Intro
Unlock elite Army Special Forces Medic Training, learning advanced tactical combat casualty care, wilderness medicine, and emergency medical skills to save lives in extreme environments.
The Army Special Forces, also known as the Green Berets, are an elite group of soldiers who undergo rigorous training to conduct unconventional warfare, foreign internal defense, and direct action missions. One of the most critical roles within the Special Forces is that of the medic, who provides medical care to teammates and indigenous forces in remote and hostile environments. Army Special Forces medic training is a grueling and comprehensive program that prepares medics to handle a wide range of medical emergencies and to operate effectively in a variety of settings.
To become a Special Forces medic, a soldier must first complete Basic Combat Training and Advanced Individual Training as a medic. They must then volunteer for Special Forces duty and meet the basic requirements, which include being a U.S. citizen, being between the ages of 20 and 35, and scoring a minimum of 110 on the General Technical segment of the Armed Services Vocational Aptitude Battery. Once selected, the soldier will attend the Special Forces Qualification Course, also known as the "Q Course," which is a 24-month training program that includes language training, cultural training, and advanced medical training.
The medical training phase of the Q Course is known as the Special Forces Medical Sergeant Course, which is an intensive 24-week program that covers a wide range of medical topics, including trauma care, pharmacology, and medical evacuation procedures. Students learn how to treat a variety of injuries and illnesses, including gunshot wounds, burns, and infectious diseases. They also learn how to perform advanced medical procedures, such as cricothyrotomy and thoracotomy, and how to use specialized medical equipment, such as ventilators and defibrillators.
Overview of Special Forces Medic Training

The training is highly realistic and immersive, with students participating in simulated missions and scenarios that mimic real-world operations. They work in teams to treat patients and to develop their skills in communication, leadership, and problem-solving. The course is designed to push students to their limits, both physically and mentally, and to prepare them for the challenges they will face in the field.
Key Components of Special Forces Medic Training
The Special Forces Medical Sergeant Course includes several key components, including: * Advanced Trauma Life Support (ATLS) training, which teaches students how to assess and manage trauma patients * Advanced Cardiac Life Support (ACLS) training, which teaches students how to manage cardiac arrest and other cardiovascular emergencies * Tactical Combat Casualty Care (TCCC) training, which teaches students how to provide medical care in a combat environment * Medical evacuation procedures, which teach students how to transport patients safely and effectivelyBenefits of Special Forces Medic Training

The benefits of Special Forces medic training are numerous. Medics who complete the course are highly skilled and highly trained, with the ability to provide advanced medical care in a variety of settings. They are also able to operate effectively in a team environment, communicating and working with other medics and with non-medical personnel to achieve a common goal. The training is highly realistic and immersive, with students participating in simulated missions and scenarios that mimic real-world operations.
Career Opportunities for Special Forces Medics
Special Forces medics have a wide range of career opportunities available to them, both within the military and in the civilian sector. They may work as medics in a variety of settings, including hospitals, clinics, and emergency medical services. They may also work as instructors, teaching other medics and healthcare professionals about advanced medical procedures and techniques.Challenges of Special Forces Medic Training

The challenges of Special Forces medic training are significant. The course is highly demanding, both physically and mentally, and students must be in top physical condition to complete it. They must also have a strong foundation in medical skills and knowledge, as well as excellent communication and leadership skills. The training is highly realistic and immersive, with students participating in simulated missions and scenarios that mimic real-world operations.
Physical and Mental Demands of Special Forces Medic Training
The physical and mental demands of Special Forces medic training are significant. Students must be able to perform advanced medical procedures, such as surgical cricothyrotomy and thoracotomy, and must be able to operate effectively in a team environment. They must also be able to communicate effectively with other medics and with non-medical personnel, and must be able to make quick and accurate decisions in high-stress situations.Real-World Applications of Special Forces Medic Training

