Intro
Discover 5 ways to join the army, including enlistment, officer programs, and special forces recruitment, to start your military career and serve your country with honor and patriotism.
The army is a prestigious and respected institution that offers a wide range of career opportunities for individuals who are passionate about serving their country. Joining the army can be a challenging and competitive process, but it can also be a highly rewarding experience that provides individuals with the skills, training, and education they need to succeed in their careers and in life. If you are considering joining the army, there are several ways to do so, each with its own unique requirements and benefits.
Joining the army can be a life-changing experience that provides individuals with a sense of purpose, direction, and fulfillment. Whether you are interested in serving your country, advancing your education and career, or simply challenging yourself to be your best, the army has something to offer. From the opportunity to serve in a variety of different roles and specialties, to the chance to receive world-class training and education, to the sense of camaraderie and esprit de corps that comes with being part of a tight-knit community, joining the army can be a highly rewarding experience that provides individuals with the skills, knowledge, and confidence they need to succeed.
The army is also a great way to advance your education and career, as it offers a wide range of training and educational programs that can help you develop the skills and knowledge you need to succeed in your chosen field. From basic training and advanced individual training, to specialized training and education in fields such as medicine, engineering, and communications, the army provides individuals with the opportunity to learn new skills, advance their education, and pursue their career goals. Additionally, the army offers a range of benefits, including competitive pay and benefits, opportunities for advancement and promotion, and the chance to serve in a variety of different roles and specialties.
Ways to Join the Army

There are several ways to join the army, each with its own unique requirements and benefits. Here are five ways to join the army:
- Enlisting: This is the most common way to join the army, and it involves signing up for a certain period of time, usually 3-6 years. To enlist, you will need to meet the army's basic eligibility requirements, which include being a U.S. citizen, being between the ages of 17 and 35, and meeting certain physical and medical standards.
- Officer Candidate School (OCS): This is a program that allows individuals to become officers in the army. To attend OCS, you will need to have a bachelor's degree, be a U.S. citizen, and meet certain physical and medical standards.
- Reserve Officers' Training Corps (ROTC): This is a program that allows individuals to become officers in the army while also attending college. To participate in ROTC, you will need to be a U.S. citizen, be between the ages of 17 and 26, and meet certain physical and medical standards.
- Direct Commission: This is a program that allows individuals to become officers in the army based on their professional experience and expertise. To be eligible for a direct commission, you will need to have a bachelor's degree, be a U.S. citizen, and meet certain physical and medical standards.
- National Guard: This is a part-time military force that allows individuals to serve their country while also pursuing their civilian careers. To join the National Guard, you will need to be a U.S. citizen, be between the ages of 17 and 35, and meet certain physical and medical standards.
Benefits of Joining the Army

Joining the army can provide individuals with a wide range of benefits, including:
- Competitive pay and benefits: The army offers competitive pay and benefits, including housing allowance, food allowance, and access to on-base facilities such as gyms, libraries, and shopping centers.
- Opportunities for advancement and promotion: The army provides individuals with opportunities for advancement and promotion, based on their performance and experience.
- Education and training: The army offers a wide range of training and educational programs, including basic training, advanced individual training, and specialized training in fields such as medicine, engineering, and communications.
- Sense of purpose and fulfillment: Joining the army can provide individuals with a sense of purpose and fulfillment, as they serve their country and contribute to the defense of their nation.
- Camaraderie and esprit de corps: The army provides individuals with a sense of camaraderie and esprit de corps, as they work together with their fellow soldiers to achieve a common goal.
Army Career Paths

The army offers a wide range of career paths, each with its own unique requirements and benefits. Some of the most popular career paths in the army include:
- Infantry: This is a combat arms specialty that involves engaging enemy forces on the ground.
- Armor: This is a combat arms specialty that involves operating tanks and other armored vehicles.
- Artillery: This is a combat arms specialty that involves operating cannons and other artillery systems.
- Engineering: This is a technical specialty that involves designing, building, and maintaining infrastructure such as roads, bridges, and buildings.
- Medicine: This is a medical specialty that involves providing medical care to soldiers and civilians.
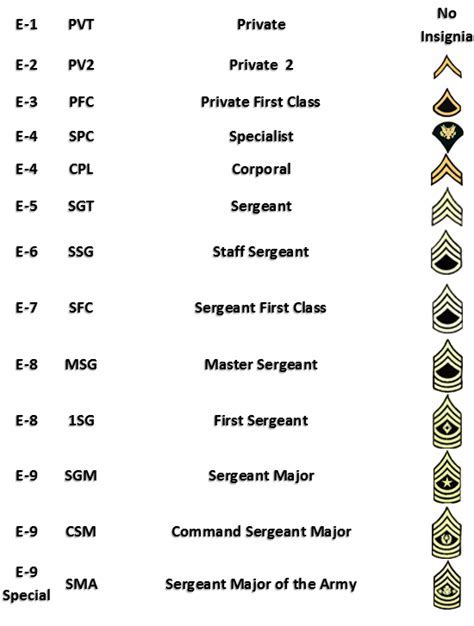
Army Ranks and Insignia

