Intro
Discover 5 ways to join the army, including enlistment, officer programs, and special forces recruitment, to start your military career and serve your country with honor and patriotism.
Joining the army can be a life-changing decision, offering a unique blend of personal growth, career development, and service to one's country. For those considering this path, understanding the various ways to join is crucial. Whether you're driven by a sense of patriotism, a desire for adventure, or the pursuit of educational and career opportunities, the army provides multiple entry points tailored to different backgrounds, skills, and goals.
The importance of serving in the army extends beyond personal benefits, contributing significantly to national security and global peacekeeping efforts. Moreover, the skills and disciplines acquired during military service are highly valued by civilian employers, making veterans attractive candidates in the job market. As such, exploring the different avenues for joining the army is not just about enlisting; it's about embarking on a journey of self-discovery, skill development, and service.
For individuals interested in a military career, the process can seem daunting, with numerous pathways and requirements to navigate. However, by breaking down these pathways into manageable, understandable components, potential recruits can make informed decisions that align with their aspirations and capabilities. From traditional enlistment to more specialized programs, the army offers a range of options designed to attract talented and dedicated individuals from diverse backgrounds.
Understanding the Army's Structure and Roles
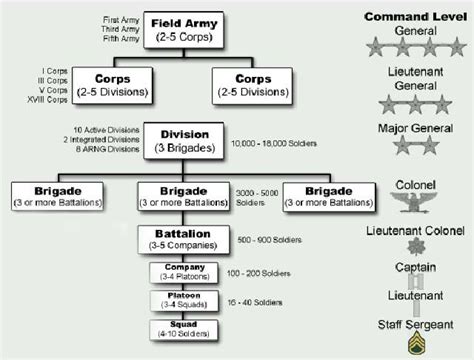
Before diving into the ways to join the army, it's essential to have a basic understanding of the army's structure and the various roles within it. The army is divided into different branches, each with its unique responsibilities and areas of expertise. These branches include infantry, artillery, engineering, and logistics, among others. Each role, whether in combat, support, or service, plays a critical part in the army's overall effectiveness and success.
Pathways to Joining the Army

1. Enlistment
Enlistment is the most common way to join the army, involving the recruitment of individuals who wish to serve as enlisted soldiers. This pathway typically requires meeting basic eligibility criteria, such as age, education, and physical fitness standards. Enlistees undergo basic training, followed by advanced individual training in their chosen Military Occupational Specialty (MOS).
2. Officer Candidate School (OCS)
For those interested in becoming officers, the Officer Candidate School (OCS) provides a pathway to commission. OCS is designed for individuals with a bachelor's degree who wish to become leaders in the army. The program involves intense training, focusing on leadership, tactics, and military skills, culminating in a commission as a second lieutenant.
3. Reserve Officers' Training Corps (ROTC)
The Reserve Officers' Training Corps (ROTC) is a college-based program that allows students to pursue a degree while receiving military training. ROTC cadets can receive scholarships and other benefits while in college, leading to a commission as an officer upon graduation.
4. Direct Commission
Certain professionals, such as lawyers, chaplains, and medical professionals, can join the army through direct commission. This pathway allows individuals with specialized skills and degrees to enter the army as officers without attending traditional officer training programs.
5. Specialized Programs
The army also offers specialized programs for individuals with unique skills or interests, such as the Army's Special Forces (Green Berets), Rangers, and Army Intelligence. These programs often have additional requirements and involve rigorous training but offer opportunities for service in elite units.
Preparation and Eligibility
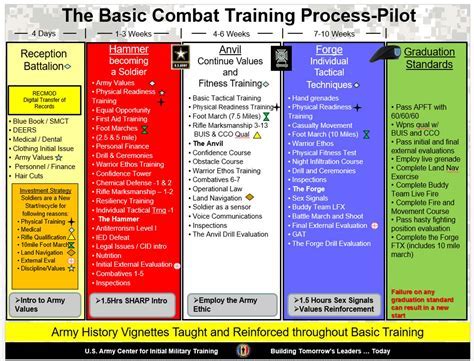
Regardless of the pathway chosen, preparation is key. This includes meeting the basic eligibility requirements, such as U.S. citizenship, being between the ages of 17 and 35 (for enlistment), and achieving a certain level of physical fitness. Additionally, preparing for the Armed Services Vocational Aptitude Battery (ASVAB) test, which assesses aptitude in various subjects, can improve an individual's chances of being assigned to their desired MOS.
Benefits of Army Service
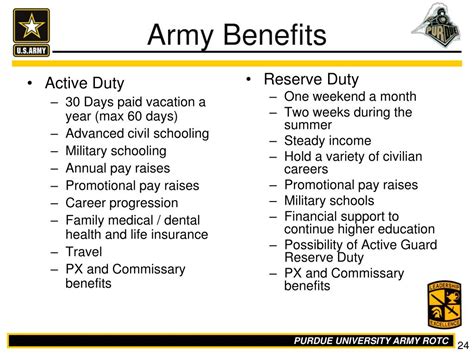
Serving in the army comes with a range of benefits, including educational assistance, such as the GI Bill, which can cover college tuition and other educational expenses. Healthcare benefits, housing allowances, and access to on-base facilities are also provided. Moreover, the army offers opportunities for career advancement, leadership development, and the chance to be part of a prestigious and respected institution.
Life After the Army

After serving in the army, veterans often find that their military experience opens doors to new career opportunities. The discipline, leadership skills, and adaptability developed during service are highly valued by employers. Additionally, many veterans go on to pursue higher education, using their GI Bill benefits to fund their studies. The transition back to civilian life can be challenging, but with the right support and resources, veterans can leverage their military experience to achieve success in their post-service careers.
Gaining Practical Experience

Practical experience is a significant aspect of army service, with opportunities to apply theoretical knowledge in real-world scenarios. From combat training to peacekeeping missions, the army provides a unique environment where individuals can develop their skills, face challenges, and grow both personally and professionally.
Embracing Challenges and Opportunities

The army is not just a job; it's a way of life that comes with its own set of challenges and opportunities. Embracing these challenges, whether they involve personal sacrifice, physical hardship, or emotional resilience, is crucial for success. In return, the army offers opportunities for personal growth, career development, and the chance to make a meaningful difference in the world.
Gallery of Army Life and Service
Army Life and Service Image Gallery










Frequently Asked Questions
What are the basic requirements to join the army?
+The basic requirements include being a U.S. citizen, being between the ages of 17 and 35 for enlistment, and meeting certain educational and physical fitness standards.
How long does basic training last?
+Basic training, also known as Basic Combat Training (BCT), typically lasts about 10 weeks.
Can I choose my job in the army?
+Yes, based on your qualifications and the needs of the army, you can choose from a variety of Military Occupational Specialties (MOS).
In conclusion, joining the army is a significant decision that can lead to a fulfilling and challenging career. With various pathways to enlistment and a range of benefits, the army offers opportunities for personal and professional growth. Whether you're driven by a sense of duty, a desire for adventure, or the pursuit of educational and career opportunities, the army has something to offer. As you consider this path, remember the importance of preparation, the value of practical experience, and the benefits that come with serving in one of the world's most respected institutions. We invite you to share your thoughts, experiences, or questions about joining the army in the comments below, and to consider the many ways in which serving can enrich your life and the lives of those around you.
