Intro
Discover the Army Ranks In Order List, including enlisted, warrant, and officer ranks, with explanations of military hierarchy, rank insignia, and promotion requirements.
The hierarchy of army ranks is a crucial aspect of military organization, as it defines the chain of command and the responsibilities of each soldier. Understanding the different ranks and their roles is essential for effective communication, teamwork, and mission accomplishment. In this article, we will delve into the world of army ranks, exploring their history, significance, and the various positions that make up the military hierarchy.
The army rank system has its roots in ancient times, with evidence of organized military structures dating back to the Roman Empire. Over the centuries, the rank system has evolved to accommodate changing military needs, technologies, and societal values. Today, the army rank system is a complex and multifaceted structure, comprising various branches, specialties, and levels of authority. From the lowest-ranking private to the highest-ranking general, each soldier plays a vital role in the military machine.
The importance of understanding army ranks cannot be overstated. Not only does it facilitate communication and coordination among soldiers, but it also provides a framework for career advancement, training, and leadership development. By recognizing the different ranks and their corresponding responsibilities, soldiers can better navigate the military bureaucracy, build strong relationships with their comrades, and contribute to the overall success of their unit. Whether you are a seasoned veteran or a new recruit, familiarity with the army rank system is essential for achieving your full potential in the military.
Army Ranks Overview

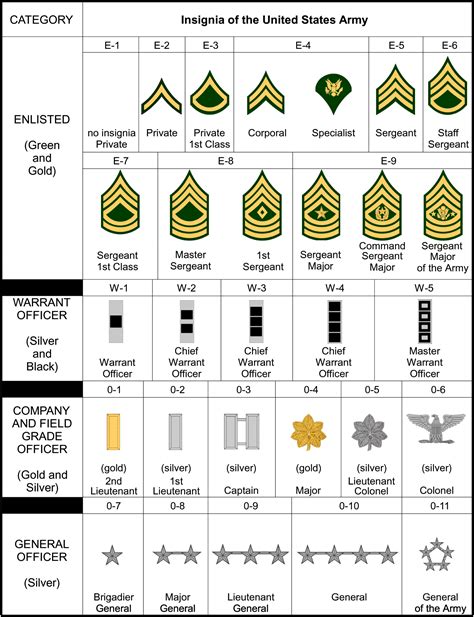
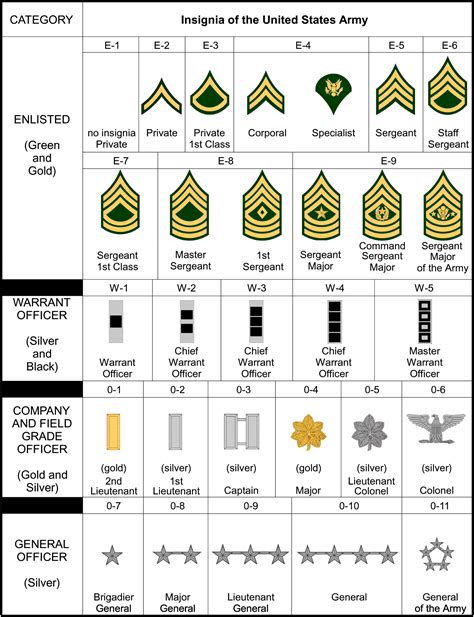
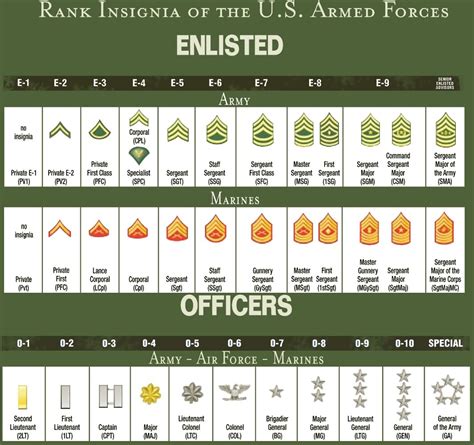
The army rank system is divided into several categories, including enlisted ranks, warrant officer ranks, and officer ranks. Enlisted ranks are the most numerous, comprising the bulk of the military personnel. These soldiers are responsible for carrying out the day-to-day tasks and operations of the army, from infantry and artillery to logistics and administration. Warrant officers, on the other hand, are technical experts who have acquired specialized skills and knowledge in a particular field. Officer ranks, which include commissioned officers and non-commissioned officers, are responsible for leading and commanding units, making strategic decisions, and overseeing the overall direction of the military.
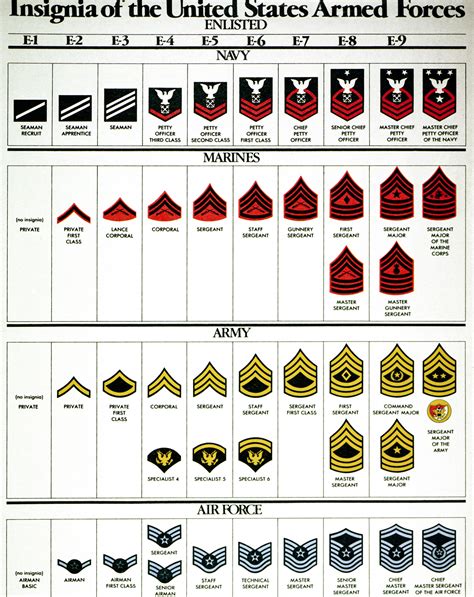
Enlisted Ranks

