Intro
Discover 5 Arctic Cold War tips to boost winter survival skills, including frostbite prevention, hypothermia treatment, and cold-weather tactics, to stay safe in extreme polar environments.
The Arctic region has become a focal point of international attention in recent years, with many countries vying for influence and access to its vast natural resources. The Arctic Cold War, as it has come to be known, is a complex and multifaceted issue that involves geopolitical, economic, and environmental considerations. As the region continues to thaw and become more accessible, it is essential to understand the key players, their interests, and the implications of their actions. In this article, we will explore five Arctic Cold War tips that can help you navigate this complex and rapidly changing landscape.
The Arctic region is home to significant reserves of oil, gas, and minerals, making it an attractive destination for countries looking to secure their energy futures. However, the region is also home to indigenous communities, fragile ecosystems, and unique biodiversity, which must be protected and preserved. The Arctic Cold War is not just about competition for resources; it is also about responsible stewardship and management of the region's delicate environment. As the region becomes more accessible, it is crucial to balance economic interests with environmental and social concerns.
The Arctic region is a vast and remote area, covering over 14 million square miles of land and sea. It is home to eight countries, including the United States, Canada, Russia, Norway, Denmark, Sweden, Finland, and Iceland. Each of these countries has its own unique interests and priorities in the region, ranging from energy exploration and fishing to tourism and scientific research. Understanding the interests and motivations of each country is essential to navigating the complex web of relationships and alliances in the Arctic.
Understanding the Key Players
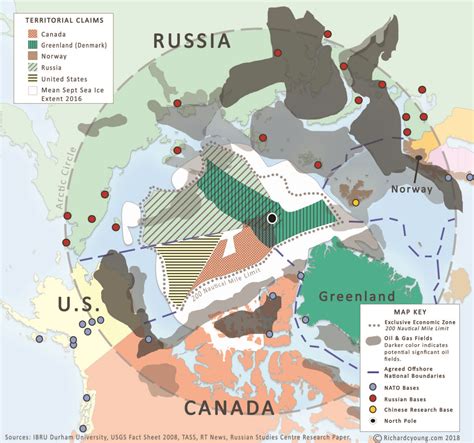
Some of the key players in the Arctic Cold War include:
- The United States: The United States has significant interests in the Arctic, including energy exploration, fishing, and national security. The country is also home to a significant number of indigenous communities, which must be taken into account in any decision-making process.
- Russia: Russia has been a major player in the Arctic for decades, with significant investments in energy exploration, mining, and transportation. The country is also home to a large number of indigenous communities, which have been impacted by climate change and other environmental factors.
- Canada: Canada has significant interests in the Arctic, including energy exploration, fishing, and tourism. The country is also home to a large number of indigenous communities, which have been impacted by climate change and other environmental factors.
Arctic Cold War Tip 1: Understand the Geopolitics

Some key geopolitical considerations in the Arctic include:
- The Northwest Passage: The Northwest Passage is a strategic waterway that connects the Atlantic and Pacific Oceans, passing through the Canadian Arctic Archipelago. The passage is becoming increasingly navigable due to climate change, which has significant implications for global trade and commerce.
- The Arctic Council: The Arctic Council is a high-level intergovernmental forum that brings together the eight Arctic countries to discuss issues related to the region. The council has been instrumental in promoting cooperation and collaboration in the region, but it has also been criticized for its limited scope and lack of representation for indigenous communities.
Arctic Cold War Tip 2: Recognize the Economic Interests

Some key economic considerations in the Arctic include:
- Energy exploration: The Arctic is home to significant reserves of oil and gas, which are becoming increasingly accessible due to climate change. Energy exploration is a major driver of economic activity in the region, but it also poses significant environmental risks.
- Mining: The Arctic is also home to significant reserves of minerals, including iron, copper, and gold. Mining is a major economic activity in the region, but it also poses significant environmental risks, including pollution and habitat destruction.
Environmental Considerations
The Arctic environment is fragile and unique, with significant biodiversity and ecosystem services. However, the region is also facing significant environmental challenges, including climate change, pollution, and habitat destruction. It is essential to balance economic interests with environmental concerns, including the protection of indigenous communities and the preservation of fragile ecosystems.Some key environmental considerations in the Arctic include:
- Climate change: Climate change is having a significant impact on the Arctic environment, including rising temperatures, sea-level rise, and changes in precipitation patterns. These changes are having a significant impact on indigenous communities, including the loss of traditional hunting and fishing grounds.
- Pollution: The Arctic is also facing significant pollution challenges, including oil spills, chemical contamination, and plastic pollution. These pollutants are having a significant impact on the region's fragile ecosystems, including the contamination of fish and other wildlife.
Arctic Cold War Tip 3: Respect Indigenous Communities

