Intro
Discover if Army Reserves are considered veterans, exploring benefits, service requirements, and veteran status for reservists, including National Guard and military personnel.
The question of whether Army Reserves are considered veterans is a complex one, with different answers depending on the context and the specific circumstances of the individual's service. In general, the term "veteran" refers to a person who has served in the armed forces, but the definition can vary depending on the organization, government agency, or benefit program. To understand whether Army Reserves are considered veterans, it's essential to delve into the details of their service and the laws that govern veteran status.
The Army Reserve is a component of the United States Army that allows citizens to serve part-time, typically one weekend a month and two weeks a year, while also pursuing civilian careers. Army Reservists may be called to active duty in times of war or national emergency, and they may also volunteer for active duty deployments. The Reserve's primary role is to provide a pool of trained soldiers who can be mobilized quickly in case of a national emergency or conflict.
Army Reservists who have served on active duty, either voluntarily or involuntarily, are generally considered veterans. This includes those who have served in combat zones, participated in humanitarian missions, or supported military operations in other ways. However, the situation is less clear-cut for Reservists who have only served part-time, without being called to active duty. In these cases, the individual's veteran status may depend on the specific laws and regulations that govern the benefit or program in question.
Understanding Veteran Status

To determine whether an Army Reservist is considered a veteran, it's essential to examine the laws and regulations that define veteran status. The Department of Veterans Affairs (VA) is the primary government agency responsible for providing benefits and services to veterans. According to the VA, a veteran is defined as a person who has served in the active military, naval, or air service, and who was discharged or released under conditions other than dishonorable.
The VA considers Army Reservists who have served on active duty to be veterans, regardless of the length of their service. This includes Reservists who have been called to active duty for training, humanitarian missions, or combat operations. However, the VA's definition of veteran status does not necessarily apply to all benefit programs or organizations. Some programs, such as the GI Bill or state-level veterans' benefits, may have different eligibility criteria or definitions of veteran status.
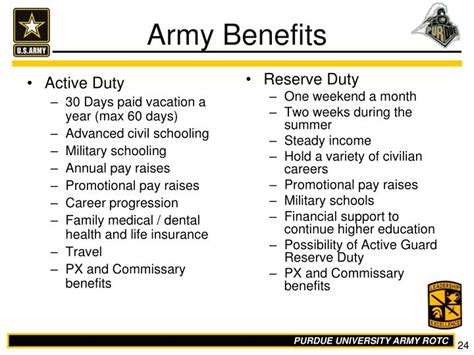
Benefits for Army Reservists
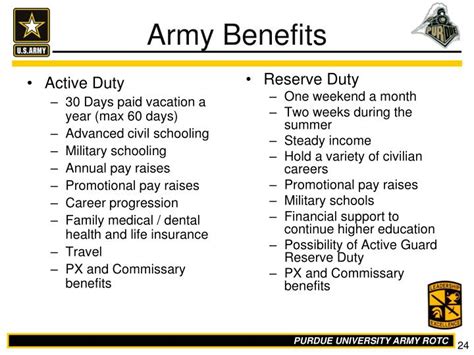
Army Reservists who are considered veterans may be eligible for a range of benefits, including healthcare, education, and employment assistance. The VA provides a comprehensive package of benefits to eligible veterans, including medical care, disability compensation, and vocational rehabilitation. Army Reservists who have served on active duty may also be eligible for the GI Bill, which provides education benefits for college, vocational training, or other educational programs.
In addition to federal benefits, many states and local governments offer benefits and incentives to veterans, including property tax exemptions, employment preferences, and educational assistance. Some private organizations, such as the Veterans of Foreign Wars (VFW) or the American Legion, also provide benefits and support to veterans. However, the eligibility criteria for these benefits and programs may vary, and not all Army Reservists may qualify.
Challenges Faced by Army Reservists

Despite their service and sacrifices, Army Reservists often face unique challenges and obstacles. One of the primary challenges is the difficulty of balancing civilian and military responsibilities. Army Reservists may be called to active duty at short notice, which can disrupt their civilian careers and personal lives. They may also face challenges in accessing benefits and services, particularly if they have not served on active duty.
Another challenge faced by Army Reservists is the lack of recognition and appreciation for their service. Unlike active-duty soldiers, Reservists may not receive the same level of recognition or support from their communities or employers. This can lead to feelings of isolation and disconnection, particularly for Reservists who have served in combat zones or experienced traumatic events.
Support for Army Reservists

To address these challenges, it's essential to provide support and resources to Army Reservists. This can include counseling and mental health services, employment assistance, and education benefits. The VA and other government agencies offer a range of programs and services to support Reservists, including the Vet Center program, which provides counseling and readjustment services to veterans and their families.
Private organizations, such as the USO or the Wounded Warrior Project, also provide support and resources to Army Reservists. These organizations offer a range of services, including entertainment and leisure activities, employment assistance, and adaptive sports programs. By providing support and resources to Army Reservists, we can help them navigate the challenges of military service and transition back to civilian life.
Gallery of Army Reservists
Army Reservists Image Gallery








Frequently Asked Questions
Are Army Reservists considered veterans?
+Army Reservists who have served on active duty are generally considered veterans. However, the definition of veteran status may vary depending on the context and the specific circumstances of the individual's service.
What benefits are available to Army Reservists?
+Army Reservists who are considered veterans may be eligible for a range of benefits, including healthcare, education, and employment assistance. The VA provides a comprehensive package of benefits to eligible veterans, including medical care, disability compensation, and vocational rehabilitation.
How can I support Army Reservists?
+There are many ways to support Army Reservists, including volunteering with organizations that provide support services, donating to charities that benefit veterans, and advocating for policies that support veterans' benefits and services.
What challenges do Army Reservists face?
+Army Reservists often face unique challenges, including the difficulty of balancing civilian and military responsibilities, accessing benefits and services, and navigating the transition back to civilian life. They may also face challenges in finding employment, accessing healthcare, and reconnecting with their families and communities.
How can I learn more about Army Reservists and their experiences?
+There are many resources available to learn more about Army Reservists and their experiences, including books, documentaries, and online forums. You can also connect with Army Reservists and veterans through social media, support groups, and community organizations.
In conclusion, the question of whether Army Reserves are considered veterans is complex and multifaceted. While some Army Reservists may be considered veterans, others may not, depending on the context and the specific circumstances of their service. By understanding the challenges and benefits faced by Army Reservists, we can work to provide them with the support and resources they need to succeed. If you have any further questions or would like to learn more about Army Reservists and their experiences, please don't hesitate to reach out. Share this article with others to help raise awareness about the important contributions and sacrifices made by Army Reservists. Together, we can make a difference in the lives of these brave men and women.
