Intro
Discover 5 ways to join reserves, including military reserves, national reserves, and community reserves, to serve and gain valuable experience in reserve forces, part-time military, and volunteer reserve roles.
Joining the military reserves can be a rewarding and challenging experience that offers numerous benefits, including education assistance, career skills, and a sense of camaraderie. For those considering joining the reserves, there are several ways to do so, each with its own unique requirements and opportunities. In this article, we will explore five ways to join the reserves, including the Army Reserve, Navy Reserve, Air Force Reserve, Marine Corps Reserve, and Coast Guard Reserve.
The decision to join the reserves is not one to be taken lightly, as it requires a significant commitment of time and energy. However, for those who are passionate about serving their country and developing new skills, the reserves can be an excellent choice. Whether you are looking to transition from active duty, pursue a career in a specific field, or simply give back to your community, the reserves offer a flexible and rewarding way to serve.
Before making the decision to join the reserves, it is essential to understand the various branches and their unique requirements. Each branch has its own culture, mission, and requirements, so it is crucial to research and find the one that best aligns with your goals and values. Additionally, it is essential to consider the time commitment, training requirements, and potential deployments when making your decision. By carefully evaluating these factors, you can make an informed decision and find a fulfilling career in the reserves.
Introduction to the Reserves
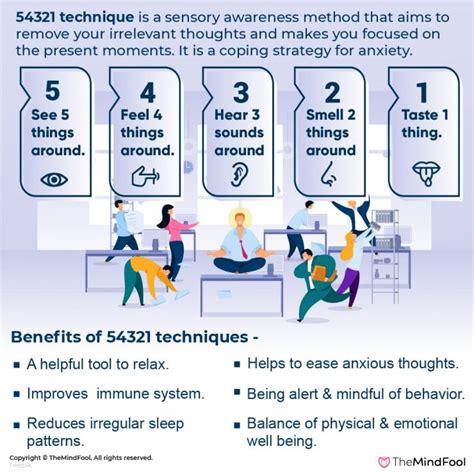
The reserves are a vital component of the military, providing a flexible and cost-effective way to maintain a strong and capable force. By joining the reserves, individuals can serve their country while also pursuing civilian careers and education. The reserves offer a range of benefits, including education assistance, career skills, and a sense of camaraderie, making them an attractive option for those looking to serve their country.
Benefits of Joining the Reserves

Joining the reserves offers numerous benefits, including education assistance, career skills, and a sense of camaraderie. The reserves provide education assistance, such as the Montgomery GI Bill, which can help individuals pay for college or vocational training. Additionally, the reserves offer career skills, such as leadership development, communication, and problem-solving, which can be applied to civilian careers. The sense of camaraderie and esprit de corps that comes with serving in the reserves can also be a powerful motivator and source of personal growth.
Education Assistance
The reserves offer education assistance, such as the Montgomery GI Bill, which can help individuals pay for college or vocational training. This benefit can be used to pursue a degree or certification, and can be a significant factor in helping individuals achieve their educational goals.Career Skills
The reserves offer career skills, such as leadership development, communication, and problem-solving, which can be applied to civilian careers. These skills can be highly valued by employers, and can help individuals advance in their careers.Five Ways to Join the Reserves

There are several ways to join the reserves, each with its own unique requirements and opportunities. The five ways to join the reserves are:
- Army Reserve: The Army Reserve is the largest of the reserve components, with over 200,000 soldiers. To join the Army Reserve, individuals must be between the ages of 17 and 35, be a U.S. citizen, and meet certain physical and moral standards.
- Navy Reserve: The Navy Reserve is a vital component of the Navy, providing support for naval operations around the world. To join the Navy Reserve, individuals must be between the ages of 17 and 39, be a U.S. citizen, and meet certain physical and moral standards.
- Air Force Reserve: The Air Force Reserve is a highly specialized force, providing support for air operations around the world. To join the Air Force Reserve, individuals must be between the ages of 17 and 39, be a U.S. citizen, and meet certain physical and moral standards.
- Marine Corps Reserve: The Marine Corps Reserve is a elite force, providing support for Marine Corps operations around the world. To join the Marine Corps Reserve, individuals must be between the ages of 17 and 28, be a U.S. citizen, and meet certain physical and moral standards.
- Coast Guard Reserve: The Coast Guard Reserve is a unique force, providing support for coastal defense and maritime law enforcement. To join the Coast Guard Reserve, individuals must be between the ages of 17 and 39, be a U.S. citizen, and meet certain physical and moral standards.
Requirements for Joining the Reserves

To join the reserves, individuals must meet certain requirements, including age, citizenship, physical and moral standards, and education. The specific requirements vary depending on the branch and the individual's circumstances, but generally include:
- Age: Individuals must be between the ages of 17 and 35 (or 39 for the Navy and Air Force Reserves).
- Citizenship: Individuals must be U.S. citizens.
- Physical standards: Individuals must meet certain physical standards, including weight, body fat percentage, and medical requirements.
- Moral standards: Individuals must meet certain moral standards, including a background check and a review of their personal conduct.
- Education: Individuals must have a high school diploma or equivalent, and may be required to have certain college credits or degrees.
Training and Deployment
Once individuals have joined the reserves, they will undergo training and may be deployed to support military operations. The training and deployment requirements vary depending on the branch and the individual's circumstances, but generally include:
- Basic training: Individuals will undergo basic training, which includes instruction in military skills, physical fitness, and first aid.
- Advanced training: Individuals may undergo advanced training, which includes instruction in specialized skills, such as leadership, communication, and problem-solving.
- Deployment: Individuals may be deployed to support military operations, which can include combat, humanitarian, and disaster relief missions.
Conclusion and Next Steps

Joining the reserves can be a rewarding and challenging experience that offers numerous benefits, including education assistance, career skills, and a sense of camaraderie. By understanding the different branches and their unique requirements, individuals can make an informed decision and find a fulfilling career in the reserves. Whether you are looking to transition from active duty, pursue a career in a specific field, or simply give back to your community, the reserves offer a flexible and rewarding way to serve.
Reserves Image Gallery









What are the benefits of joining the reserves?
+The benefits of joining the reserves include education assistance, career skills, and a sense of camaraderie. The reserves also offer a range of other benefits, including access to military facilities, discounts on travel and shopping, and eligibility for veterans' benefits.
How do I join the reserves?
+To join the reserves, individuals must meet certain requirements, including age, citizenship, physical and moral standards, and education. They must also choose a branch and enlist in the reserves, which typically involves taking the ASVAB test, undergoing a physical exam, and completing basic training.
What is the time commitment for joining the reserves?
+The time commitment for joining the reserves varies depending on the branch and the individual's circumstances, but generally includes one weekend per month and two weeks per year of training, as well as potential deployments.
Can I join the reserves if I have prior military service?
+Yes, individuals with prior military service may be eligible to join the reserves, depending on their circumstances and the branch they are interested in joining. They may be able to enlist in the reserves at a higher rank or with more advanced training, and may also be eligible for certain benefits and incentives.
How do I choose the right branch for me?
+Choosing the right branch for you depends on your individual goals, interests, and circumstances. Research the different branches and their unique requirements, and consider factors such as job opportunities, education benefits, and deployment rates. You may also want to speak with a recruiter or current service member to get a better sense of what each branch has to offer.
We hope this article has provided you with a comprehensive overview of the reserves and the benefits of joining. Whether you are looking to transition from active duty, pursue a career in a specific field, or simply give back to your community, the reserves offer a flexible and rewarding way to serve. If you have any further questions or would like to learn more about joining the reserves, please don't hesitate to comment below or share this article with others who may be interested.