Some key considerations for respecting indigenous communities in the Arctic include:
- Recognition of rights: It is essential to recognize the rights of indigenous peoples, including their right to self-determination, cultural preservation, and environmental protection.
- Consultation and collaboration: It is essential to engage with indigenous communities in a meaningful and respectful way, including through consultation, collaboration, and co-management.
Arctic Cold War Tip 4: Promote International Cooperation

Some key considerations for promoting international cooperation in the Arctic include:
- The Arctic Council: The Arctic Council is a high-level intergovernmental forum that brings together the eight Arctic countries to discuss issues related to the region. The council has been instrumental in promoting cooperation and collaboration in the region.
- International agreements: There are several international agreements that govern the Arctic region, including the United Nations Convention on the Law of the Sea (UNCLOS) and the Paris Agreement on climate change. These agreements provide a framework for cooperation and collaboration among nations.
Arctic Cold War Tip 5: Invest in Sustainable Development

Some key considerations for investing in sustainable development in the Arctic include:
- Renewable energy: The Arctic is home to significant renewable energy resources, including wind, solar, and hydro power. Investing in renewable energy can help reduce the region's dependence on fossil fuels and promote sustainable development.
- Green infrastructure: The Arctic is also home to significant green infrastructure, including parks, protected areas, and wildlife corridors. Investing in green infrastructure can help promote biodiversity and ecosystem services, while also supporting sustainable development.
Arctic Cold War Image Gallery








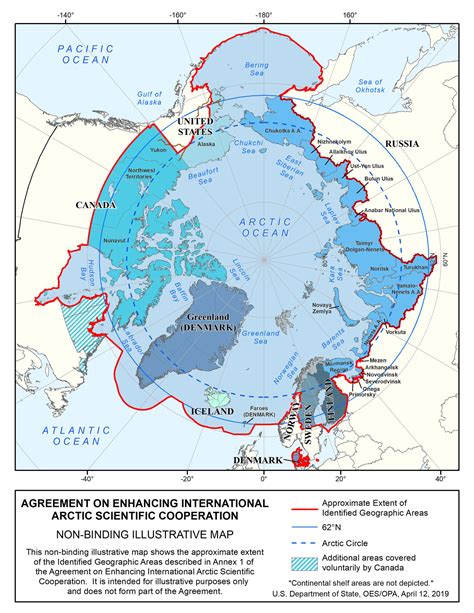
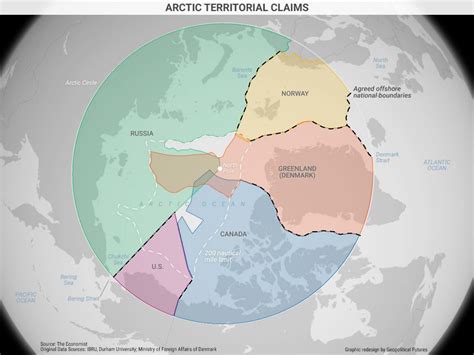
What is the Arctic Cold War?
+The Arctic Cold War refers to the increasing competition and tension between nations in the Arctic region, driven by the region's significant natural resources and strategic location.
Who are the key players in the Arctic Cold War?
+The key players in the Arctic Cold War include the eight Arctic countries (the United States, Canada, Russia, Norway, Denmark, Sweden, Finland, and Iceland), as well as other nations that have interests in the region, such as China and the European Union.
What are the main issues at stake in the Arctic Cold War?
+The main issues at stake in the Arctic Cold War include access to natural resources, territorial claims, and environmental protection. The region is home to significant reserves of oil, gas, and minerals, as well as fragile ecosystems and indigenous communities.
How can the Arctic Cold War be resolved?
+The Arctic Cold War can be resolved through international cooperation, diplomacy, and a commitment to sustainable development and environmental protection. This includes recognizing the rights and interests of indigenous peoples, promoting cooperation and collaboration among nations, and investing in sustainable infrastructure and renewable energy.
What is the future of the Arctic Cold War?
+The future of the Arctic Cold War is uncertain, but it is likely to be shaped by a combination of geopolitical, economic, and environmental factors. As the region continues to thaw and become more accessible, it is essential to promote international cooperation, sustainable development, and environmental protection to ensure a peaceful and prosperous future for all nations and communities involved.
In conclusion, the Arctic Cold War is a complex and multifaceted issue that requires a nuanced and informed approach. By understanding the key players, their interests, and the main issues at stake, we can work towards a more peaceful and sustainable future for the region. We invite you to share your thoughts and comments on this article, and to join the conversation on the future of the Arctic Cold War. Together, we can promote international cooperation, sustainable development, and environmental protection in the Arctic region, and ensure a bright future for all nations and communities involved.
