Intro
Discover the Autonomous Soviet Socialist Republic, a self-governing entity within the Soviet Union, exploring its structure, governance, and historical context, including socialist principles and regional autonomy.
The concept of an Autonomous Soviet Socialist Republic (ASSR) is a fascinating aspect of the Soviet Union's administrative and political structure. The Soviet Union, which existed from 1922 to 1991, was a vast and diverse country, comprising numerous ethnic groups, languages, and cultures. To manage this diversity, the Soviet government established a system of autonomous republics, which provided a degree of self-governance to various ethnic and national groups within the country. In this article, we will delve into the history, characteristics, and significance of Autonomous Soviet Socialist Republics, exploring their role in the Soviet Union's federal system and their impact on the country's development.
The Soviet Union's federal system was designed to accommodate the country's diverse population, with the goal of promoting national equality and unity. The system consisted of several tiers, including the Soviet Socialist Republics (SSRs), Autonomous Soviet Socialist Republics (ASSRs), Autonomous Oblasts (AOs), and Autonomous Okrugs (AOs). Each tier had a varying degree of autonomy, with the ASSRs occupying a middle position between the SSRs and the lower-level administrative units. The ASSRs were established to provide a degree of self-governance to ethnic and national groups that were not numerous enough to warrant a full-fledged Soviet Socialist Republic.
History of Autonomous Soviet Socialist Republics
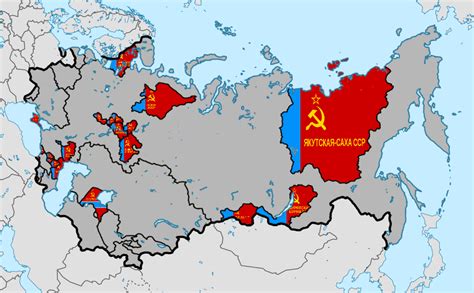
Characteristics of Autonomous Soviet Socialist Republics
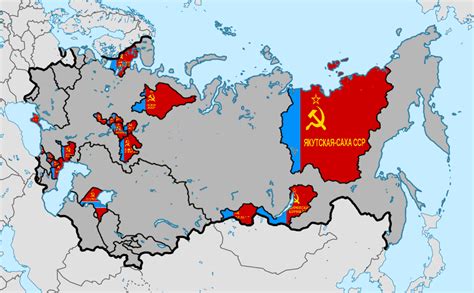
Administrative Structure
The administrative structure of Autonomous Soviet Socialist Republics was similar to that of the Soviet Socialist Republics. Each ASSR had its own government, which was headed by a chairman or president. The government was responsible for implementing Soviet policies and managing the republic's economy, education system, and cultural institutions. The ASSRs also had their own parliaments, which were elected by the population and were responsible for passing laws and approving the republic's budget.Significance of Autonomous Soviet Socialist Republics
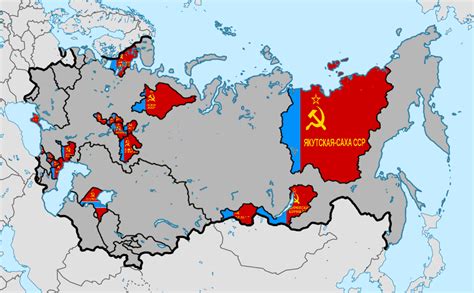
Economic Development
The Autonomous Soviet Socialist Republics made significant contributions to the Soviet Union's economic development. Each ASSR had its own economic system, which was integrated into the Soviet Union's overall economic plan. The ASSRs were responsible for managing their own industries, agriculture, and infrastructure, and for contributing to the Soviet Union's overall economic growth. The ASSRs also played a key role in the development of the Soviet Union's natural resources, including oil, gas, and minerals.Examples of Autonomous Soviet Socialist Republics
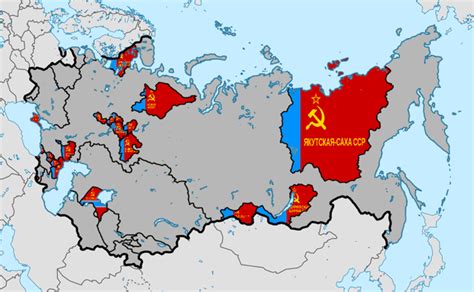
Case Study: Tatar ASSR
The Tatar ASSR was one of the most notable examples of an Autonomous Soviet Socialist Republic. Established in 1922, the Tatar ASSR was located in the Volga-Ural region and had a population of over 2 million people. The republic had its own government, parliament, and economic system, and was responsible for managing its own industries, agriculture, and infrastructure. The Tatar ASSR also had a degree of cultural and linguistic autonomy, with the ability to promote the Tatar language and culture.Legacy of Autonomous Soviet Socialist Republics