Enlisted ranks are the backbone of the army, providing the manpower and expertise needed to carry out military operations. The enlisted rank system is as follows:
- Private (PVT): The lowest-ranking enlisted soldier, responsible for carrying out basic tasks and duties.
- Private First Class (PFC): A junior enlisted soldier who has gained some experience and responsibility.
- Specialist/Corporal (SPC/CPL): A mid-level enlisted soldier who has acquired specialized skills and knowledge.
- Sergeant (SGT): A senior enlisted soldier who leads and commands small units.
- Staff Sergeant (SSG): A senior enlisted soldier who oversees and coordinates the activities of multiple units.
- Sergeant First Class (SFC): A senior enlisted soldier who provides technical expertise and guidance to junior soldiers.
- Master Sergeant/First Sergeant (MSG/1SG): A senior enlisted soldier who leads and commands large units, providing strategic guidance and direction.
- Sergeant Major (SGM): The highest-ranking enlisted soldier, responsible for advising and assisting senior officers.
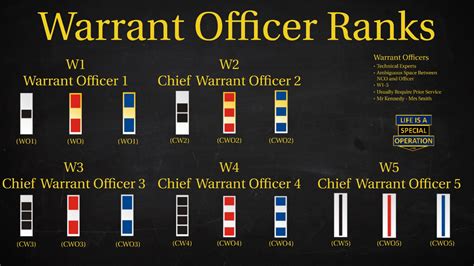
Warrant Officer Ranks
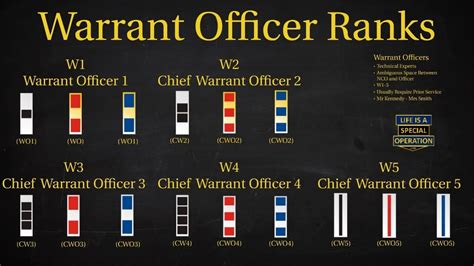
Warrant officers are technical experts who have acquired specialized skills and knowledge in a particular field. The warrant officer rank system is as follows:
- Warrant Officer 1 (WO1): A junior warrant officer who has acquired basic technical expertise.
- Chief Warrant Officer 2 (CW2): A mid-level warrant officer who has gained significant technical experience and responsibility.
- Chief Warrant Officer 3 (CW3): A senior warrant officer who provides technical guidance and expertise to junior soldiers.
- Chief Warrant Officer 4 (CW4): A senior warrant officer who oversees and coordinates the technical activities of multiple units.
- Chief Warrant Officer 5 (CW5): The highest-ranking warrant officer, responsible for providing strategic technical guidance and direction.
Officer Ranks
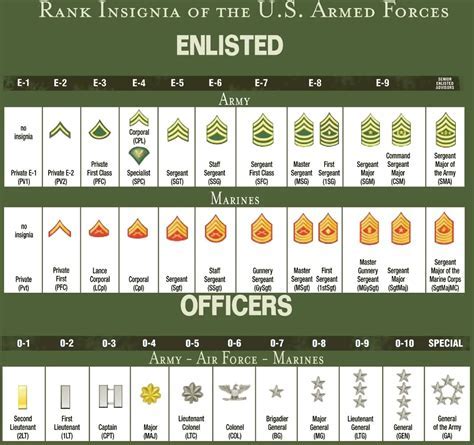
Officer ranks are responsible for leading and commanding units, making strategic decisions, and overseeing the overall direction of the military. The officer rank system is as follows:
- Second Lieutenant (2LT): The lowest-ranking commissioned officer, responsible for leading small units.
- First Lieutenant (1LT): A junior commissioned officer who has gained some experience and responsibility.
- Captain (CPT): A mid-level commissioned officer who leads and commands larger units.
- Major (MAJ): A senior commissioned officer who oversees and coordinates the activities of multiple units.
- Lieutenant Colonel (LTC): A senior commissioned officer who provides strategic guidance and direction to junior officers.
- Colonel (COL): A senior commissioned officer who leads and commands large units, providing strategic leadership and direction.
- Brigadier General (BG): A one-star general officer who oversees and coordinates the activities of multiple units.
- Major General (MG): A two-star general officer who provides strategic guidance and direction to junior officers.
- Lieutenant General (LTG): A three-star general officer who leads and commands large units, providing strategic leadership and direction.
- General (GEN): The highest-ranking officer, responsible for providing overall strategic guidance and direction to the military.
Non-Commissioned Officer Ranks
Non-commissioned officers (NCOs) are enlisted soldiers who have acquired leadership skills and responsibilities. The NCO rank system is as follows: * Corporal (CPL): A junior NCO who leads and commands small units. * Sergeant (SGT): A mid-level NCO who oversees and coordinates the activities of multiple units. * Staff Sergeant (SSG): A senior NCO who provides technical expertise and guidance to junior soldiers. * Sergeant First Class (SFC): A senior NCO who leads and commands large units, providing strategic guidance and direction. * Master Sergeant/First Sergeant (MSG/1SG): A senior NCO who oversees and coordinates the activities of multiple units, providing technical expertise and guidance to junior soldiers.Army Rank Insignia

