Intro
Discover 5 ways to join the military, including enlistment, officer programs, and special forces. Learn about military careers, recruitment, and service requirements to start your armed forces journey.
Joining the military can be a life-changing decision, offering a unique blend of challenges, opportunities, and personal growth. For those considering this path, it's essential to understand the various ways to join, as each route has its own requirements, benefits, and outcomes. Whether you're driven by a sense of patriotism, a desire for education and career advancement, or the need for discipline and structure, the military offers a multitude of entry points tailored to different backgrounds and goals.
The decision to join the military is not one to be taken lightly. It requires careful consideration of one's motivations, capabilities, and expectations. Potential recruits should be aware of the rigorous training, the possibility of deployment, and the commitment to service that comes with joining the military. Despite these challenges, many find that military service provides invaluable experiences, skills, and a sense of purpose that can be hard to find in civilian life.
For individuals looking to serve their country, gain new skills, or simply find a new direction in life, understanding the different paths to military service is crucial. From enlisting directly to pursuing a career through military academies, each method has its unique benefits and requirements. The military's diverse branches, including the Army, Navy, Air Force, Marine Corps, and Coast Guard, offer a range of roles and specialties, ensuring that there's a place for individuals with various skills and interests.
Understanding the Military Branches
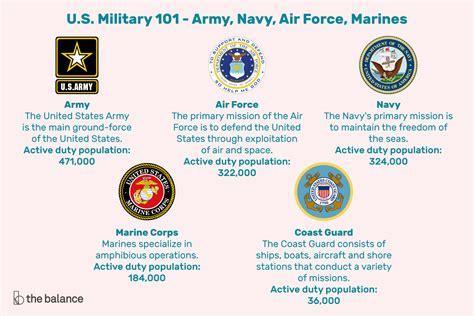
Before diving into the ways to join, it's helpful to have a basic understanding of the military branches and what they entail. The Army is the largest branch and is responsible for land-based military operations. The Navy focuses on sea-based operations, while the Air Force specializes in air and space operations. The Marine Corps is a rapid-response force that often works closely with the Navy, and the Coast Guard, which can operate under the Department of Homeland Security during peacetime, handles maritime law enforcement, search and rescue, and marine environmental protection.
Choosing the Right Branch
Each branch has its own culture, mission, and operational style, which can significantly impact an individual's experience. For example, those interested in aviation might lean towards the Air Force or Navy, while individuals looking for a more traditional combat role might consider the Army or Marine Corps. The Coast Guard, with its unique blend of military and law enforcement duties, offers a distinct experience that appeals to those interested in maritime security and environmental protection.1. Enlisting Directly

Enlisting directly into the military is one of the most common ways to join. This involves contacting a recruiter, meeting the basic qualifications (such as age, education, and physical fitness requirements), and then attending Basic Training (also known as Boot Camp) to start your military career. Direct enlistment allows individuals to choose from a variety of Military Occupational Specialties (MOS), which are essentially job categories within the military. From infantry and engineering to communications and healthcare, the options are diverse, offering something for nearly every skill set and interest.
Benefits of Direct Enlistment
Direct enlistment provides immediate entry into the military, allowing individuals to begin serving and earning benefits quickly. These benefits include competitive pay, comprehensive healthcare, education assistance through programs like the GI Bill, and the opportunity for advancement and specialized training. Additionally, the sense of camaraderie and esprit de corps that develops among enlistees during Basic Training can be a powerful and lasting aspect of military life.2. Officer Candidate School (OCS)

For those interested in becoming officers, Officer Candidate School (OCS) is a pathway that leads to a commission. OCS is designed for individuals who have a four-year college degree or higher and wish to become officers in the military. The program is challenging, both physically and academically, and prepares candidates for the responsibilities and leadership roles that come with being an officer. OCS is available in all branches of the military and typically lasts several months.
Qualifications for OCS
To qualify for OCS, candidates must meet specific requirements, including having a bachelor's degree, being a U.S. citizen, meeting physical fitness standards, and passing a background check. The process involves applying through a recruiter, undergoing a medical examination, and securing a nomination or direct commission, depending on the branch and specific circumstances.3. Military Academies

