Intro
Boost your gaming skills with 5 Armored Brigade tips, featuring tactical warfare strategies, combat techniques, and military maneuvers to enhance gameplay and dominate battles.
The world of armored warfare is complex and challenging, requiring a deep understanding of strategy, tactics, and logistics. For those who are new to the genre, or even for seasoned veterans, navigating the intricacies of commanding an armored brigade can be daunting. However, with the right approach and mindset, anyone can improve their skills and become a formidable force on the battlefield.
Understanding the basics of armored warfare is crucial. This includes knowing the strengths and weaknesses of different types of tanks and armored vehicles, as well as how to use terrain to your advantage. It also involves developing a keen sense of situational awareness, being able to read the battlefield and make quick, informed decisions. Whether you're fighting in a historical context or in a fictional scenario, the principles of armored warfare remain largely the same.
As you delve deeper into the world of armored brigades, you'll discover that success is not just about the hardware at your disposal, but also about the strategy and tactics you employ. This includes everything from how you organize your units and allocate resources, to how you execute maneuvers and respond to enemy actions. It's a delicate balance of offense and defense, where the ability to adapt and innovate can be the difference between victory and defeat.
Introduction to Armored Brigades

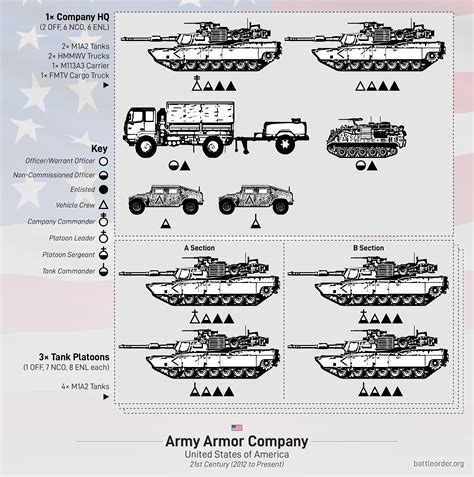
Key Components of an Armored Brigade
The key components of an armored brigade include: - Tank battalions: These are the main fighting force of the brigade, equipped with main battle tanks. - Infantry battalions: These are mechanized infantry units that provide supporting firepower and assist in securing terrain. - Artillery battalions: These provide indirect fire support to the brigade, using guns, howitzers, and rocket launchers. - Engineer battalions: These provide combat engineering support, including mine clearance, bridge laying, and fortification construction.Armored Brigade Tactics

Principles of Armored Warfare
Some key principles of armored warfare include: - Speed and surprise: Armored units should seek to move quickly and catch the enemy off guard. - Concentration of force: Armored units should be concentrated at the point of attack, to achieve a decisive advantage. - Economy of force: Armored units should be used sparingly, to avoid unnecessary losses and conserve resources. - Flexibility: Armored units should be able to adapt quickly to changing circumstances, and respond to unexpected threats or opportunities.Armored Brigade Operations

Phases of Armored Brigade Operations
The phases of armored brigade operations include: - Planning: This involves the development of a plan, including the identification of objectives, the allocation of resources, and the coordination of units. - Preparation: This involves the preparation of units, equipment, and supplies, as well as the conduct of reconnaissance and intelligence gathering. - Execution: This involves the actual conduct of the operation, including the movement of units, the engagement of the enemy, and the achievement of objectives. - Sustainment: This involves the maintenance and repair of equipment, as well as the provision of logistical support.Armored Brigade Logistics

Key Logistics Considerations
Some key logistics considerations for armored brigades include: - Supply chain management: This involves the management of the supply chain, from the procurement of supplies and equipment, to their delivery to the brigade. - Maintenance and repair: This involves the maintenance and repair of equipment, to ensure that it remains operational and effective. - Fuel and ammunition: This involves the provision of fuel and ammunition, to support the conduct of armored warfare. - Medical care: This involves the provision of medical care, to support the health and well-being of brigade personnel.Armored Brigade Training

Types of Armored Brigade Training
Some types of armored brigade training include: - Basic training: This involves the development of basic skills, such as marksmanship, first aid, and vehicle operation. - Advanced training: This involves the development of specialized skills, such as tank gunnery, armored reconnaissance, and combat engineering. - Collective training: This involves the training of units, to develop their ability to work together and conduct armored warfare. - Simulation training: This involves the use of simulators, to replicate the conditions of armored warfare and develop the skills and knowledge necessary to succeed.Armored Brigade Leadership

Key Leadership Considerations
Some key leadership considerations for armored brigades include: - Command and control: This involves the exercise of command and control, to direct and coordinate the actions of armored units. - Decision-making: This involves the development of decision-making skills, to make quick and effective decisions in the heat of battle. - Communication: This involves the development of communication skills, to effectively communicate with units and coordinate their actions. - Motivation: This involves the development of motivation skills, to inspire and motivate brigade personnel to achieve their objectives.Armored Brigade Image Gallery








What is the primary role of an armored brigade?
+The primary role of an armored brigade is to conduct armored warfare, which involves the use of armored vehicles to break through enemy lines, exploit weaknesses, and rapidly advance deep into enemy territory.
What are the key components of an armored brigade?
+The key components of an armored brigade include tank battalions, infantry battalions, artillery battalions, and engineer battalions.
What are some key principles of armored warfare?
+Some key principles of armored warfare include speed and surprise, concentration of force, economy of force, and flexibility.
What is the importance of logistics in armored brigade operations?
+Logistics is critical for the success of an armored brigade, involving the provision of supplies, equipment, and services to support the conduct of armored warfare.
What are some key leadership considerations for armored brigades?
+Some key leadership considerations for armored brigades include command and control, decision-making, communication, and motivation.
In conclusion, commanding an armored brigade is a complex and challenging task, requiring a deep understanding of strategy, tactics, and logistics. By following these tips and principles, you can improve your skills and become a more effective commander. Remember to stay flexible, adapt to changing circumstances, and always keep your units trained and ready for action. With the right mindset and approach, you can achieve success on the battlefield and lead your armored brigade to victory. We invite you to share your thoughts and experiences with armored brigades, and to ask any questions you may have about this fascinating topic.
