fly at subsonic speeds, making them less detectable by radar. * Long range: Cruise missiles can travel hundreds or thousands of kilometers, depending on their design and fuel capacity. * Low altitude: Cruise missiles fly at low altitudes, using terrain-following radar to avoid obstacles and evade defenses. * Precision guidance: Cruise missiles use advanced guidance systems, including GPS and terrain-following radar, to accurately target specific locations.Surface-to-Air Missiles

Surface-to-air missiles (SAMs) are designed to intercept and destroy incoming aircraft, missiles, or other airborne threats. They are typically launched from ground-based platforms and use radar or infrared guidance to track their targets. SAMs can be further divided into subcategories, including short-range, medium-range, and long-range systems.
Characteristics of Surface-to-Air Missiles
Surface-to-air missiles have several key characteristics that distinguish them from other types: * Radar guidance: SAMs use radar systems to detect, track, and engage airborne targets. * Infrared guidance: Some SAMs use infrared seekers to track targets, particularly in environments with heavy electronic countermeasures. * Range and altitude: SAMs have varying ranges and altitude ceilings, depending on their design and purpose. * Warhead types: SAMs typically use fragmentation or high-explosive warheads to destroy or disable airborne targets.Air-to-Air Missiles

Air-to-air missiles are designed to intercept and destroy enemy aircraft. They are typically launched from fighter jets or other airborne platforms and use radar, infrared, or optical guidance to track their targets. Air-to-air missiles can be further divided into subcategories, including short-range, medium-range, and long-range systems.
Characteristics of Air-to-Air Missiles
Air-to-air missiles have several key characteristics that distinguish them from other types: * Radar guidance: Air-to-air missiles use radar systems to detect, track, and engage enemy aircraft. * Infrared guidance: Some air-to-air missiles use infrared seekers to track targets, particularly in environments with heavy electronic countermeasures. * Range and altitude: Air-to-air missiles have varying ranges and altitude ceilings, depending on their design and purpose. * Warhead types: Air-to-air missiles typically use fragmentation or high-explosive warheads to destroy or disable enemy aircraft.Anti-Ship Missiles

Anti-ship missiles are designed to destroy or disable enemy ships. They are typically launched from aircraft, submarines, or surface ships and use radar, infrared, or optical guidance to track their targets. Anti-ship missiles can be further divided into subcategories, including anti-ship cruise missiles and anti-ship ballistic missiles.
Characteristics of Anti-Ship Missiles
Anti-ship missiles have several key characteristics that distinguish them from other types: * Radar guidance: Anti-ship missiles use radar systems to detect, track, and engage enemy ships. * Infrared guidance: Some anti-ship missiles use infrared seekers to track targets, particularly in environments with heavy electronic countermeasures. * Range and altitude: Anti-ship missiles have varying ranges and altitude ceilings, depending on their design and purpose. * Warhead types: Anti-ship missiles typically use high-explosive or armor-piercing warheads to damage or sink enemy ships.Missile Image Gallery








What is the primary difference between ballistic and cruise missiles?
+The primary difference between ballistic and cruise missiles is their trajectory and guidance system. Ballistic missiles follow a ballistic trajectory and are guided by inertial navigation systems, while cruise missiles fly at low altitudes and use terrain-following radar to navigate.
What is the purpose of surface-to-air missiles?
+The primary purpose of surface-to-air missiles is to intercept and destroy incoming aircraft, missiles, or other airborne threats. They are used to defend against aerial attacks and protect ground-based assets.
What is the difference between air-to-air and anti-ship missiles?
+The primary difference between air-to-air and anti-ship missiles is their target and guidance system. Air-to-air missiles are designed to intercept and destroy enemy aircraft, while anti-ship missiles are designed to destroy or disable enemy ships. Air-to-air missiles typically use radar or infrared guidance, while anti-ship missiles use radar, infrared, or optical guidance.
In conclusion, understanding the differences between various missiles is crucial for military strategists, defense analysts, and anyone interested in global security. By examining the characteristics, capabilities, and applications of different missile types, we can gain insights into the strategic calculations of nations, the evolution of military technologies, and the potential consequences of missile proliferation. As the world continues to evolve and new technologies emerge, it's essential to stay informed about the latest developments in the field of missiles and their impact on international relations and global stability. We invite you to share your thoughts and questions about missiles in the comments section below and explore our other articles on related topics.