The United States Military Academies, including West Point (Army), the Naval Academy (Navy and Marine Corps), the Air Force Academy, and the Coast Guard Academy, offer a prestigious and highly competitive route to becoming a military officer. These academies provide a four-year education that balances academic rigor with military training, culminating in a bachelor's degree and a commission as an officer in the respective branch. Admission is highly competitive and typically requires a nomination from a member of Congress, high academic achievement, and passing a physical fitness test.
Life at a Military Academy
Life at a military academy is demanding, with a strict regimen that includes academic classes, military training, physical fitness, and leadership development. Cadets (or midshipmen at the Naval Academy) are immersed in a culture of discipline, honor, and service, preparing them for the responsibilities of leadership in the military. Graduates of the military academies have gone on to distinguished careers in both the military and civilian sectors.4. Reserve Officers' Training Corps (ROTC)

The Reserve Officers' Training Corps (ROTC) is another pathway to becoming an officer, offered at hundreds of colleges and universities across the United States. ROTC allows students to pursue a normal college experience while also receiving military training and education. In exchange for a scholarship and a monthly stipend, students commit to serve in the military after graduation. ROTC programs are available for all branches of the military and provide a flexible way to balance academic and military pursuits.
Benefits of ROTC
ROTC offers several benefits, including scholarships that can cover full or partial tuition, a monthly stipend, and the opportunity to develop leadership and military skills while earning a degree. Upon graduation, ROTC cadets are commissioned as officers and can choose from a variety of career fields within their branch of service.5. Direct Commission

A direct commission is a pathway to officer status that is typically reserved for individuals with specialized skills or professional degrees, such as doctors, lawyers, chaplains, and cyber security experts. This route allows the military to tap into the expertise of professionals who can contribute immediately to specific fields. The process involves applying through a recruiter and meeting specific qualifications related to one's profession or skill area.
Professions Eligible for Direct Commission
Professions eligible for direct commission vary by branch but often include medical professionals (doctors, nurses, dentists), legal professionals (lawyers), religious leaders (chaplain candidates), and individuals with advanced degrees in fields like engineering, physics, or computer science. Direct commission officers undergo a shorter training period than those from OCS or the academies, as their professional experience is seen as equivalent to some aspects of officer training.Military Career Paths Image Gallery








What are the basic requirements to join the military?
+The basic requirements include being a U.S. citizen, being between the ages of 17 and 35 (with some exceptions), having a high school diploma, and meeting physical fitness standards. Additionally, applicants must pass the Armed Services Vocational Aptitude Battery (ASVAB) test and undergo a background check.
How long does it take to complete Basic Training?
+The length of Basic Training varies by branch but typically lasts between 7 to 12 weeks. During this time, recruits learn basic military skills, undergo physical conditioning, and are introduced to military life and protocol.
Can I choose my job in the military?
+Yes, to some extent. When enlisting, individuals can express their preference for a specific Military Occupational Specialty (MOS) based on their skills and interests. However, the military also considers its current needs, and assignments are made based on a combination of personal preference, aptitude, and the needs of the service.
What kind of education benefits does the military offer?
+The military offers several education benefits, including the GI Bill, which can cover up to 100% of tuition and fees for public colleges and universities, and a significant portion for private institutions. Additionally, active-duty personnel can take advantage of tuition assistance to pursue higher education while serving.
How do I get started with the process of joining the military?
+To get started, visit the official website of the branch you're interested in joining, or contact a local recruiter. They can guide you through the eligibility requirements, application process, and answer any questions you may have about military service.
In conclusion, joining the military is a significant decision that can lead to a rewarding and challenging career. Whether through direct enlistment, Officer Candidate School, military academies, ROTC, or direct commission, there are multiple paths to serve. Each route has its unique benefits, requirements, and outcomes, offering something for individuals with various backgrounds, skills, and goals. For those considering military service, it's essential to research thoroughly, understand the commitment involved, and find the pathway that best aligns with their aspirations and capabilities. By doing so, individuals can embark on a journey of personal growth, service to their country, and the development of skills and friendships that last a lifetime. We invite you to share your thoughts, experiences, or questions about joining the military in the comments below, and to consider sharing this article with others who may be exploring their options for military service.
