Intro
Discover the 7 BMT requirements for a successful career, including physical fitness, education, and medical standards, to help you prepare for Basic Military Training and achieve your military goals with confidence and readiness.
Bone Marrow Transplantation (BMT) is a complex medical procedure that requires careful consideration and planning. The requirements for BMT are multifaceted and involve various aspects of patient care, donor selection, and transplant protocols. Understanding these requirements is crucial for patients, families, and healthcare providers to navigate the BMT process effectively.
The importance of BMT cannot be overstated, as it offers a potentially life-saving treatment option for individuals with certain types of cancer, blood disorders, and immune system diseases. However, the journey to BMT is often marked by uncertainty, anxiety, and a steep learning curve. By exploring the key requirements for BMT, patients and their loved ones can better prepare themselves for the challenges and opportunities that lie ahead.
As patients embark on the BMT journey, they must confront a range of physical, emotional, and psychological demands. From the initial diagnosis and treatment planning to the actual transplant procedure and post-transplant care, each stage of the BMT process presents unique challenges and requirements. By examining these requirements in detail, patients and healthcare providers can work together to optimize outcomes, minimize risks, and enhance the overall quality of care.
Introduction to BMT Requirements

BMT requirements can be broadly categorized into several key areas, including patient selection, donor matching, transplant protocols, and post-transplant care. Each of these areas involves a distinct set of criteria, guidelines, and best practices that must be carefully considered to ensure a successful transplant outcome.
Patient Selection Criteria
Patient selection is a critical component of the BMT process, as it involves evaluating the individual's suitability for transplantation. The key criteria for patient selection include:
- Diagnosis and disease status: Patients must have a confirmed diagnosis of a condition that is treatable with BMT, such as leukemia, lymphoma, or multiple myeloma.
- Age and overall health: Patients must be in relatively good health, with adequate organ function and a suitable performance status.
- Disease staging and prognosis: Patients must have a disease that is responsive to BMT, with a favorable prognosis and minimal comorbidities.
- Informed consent: Patients must provide informed consent, demonstrating a clear understanding of the risks, benefits, and uncertainties associated with BMT.
Donor Matching and Selection

Donor matching and selection are essential components of the BMT process, as they involve identifying a suitable donor who can provide a compatible graft. The key considerations for donor matching and selection include:
- Human leukocyte antigen (HLA) typing: Donors must be HLA-matched to the recipient, with a compatible HLA profile to minimize the risk of graft-versus-host disease (GVHD).
- Donor-recipient compatibility: Donors must be compatible with the recipient in terms of blood type, Rh factor, and other immunological parameters.
- Donor health and suitability: Donors must be in good health, with no underlying medical conditions that could compromise the safety of the donation process.
Transplant Protocols and Procedures
Transplant protocols and procedures are critical components of the BMT process, as they involve the actual transplantation of the donor graft. The key considerations for transplant protocols and procedures include:
- Conditioning regimens: Patients must undergo a conditioning regimen to prepare their body for the transplant, involving chemotherapy, radiation, or immunosuppressive therapy.
- Graft infusion: The donor graft must be infused into the patient, using a sterile and controlled environment to minimize the risk of infection and GVHD.
- Post-transplant care: Patients must receive comprehensive post-transplant care, involving monitoring for GVHD, infection, and other complications, as well as supportive care to manage symptoms and promote recovery.
Post-Transplant Care and Follow-Up

Post-transplant care and follow-up are essential components of the BMT process, as they involve monitoring the patient's recovery and managing any complications that may arise. The key considerations for post-transplant care and follow-up include:
- GVHD prophylaxis: Patients must receive prophylactic therapy to prevent GVHD, involving immunosuppressive medications and other supportive care measures.
- Infection monitoring: Patients must be monitored for infection, involving regular blood tests, cultures, and other diagnostic procedures.
- Long-term follow-up: Patients must receive long-term follow-up care, involving regular check-ups, monitoring for late complications, and supportive care to promote overall health and well-being.
BMT Image Gallery


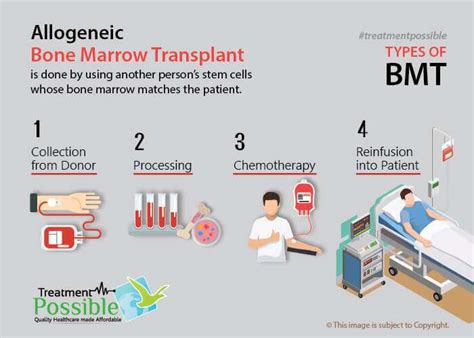





What are the main types of BMT?
+The main types of BMT include autologous BMT, allogeneic BMT, and syngeneic BMT.
What are the risks and complications of BMT?
+The risks and complications of BMT include GVHD, infection, organ damage, and secondary cancers.
How long does the BMT process take?
+The BMT process typically takes several weeks to several months, depending on the individual's condition and the type of transplant.
In conclusion, the BMT requirements are complex and multifaceted, involving various aspects of patient care, donor selection, and transplant protocols. By understanding these requirements, patients and healthcare providers can work together to optimize outcomes, minimize risks, and enhance the overall quality of care. We invite readers to share their thoughts, experiences, and questions about BMT, and to explore the resources and support available to those navigating this life-changing journey.
