Intro
Discover 2013 Army pay rates, including military salary scales, allowances, and benefits for enlisted personnel and officers, with detailed breakdowns of basic pay, special pays, and compensation packages.
The 2013 army pay rates were an essential aspect of the compensation package for military personnel serving in the United States Army. Understanding these rates is crucial for both current and prospective service members, as they directly impact the financial well-being of soldiers and their families. In this article, we will delve into the 2013 army pay rates, exploring the various factors that influence military compensation, the different types of pay, and the benefits that accompany military service.
The military pay scale is based on a combination of factors, including rank, time in service, and job specialty. The 2013 army pay rates reflected the ongoing efforts to ensure that military compensation remains competitive with civilian pay scales. The pay rates were adjusted to account for the rising cost of living, ensuring that soldiers and their families could maintain a decent standard of living. For instance, the basic pay for an entry-level private (E-1) in 2013 was $1,516.20 per month, while a seasoned sergeant major (E-9) could earn up to $7,435.40 per month.
2013 Army Pay Scale

The 2013 army pay scale was divided into several categories, including basic pay, allowances, and special pays. Basic pay is the primary component of military compensation, and it varies based on rank and time in service. Allowances, on the other hand, are designed to help soldiers cover specific expenses, such as housing and food. Special pays are awarded to soldiers who possess unique skills or serve in high-demand specialties.
Basic Pay Rates
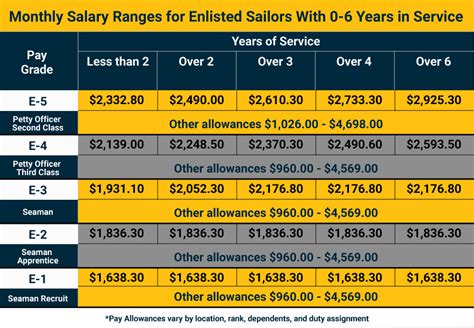
The basic pay rates for 2013 were as follows:
- Private (E-1): $1,516.20 per month
- Private First Class (E-2): $1,699.80 per month
- Specialist/Corporal (E-4): $2,161.10 per month
- Sergeant (E-5): $2,541.60 per month
- Staff Sergeant (E-6): $3,041.40 per month
- Sergeant First Class (E-7): $3,541.80 per month
- Master Sergeant/First Sergeant (E-8): $4,341.90 per month
- Sergeant Major (E-9): $7,435.40 per month
Allowances and Special Pays

In addition to basic pay, soldiers may be eligible for various allowances and special pays. These include:
- Basic Allowance for Housing (BAH): a monthly stipend to help cover housing expenses
- Basic Allowance for Subsistence (BAS): a monthly stipend to help cover food expenses
- Special Duty Pay: awarded to soldiers who serve in high-stress or high-demand specialties
- Hazardous Duty Pay: awarded to soldiers who serve in hazardous environments
- Jump Pay: awarded to soldiers who are qualified parachutists
Benefits and Privileges

Military service comes with a range of benefits and privileges, including:
- Comprehensive health insurance
- Education assistance
- Retirement benefits
- Access to on-base facilities, such as gyms and commissaries
- Tax-free allowances and special pays
- Opportunities for advancement and professional development
Impact of 2013 Army Pay Rates
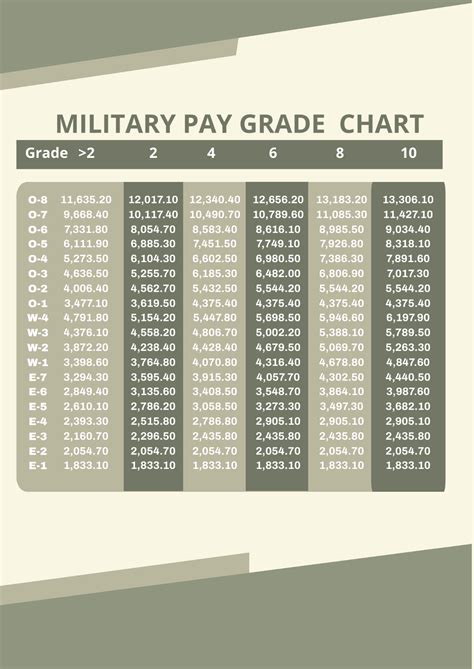
The 2013 army pay rates had a significant impact on the lives of soldiers and their families. The increased pay rates helped to offset the rising cost of living, ensuring that military personnel could maintain a decent standard of living. The various allowances and special pays also helped to recognize the unique challenges and sacrifices made by soldiers, providing them with additional financial support.
Comparison to Civilian Pay Scales
The 2013 army pay rates were competitive with civilian pay scales, especially when factoring in the various allowances and benefits. However, the pay rates varied significantly depending on rank and job specialty. For instance, a senior non-commissioned officer (NCO) with 20 years of service could earn a higher salary than a civilian counterpart, while a junior enlisted soldier might earn less.
Gallery of Army Pay Rates
Army Pay Rates Image Gallery

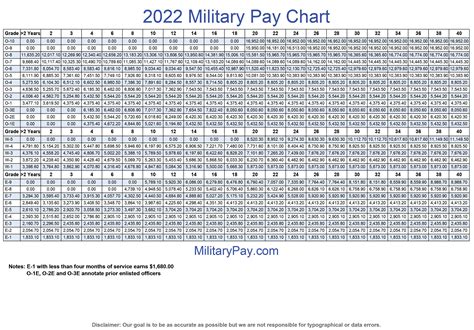







What were the 2013 army pay rates for enlisted personnel?
+The 2013 army pay rates for enlisted personnel varied based on rank and time in service, ranging from $1,516.20 per month for a private (E-1) to $7,435.40 per month for a sergeant major (E-9).
What allowances and special pays were available to soldiers in 2013?
+Soldiers in 2013 were eligible for various allowances, including Basic Allowance for Housing (BAH) and Basic Allowance for Subsistence (BAS), as well as special pays, such as Special Duty Pay and Hazardous Duty Pay.
How did the 2013 army pay rates compare to civilian pay scales?
+The 2013 army pay rates were competitive with civilian pay scales, especially when factoring in the various allowances and benefits, although the pay rates varied significantly depending on rank and job specialty.
What benefits and privileges came with military service in 2013?
+Military service in 2013 came with a range of benefits and privileges, including comprehensive health insurance, education assistance, retirement benefits, and access to on-base facilities.
How did the 2013 army pay rates impact the lives of soldiers and their families?
+The 2013 army pay rates had a significant impact on the lives of soldiers and their families, helping to offset the rising cost of living and providing additional financial support through various allowances and special pays.
In conclusion, the 2013 army pay rates played a critical role in ensuring the financial well-being of military personnel and their families. By understanding the various components of military compensation, including basic pay, allowances, and special pays, soldiers can better navigate the complexities of military finance and plan for their future. We invite our readers to share their thoughts and experiences regarding the 2013 army pay rates, and to explore the various resources available to support military personnel and their families. Whether you are a current or prospective service member, we encourage you to take advantage of the many benefits and privileges that come with military service, and to stay informed about the latest developments in military compensation and finance.
