Intro
Discover the 5 Air Force Core Functions, including air superiority, space superiority, and cyberspace superiority, to understand military operations, global vigilance, and rapid response capabilities.
The Air Force is a vital component of a country's defense system, and its core functions are designed to protect the nation and its interests from airborne threats. The 5 Air Force core functions are the foundation of the Air Force's mission and are essential for maintaining air superiority, supporting ground operations, and defending against enemy aircraft and missiles. In this article, we will explore each of the 5 Air Force core functions in detail, discussing their importance, benefits, and working mechanisms.
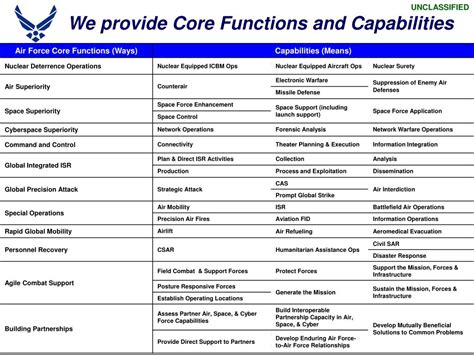
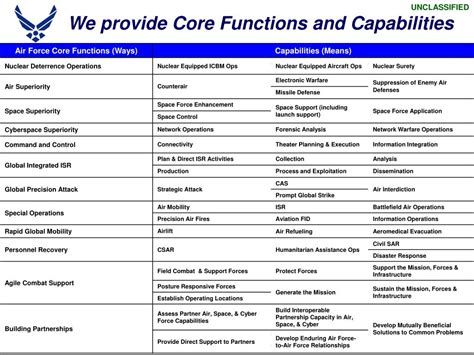
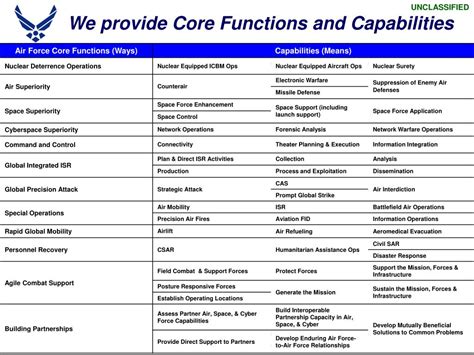
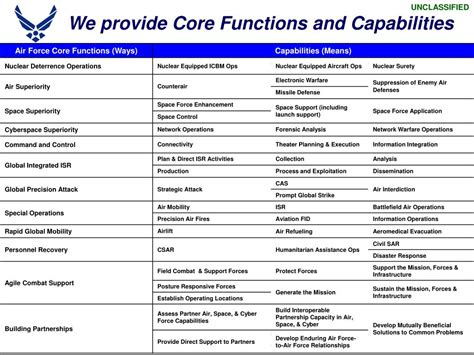
Air power has become an essential aspect of modern warfare, and the Air Force plays a critical role in defending the nation and its interests. The Air Force's core functions are designed to provide a robust defense against airborne threats, support ground operations, and maintain air superiority. The 5 Air Force core functions are: Air and Space Superiority, Intelligence, Surveillance, and Reconnaissance, Rapid Global Mobility, Global Strike, and Command and Control. Each of these functions is crucial for maintaining the Air Force's effectiveness and ensuring the nation's security.
The importance of the Air Force's core functions cannot be overstated. In today's complex and rapidly changing world, the Air Force must be able to respond quickly and effectively to a wide range of threats. The 5 Air Force core functions provide the foundation for the Air Force's mission, enabling it to protect the nation and its interests from airborne threats, support ground operations, and maintain air superiority. By understanding the 5 Air Force core functions, we can better appreciate the critical role that the Air Force plays in defending the nation and its interests.
Air and Space Superiority

The benefits of Air and Space Superiority are numerous. By gaining and maintaining control of the air and space domains, the Air Force can operate freely and effectively, supporting ground operations and defending against enemy aircraft and missiles. Air and Space Superiority also enables the Air Force to project power and influence across the globe, providing a robust defense against airborne threats. The working mechanism of Air and Space Superiority involves a combination of fighter aircraft, air defense systems, and space-based assets, all working together to gain and maintain control of the air and space domains.
Intelligence, Surveillance, and Reconnaissance

The benefits of ISR are numerous. By collecting, analyzing, and disseminating information about enemy forces and operations, the Air Force can make informed decisions and take effective action. ISR also enables the Air Force to identify and track enemy aircraft and missiles, providing a robust defense against airborne threats. The working mechanism of ISR involves a combination of manned and unmanned aircraft, space-based assets, and ground-based sensors, all working together to collect, analyze, and disseminate information about enemy forces and operations.
Rapid Global Mobility

The benefits of Rapid Global Mobility are numerous. By transporting personnel, equipment, and supplies quickly and efficiently across the globe, the Air Force can respond rapidly to emerging threats and crises. Rapid Global Mobility also enables the Air Force to project power and influence across the globe, providing a robust defense against airborne threats. The working mechanism of Rapid Global Mobility involves a combination of airlift and aerial refueling aircraft, all working together to transport personnel, equipment, and supplies quickly and efficiently across the globe.
Global Strike

The benefits of Global Strike are numerous. By conducting precision strikes against enemy targets, the Air Force can destroy enemy aircraft, missiles, and other assets, providing a robust defense against airborne threats. Global Strike also enables the Air Force to project power and influence across the globe, providing a deterrent against enemy aggression. The working mechanism of Global Strike involves a combination of fighter and bomber aircraft, precision-guided munitions, and space-based assets, all working together to conduct precision strikes against enemy targets.
Command and Control

The benefits of Command and Control are numerous. By directing and controlling Air Force operations, the Air Force can respond effectively to emerging threats and crises. Command and Control also enables the Air Force to coordinate with other military services and coalition partners, providing a robust defense against airborne threats. The working mechanism of Command and Control involves a combination of command centers, communications networks, and decision-support systems, all working together to direct and control Air Force operations.
Gallery of Air Force Core Functions
Air Force Core Functions Image Gallery






What are the 5 Air Force core functions?
+The 5 Air Force core functions are: Air and Space Superiority, Intelligence, Surveillance, and Reconnaissance, Rapid Global Mobility, Global Strike, and Command and Control.
What is the importance of Air and Space Superiority?
+Air and Space Superiority is essential for maintaining air superiority, supporting ground operations, and defending against enemy aircraft and missiles.
What is the role of Intelligence, Surveillance, and Reconnaissance in the Air Force?
+Intelligence, Surveillance, and Reconnaissance involves collecting, analyzing, and disseminating information about enemy forces and operations, enabling the Air Force to make informed decisions and take effective action.
What is the benefit of Rapid Global Mobility?
+Rapid Global Mobility enables the Air Force to respond rapidly to emerging threats and crises, and to project power and influence across the globe.
What is the role of Command and Control in the Air Force?
+Command and Control involves directing and controlling Air Force operations, enabling the Air Force to respond effectively to emerging threats and crises.
In conclusion, the 5 Air Force core functions are essential for maintaining air superiority, supporting ground operations, and defending against enemy aircraft and missiles. By understanding the importance and benefits of each core function, we can better appreciate the critical role that the Air Force plays in defending the nation and its interests. We encourage readers to share their thoughts and comments on the 5 Air Force core functions, and to explore further the many resources available on this topic. By working together, we can ensure that the Air Force remains a robust and effective force for defending the nation and its interests.
