Intro
Discover Article IV Section 3 explained, covering federal powers, state relations, and US obligations, with insights on constitutional law, interstate compact, and national sovereignty.
The importance of understanding Article IV, Section 3 cannot be overstated, as it plays a crucial role in the functioning of the United States government. This section of the US Constitution outlines the procedures for admitting new states to the Union and the rules governing the ownership of federal property. In essence, it provides a framework for the expansion and management of the country's territory. For those interested in the intricacies of American governance, delving into the specifics of Article IV, Section 3 is essential. It not only sheds light on historical state admissions but also offers insights into the potential for future territorial adjustments.
The relevance of Article IV, Section 3 extends beyond the realm of historical or legal curiosity. It has significant implications for contemporary political, economic, and social issues. For instance, the process of admitting new states can affect the balance of power in Congress, influence the distribution of federal funds, and even impact the outcome of presidential elections. Moreover, the management of federal property, as dictated by this section, can have profound effects on environmental policies, public land usage, and the rights of indigenous communities. Therefore, grasping the nuances of Article IV, Section 3 is vital for anyone seeking a comprehensive understanding of American politics and governance.
As one explores the depths of Article IV, Section 3, it becomes apparent that its significance is multifaceted. It reflects the dynamic nature of the United States, a country that has expanded its territory over the centuries through the admission of new states. This process, while often complex and contentious, has been instrumental in shaping the nation's identity and its role on the global stage. By examining the historical context and the legal framework provided by Article IV, Section 3, readers can gain a deeper appreciation for the challenges and opportunities that arise from the country's ongoing evolution. Whether one is a scholar, a policy maker, or simply an engaged citizen, understanding this aspect of the Constitution is indispensable for navigating the intricacies of American democracy.
Introduction to Article IV, Section 3

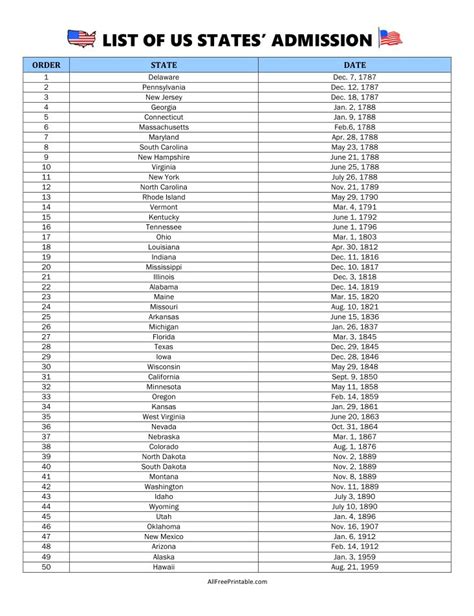
Article IV, Section 3 of the US Constitution is divided into two clauses: the Admission Clause and the Property Clause. The Admission Clause grants Congress the authority to admit new states to the Union, provided that the admission is approved by a majority vote in both the House of Representatives and the Senate. This clause has been instrumental in the expansion of the United States, enabling the country to grow from the original 13 states to its current 50. The process of statehood involves several steps, including the drafting of a state constitution, the holding of a referendum where residents vote on whether to seek statehood, and finally, the approval by Congress.
Understanding the Admission Clause
The Admission Clause is a pivotal component of Article IV, Section 3, as it outlines the procedure for admitting new states. This process is not merely a formality but involves a series of complex steps and considerations. For a territory to become a state, it must first meet certain criteria, such as having a defined boundary, a functioning government, and a sufficient population. Once these prerequisites are met, the territory can draft a constitution and hold a referendum on statehood. If the referendum is successful, the territory then petitions Congress for admission as a state. Congress must then approve the admission through a majority vote in both the House and the Senate.The Property Clause

The Property Clause, on the other hand, grants Congress the authority to manage and dispose of federal property. This includes lands acquired through the Louisiana Purchase, the Mexican-American War, and other means. The management of federal property is crucial, as it involves decisions on land use, conservation, and the rights of indigenous peoples. The clause gives Congress considerable discretion in these matters, allowing it to make decisions that balance competing interests and priorities. However, this authority is not without its challenges and controversies, particularly when it comes to issues such as public land usage, environmental protection, and the sovereignty of Native American reservations.
Implications of the Property Clause
The implications of the Property Clause are far-reaching and multifaceted. On one hand, it provides Congress with the flexibility to adapt to changing circumstances and priorities. For example, the clause has been used to establish national parks and wildlife refuges, protecting vast areas of natural beauty and biodiversity. On the other hand, the management of federal property can be contentious, especially when it involves conflicting interests such as mining, logging, and conservation. The clause has also been at the center of disputes over Native American land rights, highlighting the need for a balanced and equitable approach to federal property management.Historical Context and Evolution