The real-world applications of Special Forces medic training are numerous. Medics who complete the course are highly skilled and highly trained, with the ability to provide advanced medical care in a variety of settings. They may work in a variety of roles, including as medics in hospitals, clinics, and emergency medical services, and as instructors, teaching other medics and healthcare professionals about advanced medical procedures and techniques.
Examples of Special Forces Medics in Action
There are many examples of Special Forces medics in action, providing medical care in a variety of settings and environments. For example, during the Vietnam War, Special Forces medics played a critical role in providing medical care to indigenous forces and to civilians. They worked in remote and hostile environments, often with limited medical supplies and equipment, and were able to provide advanced medical care and to save countless lives.Gallery of Special Forces Medic Training
Special Forces Medic Training Image Gallery




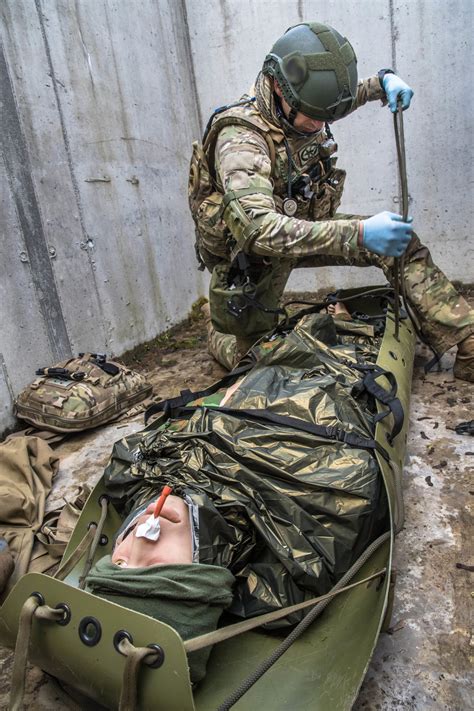
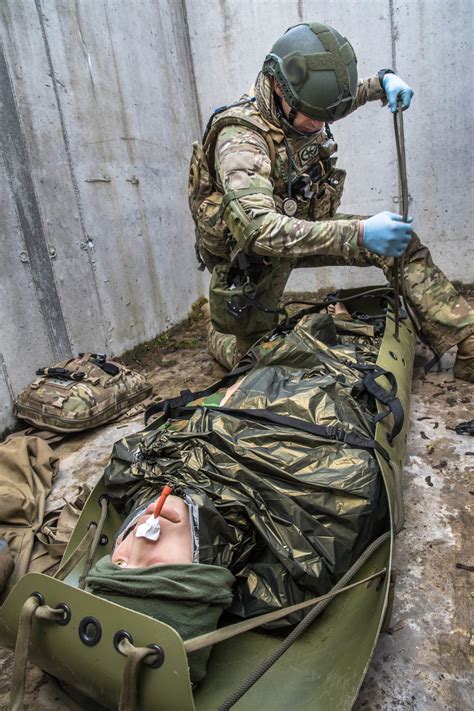




Frequently Asked Questions
What is the purpose of Special Forces medic training?
+The purpose of Special Forces medic training is to provide advanced medical training to Special Forces medics, enabling them to provide medical care in a variety of settings and environments.
What are the requirements for becoming a Special Forces medic?
+To become a Special Forces medic, a soldier must first complete Basic Combat Training and Advanced Individual Training as a medic, and then volunteer for Special Forces duty and meet the basic requirements, which include being a U.S. citizen, being between the ages of 20 and 35, and scoring a minimum of 110 on the General Technical segment of the Armed Services Vocational Aptitude Battery.
What is the duration of the Special Forces Medical Sergeant Course?
+The Special Forces Medical Sergeant Course is a 24-week program that covers a wide range of medical topics, including trauma care, pharmacology, and medical evacuation procedures.
In conclusion, Army Special Forces medic training is a highly demanding and comprehensive program that prepares medics to provide advanced medical care in a variety of settings and environments. The training is highly realistic and immersive, with students participating in simulated missions and scenarios that mimic real-world operations. Medics who complete the course are highly skilled and highly trained, with the ability to provide advanced medical care and to operate effectively in a team environment. If you are considering a career as a Special Forces medic, we encourage you to learn more about the training and the opportunities available to you. Share this article with others who may be interested in learning more about this exciting and rewarding career path.