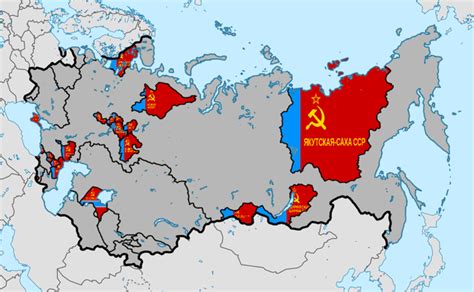
Modern-Day Implications
The modern-day implications of the Autonomous Soviet Socialist Republics are significant. The ASSRs played a key role in shaping the Soviet Union's federal system and contributed to the country's economic development. Today, the legacy of the ASSRs can be seen in the modern-day republics of Russia, which continue to grapple with issues of autonomy, self-governance, and cultural identity. The experience of the ASSRs also provides valuable lessons for modern-day policymakers, who are seeking to balance the needs of diverse ethnic and national groups with the requirements of a unified state.Autonomous Soviet Socialist Republic Image Gallery
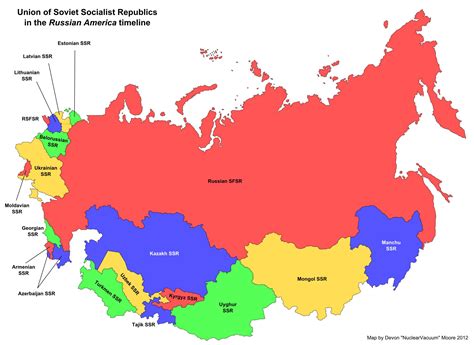


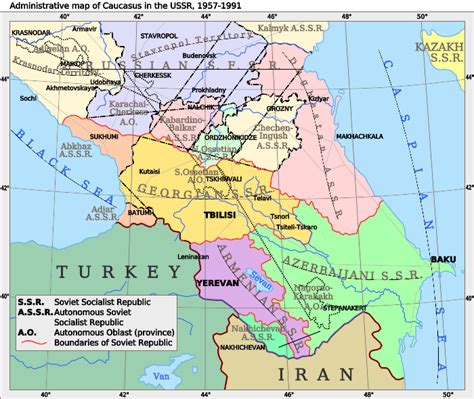



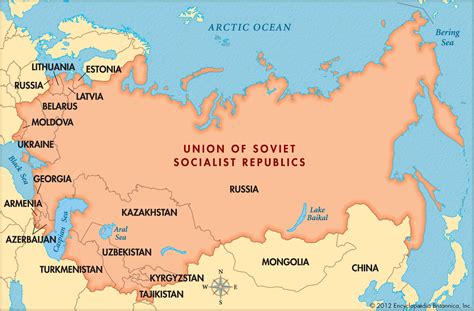
What was the main purpose of Autonomous Soviet Socialist Republics?
+The main purpose of Autonomous Soviet Socialist Republics was to provide a degree of autonomy to ethnic and national groups within the Soviet Union, allowing them to promote their own languages, cultures, and traditions.
How many Autonomous Soviet Socialist Republics were there in the Soviet Union?
+There were over 20 Autonomous Soviet Socialist Republics in the Soviet Union, each with its own government, parliament, and economic system.
What was the relationship between Autonomous Soviet Socialist Republics and the Soviet government?
+The Autonomous Soviet Socialist Republics were subject to Soviet control and repression, with the Soviet government maintaining control over key areas such as defense, foreign policy, and economic planning.
What is the legacy of Autonomous Soviet Socialist Republics today?
+The legacy of Autonomous Soviet Socialist Republics can be seen in the modern-day republics of Russia, which have inherited the administrative structures and institutions of the Soviet era. The experience of the ASSRs also provides valuable lessons for modern-day policymakers, who are seeking to balance the needs of diverse ethnic and national groups with the requirements of a unified state.
How did the Autonomous Soviet Socialist Republics contribute to the Soviet Union's economic development?
+The Autonomous Soviet Socialist Republics made significant contributions to the Soviet Union's economic development, by managing their own economic systems and contributing to the country's overall economic growth. The ASSRs also played a key role in the development of the Soviet Union's natural resources, including oil, gas, and minerals.
In conclusion, the Autonomous Soviet Socialist Republics played a significant role in the Soviet Union's federal system, providing a degree of autonomy to ethnic and national groups and contributing to the country's economic development. The legacy of the ASSRs can be seen in the modern-day republics of Russia, which continue to grapple with issues of autonomy, self-governance, and cultural identity. As we reflect on the history and significance of the Autonomous Soviet Socialist Republics, we are reminded of the importance of balancing the needs of diverse ethnic and national groups with the requirements of a unified state. We invite you to share your thoughts and comments on this topic, and to explore the rich history and culture of the Soviet Union and its successor states.