The historical context of Article IV, Section 3 is essential for understanding its significance and evolution. The clause has been instrumental in the expansion of the United States, from the early 19th century to the present day. The admission of new states has not only changed the political landscape of the country but has also had profound economic and social impacts. For instance, the admission of states such as California and Texas has contributed significantly to the country's economic growth and cultural diversity. Similarly, the management of federal property has played a crucial role in shaping the nation's environmental policies and its relationship with indigenous communities.
Key Milestones in the Evolution of Article IV, Section 3
Several key milestones mark the evolution of Article IV, Section 3. One of the most significant was the Northwest Ordinance of 1787, which established the procedure for admitting new states to the Union. This ordinance set a precedent for the expansion of the United States and the principles that would guide the admission of future states. Another milestone was the Louisiana Purchase of 1803, which doubled the size of the United States and presented new challenges and opportunities for federal property management. More recently, the admission of Hawaii and Alaska as states in 1959 marked the culmination of the country's continental expansion and highlighted the ongoing relevance of Article IV, Section 3.Contemporary Relevance and Challenges

Despite being crafted over two centuries ago, Article IV, Section 3 remains highly relevant in contemporary American politics. The clause continues to shape the country's territorial composition and its approach to federal property management. One of the current challenges facing the implementation of Article IV, Section 3 is the debate over the admission of new states, such as Puerto Rico and the District of Columbia. This debate highlights the ongoing importance of the Admission Clause and the need for a nuanced understanding of its implications. Additionally, the management of federal property continues to be a contentious issue, with debates over public land usage, environmental protection, and indigenous rights remaining at the forefront of national discourse.
Future Directions and Considerations
As the United States looks to the future, Article IV, Section 3 will undoubtedly play a significant role in shaping the country's territorial and environmental policies. One of the key considerations will be the balance between economic development and environmental protection. The clause provides Congress with the authority to make decisions that impact the nation's natural resources and public lands, decisions that will have lasting impacts on future generations. Furthermore, the potential admission of new states will require careful consideration of the political, economic, and social implications, underscoring the need for a thoughtful and inclusive approach to the expansion of the Union.Gallery of Article IV, Section 3
Article IV, Section 3 Image Gallery









What is Article IV, Section 3 of the US Constitution?
+Article IV, Section 3 of the US Constitution outlines the procedures for admitting new states to the Union and the rules governing the ownership of federal property.
What are the implications of the Admission Clause?
+The Admission Clause has significant implications for the balance of power in Congress, the distribution of federal funds, and the outcome of presidential elections. It also reflects the dynamic nature of the United States, shaping the nation's identity and its role on the global stage.
How does the Property Clause impact federal property management?
+The Property Clause grants Congress the authority to manage and dispose of federal property, including decisions on land use, conservation, and the rights of indigenous peoples. This authority is crucial for balancing competing interests and priorities in federal property management.
What are the contemporary challenges facing the implementation of Article IV, Section 3?
+The contemporary challenges include the debate over the admission of new states, such as Puerto Rico and the District of Columbia, and the management of federal property in the face of competing demands for public land usage, environmental protection, and indigenous rights.
Why is understanding Article IV, Section 3 important for American governance?
+Understanding Article IV, Section 3 is crucial for grasping the complexities of American governance, including the process of state admission, federal property management, and the balance of power in Congress. It also provides insights into the historical and contemporary challenges facing the United States, from territorial expansion to environmental protection.
In conclusion, Article IV, Section 3 of the US Constitution is a foundational element of American governance, shaping the country's territorial composition and its approach to federal property management. As the United States continues to evolve, this clause will remain a critical component of the nation's legal and political framework. By exploring the intricacies of Article IV, Section 3, readers can deepen their understanding of American history, politics, and the ongoing challenges and opportunities that the country faces. Whether you are a scholar, a policy maker, or simply an engaged citizen, delving into the world of Article IV, Section 3 is an enriching and enlightening experience that offers valuable insights into the complexities of American democracy. We invite you to share your thoughts, ask questions, and explore further the fascinating realm of Article IV, Section 3, as together, we navigate the intricacies of the US Constitution and its enduring impact on American society.
