Intro
Discover Ethiopian bad words, phrases, and insults. Learn Amharic profanity, curses, and swear words with cultural context and translations, understanding Ethiopian language nuances.
The importance of understanding cultural nuances, including language, cannot be overstated. In every culture, there are words and phrases that are considered inappropriate or offensive. Ethiopia, with its rich cultural heritage and over 80 ethnic groups, is no exception. The country has a complex linguistic landscape, with many languages spoken across its territories, including Amharic, Oromo, Tigrinya, and Somali, among others. Each of these languages has its own set of expressions that are deemed unacceptable in polite conversation.
Language plays a crucial role in Ethiopian culture, reflecting the country's history, values, and beliefs. However, like in any other society, there are words and expressions that are considered bad or offensive. These can range from swear words and insults to derogatory terms that target specific groups of people. Understanding what constitutes offensive language is essential for anyone interested in Ethiopian culture, whether for academic, professional, or personal reasons.
The diversity of Ethiopia means that what might be considered a bad word in one language or community might not be in another. This complexity highlights the need for cultural sensitivity and awareness, especially in a globalized world where interactions across cultures are increasingly common. Misunderstandings can easily arise from the misuse or misunderstanding of language, leading to unintended offense or conflict.
Introduction to Ethiopian Languages

Ethiopia is home to a significant number of languages, each with its unique characteristics and cultural significance. The official working language of the federal government is Amharic, which is also the most widely spoken language in the country. Other major languages include Oromo, spoken by the largest ethnic group, the Oromo people, and Tigrinya, predominantly spoken in the Tigray region. Understanding the basics of these languages can provide insight into the cultural context of offensive language.
Amharic: The Official Language
Amharic is a Semitic language and has its own set of words and expressions that are considered inappropriate. Like many languages, Amharic has a range of swear words and insults that are used in informal settings but are generally avoided in polite conversation. The use of such language can depend heavily on the context and the relationship between the speakers.Cultural Sensitivity and Language

Cultural sensitivity is key when navigating the complex linguistic landscape of Ethiopia. What might seem like a harmless word or phrase in one culture could be deeply offensive in another. This is particularly important in a country with as much ethnic and linguistic diversity as Ethiopia. Educating oneself about the local customs, traditions, and language can help avoid unintended offense and foster more positive interactions.
Learning About Offensive Language
Learning about the offensive language in any culture requires a delicate approach. It's essential to understand the context in which certain words or phrases are used and to be aware of one's own position and potential impact. For outsiders, this might involve seeking guidance from local friends, mentors, or language instructors who can provide insights into what is considered acceptable and what is not.The Role of Language in Ethiopian Society

Language plays a pivotal role in Ethiopian society, serving not only as a means of communication but also as a carrier of culture, history, and identity. The use of language can reflect social status, education level, and ethnic affiliation, among other factors. In this context, the use of offensive language can have significant social implications, affecting relationships and reputations.
Language and Social Harmony
Promoting social harmony through respectful language use is a valued aspect of Ethiopian culture. Encouraging dialogue and understanding among different linguistic and ethnic groups can help in building a more cohesive society. This involves not only avoiding offensive language but also fostering an environment where diverse voices can be heard and respected.Challenges and Opportunities

The linguistic diversity of Ethiopia presents both challenges and opportunities. On one hand, it can lead to misunderstandings and conflicts rooted in linguistic and cultural differences. On the other hand, it offers a rich tapestry of languages and cultures that can enrich the country's social, educational, and economic landscapes.
Language Education and Awareness
Enhancing language education and promoting cultural awareness are crucial steps in navigating the complexities of Ethiopian languages. By incorporating diverse languages into educational curricula and promoting intercultural dialogue, Ethiopia can foster a more inclusive and respectful society. This approach can also help in preserving the country's linguistic heritage for future generations.Gallery of Ethiopian Languages
Ethiopian Languages Image Gallery

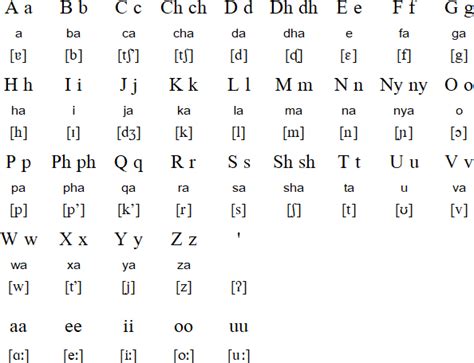








Frequently Asked Questions
What are some common bad words in Amharic?
+While it's not appropriate to list them here, it's essential to understand that Amharic, like any other language, has its set of words and expressions considered inappropriate. It's crucial to learn about these from a respectful and culturally sensitive source.
How can I learn about offensive language in Ethiopian cultures without offending anyone?
+Seeking guidance from local mentors, language instructors, or cultural guides can provide valuable insights. Approaching the topic with respect and a willingness to learn can help in avoiding unintended offense.
What role does language play in promoting social harmony in Ethiopia?
+Language plays a crucial role in promoting social harmony by facilitating communication, understanding, and respect among different ethnic and linguistic groups. Encouraging the use of respectful language and promoting linguistic diversity can contribute to a more cohesive society.
In conclusion, navigating the complexities of language in Ethiopia requires a deep understanding of the country's cultural, historical, and social contexts. By approaching the topic with sensitivity and respect, individuals can foster more positive and respectful interactions. Whether for personal, academic, or professional purposes, learning about Ethiopian languages and cultures can be a rewarding and enriching experience. We invite readers to share their thoughts and experiences on the importance of language and cultural awareness in the comments below, and to consider sharing this article with others who might benefit from this insight into the fascinating world of Ethiopian languages and cultures.