Army rank insignia are the symbols and emblems that represent a soldier's rank and position. These insignia are worn on the uniform and are used to identify a soldier's rank and branch of service. The most common types of army rank insignia include:
- Chevrons: Inverted V-shaped symbols that represent enlisted ranks.
- Bars: Horizontal bars that represent officer ranks.
- Oak leaves: Symbols that represent field-grade officer ranks.
- Stars: Symbols that represent general officer ranks.
- Eagles: Symbols that represent senior enlisted ranks.
Army Rank Structure
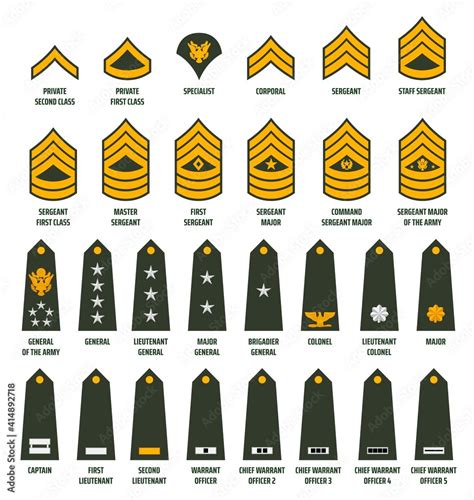

The army rank structure is a hierarchical system that defines the chain of command and the responsibilities of each soldier. The rank structure is as follows:
- Enlisted ranks: Private to Sergeant Major
- Warrant officer ranks: Warrant Officer 1 to Chief Warrant Officer 5
- Officer ranks: Second Lieutenant to General
- Non-commissioned officer ranks: Corporal to Sergeant Major
Gallery of Army Ranks
Army Ranks Image Gallery



What is the highest rank in the army?
+The highest rank in the army is General (GEN).
What is the difference between enlisted and officer ranks?
+Enlisted ranks are the most numerous and comprise the bulk of the military personnel, while officer ranks are responsible for leading and commanding units.
What is the purpose of army rank insignia?
+Army rank insignia are used to identify a soldier's rank and position, and to provide a visual representation of the chain of command.
How do army ranks affect career advancement?
+Army ranks play a significant role in career advancement, as they determine a soldier's level of responsibility, pay, and opportunities for promotion.
What is the difference between a commissioned officer and a non-commissioned officer?
+A commissioned officer is a higher-ranking officer who has been commissioned by the president, while a non-commissioned officer is an enlisted soldier who has acquired leadership skills and responsibilities.
In conclusion, the army rank system is a complex and multifaceted structure that defines the chain of command and the responsibilities of each soldier. Understanding the different ranks and their corresponding insignia is essential for effective communication, teamwork, and mission accomplishment. Whether you are a seasoned veteran or a new recruit, familiarity with the army rank system is crucial for achieving your full potential in the military. We invite you to share your thoughts and experiences with army ranks in the comments below, and to explore the various resources and references available for further learning. By working together and supporting one another, we can build a stronger, more effective military that serves our nation with pride and distinction.
