Intro
Discover key differences between B2 and B21, including bolt pattern, engine specs, and performance features, to make an informed decision in the B-series engine market.
The world of vitamins and supplements can be overwhelming, especially when it comes to differentiating between various types of vitamins. Two such vitamins that are often confused with each other are B2 and B21. While they may sound similar, they have distinct differences in terms of their composition, functions, and benefits. In this article, we will delve into the key differences between B2 and B21, exploring their unique characteristics, advantages, and uses.
Vitamins are essential nutrients that play a crucial role in maintaining our overall health and well-being. They help regulate various bodily functions, such as energy production, immune function, and nerve function. With so many vitamins available, it's essential to understand the specific benefits and differences between each type. B2 and B21 are two such vitamins that have gained significant attention in recent years due to their potential health benefits. However, before we dive into their differences, let's first understand what each vitamin is and what it does.
B2, also known as riboflavin, is a water-soluble vitamin that plays a vital role in energy production, nerve function, and eye health. It's an essential nutrient that helps convert carbohydrates, fats, and proteins into energy, making it a crucial component of our diet. B2 is found in various food sources, including dairy products, leafy green vegetables, and whole grains. On the other hand, B21 is not a recognized vitamin by the scientific community. There is no such vitamin as B21, and it's possible that it may be a marketing term or a misnomer.
Introduction to B2

Now that we've established the difference between B2 and B21, let's take a closer look at the benefits and functions of B2. Vitamin B2, or riboflavin, is an essential nutrient that offers numerous health benefits. It plays a critical role in energy production, helping to convert carbohydrates, fats, and proteins into energy. This makes it an essential component of our diet, particularly for individuals who engage in regular physical activity or have high energy demands.
Benefits of B2
Some of the key benefits of B2 include: * Energy production: B2 helps convert carbohydrates, fats, and proteins into energy, making it an essential nutrient for individuals with high energy demands. * Nerve function: B2 plays a crucial role in maintaining healthy nerve function, which is essential for transmitting signals between nerve cells. * Eye health: B2 helps protect the eyes against damage, reducing the risk of age-related macular degeneration and cataracts. * Skin health: B2 is essential for maintaining healthy skin, reducing the appearance of fine lines and wrinkles.Comparison with B21
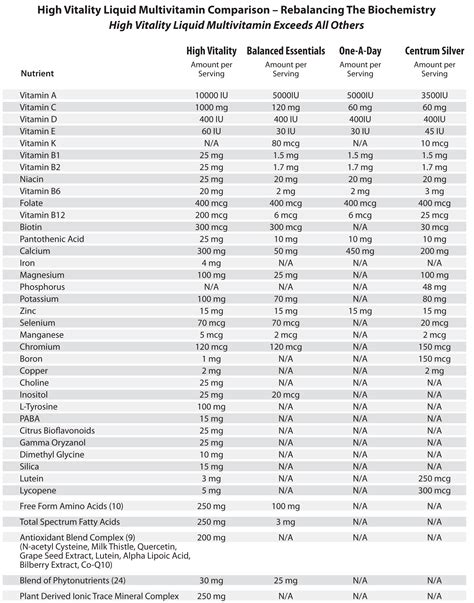
As we've established, there is no such vitamin as B21. However, for the sake of comparison, let's assume that B21 refers to a hypothetical vitamin that offers similar benefits to B2. In this scenario, the key differences between B2 and B21 would be their composition, functions, and benefits. B2 is a well-established vitamin with a proven track record of health benefits, while B21 is not recognized by the scientific community.
Differences between B2 and B21
Some of the key differences between B2 and B21 include: * Composition: B2 is a water-soluble vitamin, while B21 is not a recognized vitamin. * Functions: B2 plays a critical role in energy production, nerve function, and eye health, while B21 has no established functions. * Benefits: B2 offers numerous health benefits, including energy production, nerve function, and eye health, while B21 has no proven benefits.Food Sources of B2

B2 is found in various food sources, including:
- Dairy products: Milk, cheese, and yogurt are rich in B2.
- Leafy green vegetables: Spinach, kale, and collard greens are excellent sources of B2.
- Whole grains: Brown rice, quinoa, and whole wheat bread are good sources of B2.
- Nuts and seeds: Almonds, sunflower seeds, and pumpkin seeds are rich in B2.
Deficiency of B2
A deficiency in B2 can lead to various health problems, including: * Fatigue: B2 plays a critical role in energy production, and a deficiency can lead to fatigue and weakness. * Numbness or tingling: B2 is essential for nerve function, and a deficiency can cause numbness or tingling in the hands and feet. * Eye problems: B2 helps protect the eyes against damage, and a deficiency can increase the risk of age-related macular degeneration and cataracts.Gallery of Vitamin B2
Vitamin B2 Image Gallery









FAQs
What is Vitamin B2?
+Vitamin B2, also known as riboflavin, is a water-soluble vitamin that plays a vital role in energy production, nerve function, and eye health.
What are the benefits of Vitamin B2?
+Vitamin B2 offers numerous health benefits, including energy production, nerve function, and eye health. It also helps protect the eyes against damage, reducing the risk of age-related macular degeneration and cataracts.
What are the symptoms of Vitamin B2 deficiency?
+A deficiency in Vitamin B2 can lead to various health problems, including fatigue, numbness or tingling, and eye problems. It can also increase the risk of age-related macular degeneration and cataracts.
In conclusion, while B2 and B21 may sound similar, they have distinct differences in terms of their composition, functions, and benefits. B2 is a well-established vitamin with a proven track record of health benefits, while B21 is not recognized by the scientific community. By understanding the key differences between these two vitamins, individuals can make informed decisions about their dietary needs and supplement routine. We encourage readers to share their thoughts and experiences with Vitamin B2 in the comments section below. If you found this article informative, please consider sharing it with your friends and family to help spread awareness about the importance of Vitamin B2.