The army uses a system of ranks and insignia to identify an individual's level of experience and responsibility. The ranks in the army are:
- Private (PVT): This is the lowest rank in the army, and it is typically held by new recruits.
- Private First Class (PFC): This rank is typically held by individuals who have completed basic training and have some experience in the army.
- Specialist/Corporal (SPC/CPL): This rank is typically held by individuals who have completed advanced individual training and have some experience in the army.
- Sergeant (SGT): This rank is typically held by individuals who have completed advanced leadership training and have significant experience in the army.
- Staff Sergeant (SSG): This rank is typically held by individuals who have completed advanced leadership training and have significant experience in the army.
- Sergeant First Class (SFC): This rank is typically held by individuals who have completed advanced leadership training and have significant experience in the army.
- Master Sergeant/First Sergeant (MSG/1SG): This rank is typically held by individuals who have completed advanced leadership training and have significant experience in the army.
- Sergeant Major (SGM): This is the highest enlisted rank in the army, and it is typically held by individuals who have completed advanced leadership training and have significant experience in the army.
Army Training and Education

The army provides individuals with a wide range of training and educational programs, including:
- Basic Combat Training (BCT): This is a 10-week training program that teaches new recruits the basics of soldiering, including first aid, map reading, and combat skills.
- Advanced Individual Training (AIT): This is a training program that teaches individuals the skills they need to perform their specific job in the army.
- Officer Candidate School (OCS): This is a 12-week training program that teaches individuals the skills they need to become officers in the army.
- Reserve Officers' Training Corps (ROTC): This is a college-based training program that teaches individuals the skills they need to become officers in the army.
- Specialized Training: The army offers a wide range of specialized training programs, including training in fields such as medicine, engineering, and communications.
Army Deployments and Missions

The army is involved in a wide range of deployments and missions, including:
- Combat operations: The army is involved in combat operations in countries such as Afghanistan and Iraq.
- Peacekeeping operations: The army is involved in peacekeeping operations in countries such as Bosnia and Kosovo.
- Humanitarian assistance: The army provides humanitarian assistance to countries affected by natural disasters and other crises.
- Homeland security: The army is involved in homeland security operations, including border security and disaster response.
Army Gallery









What are the requirements to join the army?
+To join the army, you must be a U.S. citizen, be between the ages of 17 and 35, and meet certain physical and medical standards. You must also have a high school diploma or equivalent, and score well on the Armed Services Vocational Aptitude Battery (ASVAB) test.
What are the benefits of joining the army?
+The benefits of joining the army include competitive pay and benefits, opportunities for advancement and promotion, education and training, and a sense of purpose and fulfillment. You will also have access to on-base facilities such as gyms, libraries, and shopping centers.
What are the different career paths in the army?
+The army offers a wide range of career paths, including infantry, armor, artillery, engineering, and medicine. You can also choose to specialize in a particular field, such as communications, intelligence, or logistics.
How long does army training last?
+Army training typically lasts for 10-12 weeks, although some specialized training programs can last longer. You will attend basic combat training (BCT) and advanced individual training (AIT), and may also attend additional training programs depending on your career path.
Can I join the army with a medical condition?
+It depends on the medical condition. Some medical conditions may disqualify you from joining the army, while others may require a waiver. You will need to consult with a recruiter and a medical professional to determine whether you are eligible to join the army with a medical condition.
If you are considering joining the army, we encourage you to do your research and learn as much as you can about the different career paths and benefits that are available. You can talk to a recruiter, visit the army's website, and read about the experiences of other soldiers to get a better understanding of what it's like to serve in the army. We also invite you to share your thoughts and questions with us, and to join the conversation on social media using the hashtag #armyrecruitment. Whether you are interested in serving your country, advancing your education and career, or simply challenging yourself to be your best, the army has something to offer. So why not take the first step today and learn more about the opportunities and benefits of joining the army?

