Intro
Compare active duty vs reserve military service, weighing pros and cons, benefits, and commitment levels to make an informed decision about full-time or part-time military careers.
Active duty and reserve are two different ways to serve in the military, each with its own unique benefits, drawbacks, and requirements. Understanding the differences between these two options is essential for individuals considering a career in the military. In this article, we will delve into the details of active duty and reserve, exploring their distinct characteristics, advantages, and disadvantages.
The decision to join the military is a significant one, and it's crucial to make an informed choice. Both active duty and reserve offer a sense of pride, camaraderie, and purpose, but they differ significantly in terms of commitment, lifestyle, and benefits. Active duty requires a full-time commitment, typically for a period of 3-6 years, during which individuals are expected to be available for deployment and training at all times. On the other hand, reserve service is part-time, with members typically serving one weekend per month and two weeks per year.
As we explore the differences between active duty and reserve, it's essential to consider the various factors that influence this decision. These include personal circumstances, career goals, financial situation, and individual preferences. By examining the benefits and drawbacks of each option, individuals can make a more informed decision about which path to take. Whether you're considering a career in the military or simply want to learn more about the different ways to serve, this article aims to provide a comprehensive comparison of active duty and reserve.
Introduction to Active Duty

Benefits of Active Duty
The benefits of active duty are numerous, including comprehensive healthcare, education assistance, and access to on-base facilities such as gyms, libraries, and shopping centers. Active duty personnel also receive a steady income, food and housing allowances, and opportunities for career advancement. Additionally, active duty service provides a sense of purpose, camaraderie, and pride in serving one's country.Drawbacks of Active Duty
However, active duty also has its drawbacks. The military lifestyle can be demanding, with long hours, frequent deployments, and time spent away from family and friends. Active duty personnel may also face danger and uncertainty, particularly in combat zones. Furthermore, the military's strict rules and regulations can be restrictive, and individuals may have limited freedom to make personal choices.Introduction to Reserve

Benefits of Reserve
The benefits of reserve service include the opportunity to serve one's country while maintaining a civilian career and lifestyle. Reserve personnel receive education assistance, access to healthcare, and opportunities for career advancement. They also experience a sense of pride and camaraderie, while having more control over their personal lives.Drawbacks of Reserve
However, reserve service also has its drawbacks. Reserve personnel may face uncertainty and unpredictability, as they can be called upon to deploy or participate in training exercises at short notice. They may also experience difficulties balancing their civilian and military responsibilities, particularly if they have family or work commitments.Comparison of Active Duty and Reserve
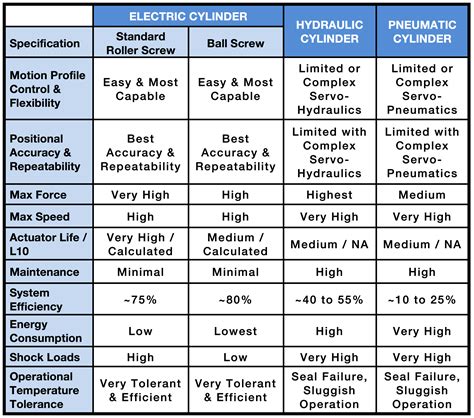
- Commitment: Active duty requires a full-time commitment, while reserve service is part-time.
- Lifestyle: Active duty personnel typically live on or near military bases, while reserve personnel maintain their own lives and pursue civilian careers.
- Benefits: Both active duty and reserve offer comprehensive healthcare, education assistance, and access to on-base facilities.
- Career advancement: Active duty personnel may have more opportunities for career advancement, while reserve personnel can still advance in their careers, albeit at a slower pace.
Steps to Join Active Duty or Reserve
For those interested in joining the military, the following steps can be taken: 1. Research the different branches of the military and their respective requirements. 2. Meet with a recruiter to discuss options and determine eligibility. 3. Take the Armed Services Vocational Aptitude Battery (ASVAB) test to determine career suitability. 4. Complete basic training and any additional training required for the chosen career path. 5. Consider enlisting in the reserve or active duty, depending on personal circumstances and goals.Gallery of Military Service
Military Service Image Gallery









Frequently Asked Questions
What is the difference between active duty and reserve?
+Active duty requires a full-time commitment, while reserve service is part-time. Active duty personnel typically live on or near military bases, while reserve personnel maintain their own lives and pursue civilian careers.
How do I join the military?
+To join the military, research the different branches and their requirements, meet with a recruiter, take the ASVAB test, complete basic training, and consider enlisting in the reserve or active duty.
What benefits do military personnel receive?
+Military personnel receive comprehensive healthcare, education assistance, access to on-base facilities, and opportunities for career advancement. They also experience a sense of pride and camaraderie, while serving their country.
Can I balance my civilian and military responsibilities?
+Yes, many military personnel balance their civilian and military responsibilities successfully. However, it's essential to consider the demands of military service and plan accordingly to ensure a smooth transition between civilian and military life.
How long do I have to serve in the military?
+The length of service varies depending on the individual's circumstances and goals. Active duty personnel typically serve for 3-6 years, while reserve personnel serve for a minimum of 6 years.
In conclusion, the decision to join the military as active duty or reserve personnel is a significant one, and it's crucial to make an informed choice. By understanding the differences between active duty and reserve, individuals can determine which path is best for them. Whether you're considering a career in the military or simply want to learn more about the different ways to serve, this article has provided a comprehensive comparison of active duty and reserve. We encourage you to share your thoughts and experiences in the comments below and to explore the various resources available to those considering a career in the military.
