Intro
Compare active duty vs reserve pay, including military compensation, benefits, and allowances, to understand the differences in salary, bonuses, and career opportunities for armed forces personnel.
The decision to join the military as active duty or reserve is a significant one, with various factors to consider, including pay, benefits, and lifestyle. For those who are weighing their options, understanding the differences in pay between active duty and reserve is crucial. In this article, we will delve into the world of military pay, exploring the similarities and differences between active duty and reserve compensation.
For individuals who are considering a career in the military, it is essential to understand the pay structures and how they can impact their financial stability and security. The military offers a unique set of benefits and compensation packages, which can be complex and difficult to navigate. However, by breaking down the differences between active duty and reserve pay, individuals can make informed decisions about their military service.
The military pay system is designed to provide a fair and equitable compensation package for all service members, regardless of their branch or status. However, there are significant differences between active duty and reserve pay, which can impact an individual's financial situation. Active duty personnel are paid a higher basic pay rate than reservists, which can result in significant differences in take-home pay.
Understanding Active Duty Pay
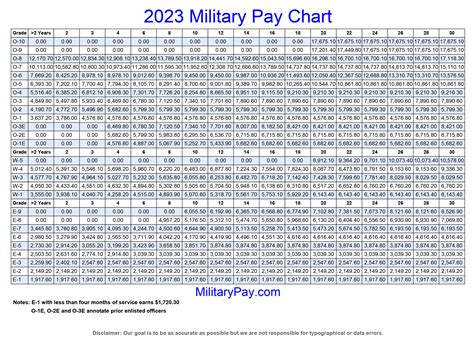
Understanding Reserve Pay

Key Differences Between Active Duty and Reserve Pay
Pay Rates and Allowances
Active duty personnel are paid based on their rank and time in service, with higher ranks and more time in service resulting in higher pay rates. Reservists are also paid based on their rank and time in service, but at a lower rate than active duty personnel. Allowances, such as housing and food allowances, are also provided to active duty personnel to help offset the costs of living. Reservists may be eligible for some allowances, but at a lower rate than active duty personnel.Special Pays and Bonuses
Active duty personnel may be eligible for special pays and bonuses, such as hazardous duty pay and jump pay, for specific duties or qualifications. Reservists may also be eligible for special pays and bonuses, but at a lower rate than active duty personnel. Additionally, active duty personnel may be eligible for bonuses, such as enlistment bonuses and reenlistment bonuses, that are not available to reservists.Benefits and Perks of Active Duty and Reserve Service

Health Insurance and Medical Benefits
Active duty personnel are eligible for comprehensive health insurance, including medical, dental, and vision coverage. Reservists may be eligible for some health insurance benefits, but at a lower level than active duty personnel. Additionally, active duty personnel may be eligible for medical benefits, such as access to military hospitals and clinics, that are not available to reservists.Retirement Pay and Pension Benefits
Active duty personnel are eligible for retirement pay and pension benefits after 20 years of service. Reservists may be eligible for retirement pay and pension benefits after 20 years of service, but at a lower level than active duty personnel. Additionally, active duty personnel may be eligible for other benefits, such as disability pay and survivor benefits, that are not available to reservists.Making the Decision: Active Duty or Reserve

Considering Lifestyle and Career Goals
Active duty personnel are required to be on full-time duty, which can impact their lifestyle and career goals. Reservists, on the other hand, are not required to be on full-time duty, which can provide more flexibility and freedom. Additionally, active duty personnel may be required to relocate frequently, which can impact their family and career stability.Considering Financial Goals and Security
Active duty personnel are paid a higher basic pay rate than reservists, which can result in significant differences in take-home pay. Additionally, active duty personnel are eligible for a wider range of allowances and special pays than reservists. However, reservists may be eligible for certain benefits, such as education assistance and retirement pay, that are not available to active duty personnel.Active Duty and Reserve Pay Gallery
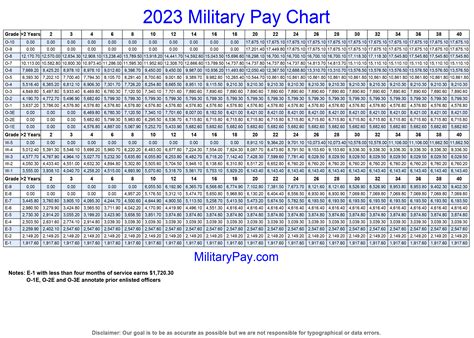
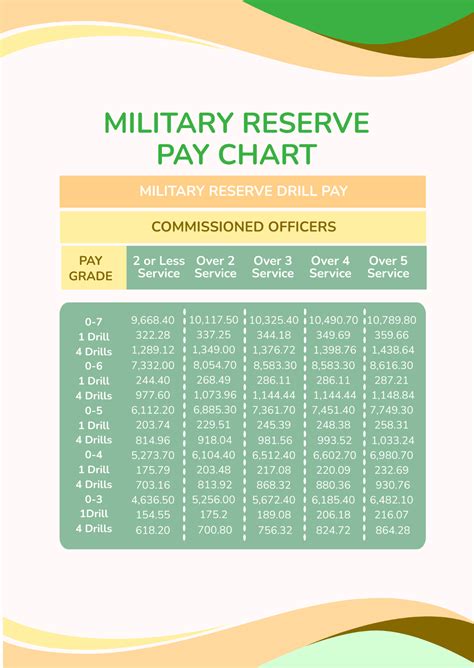







What is the main difference between active duty and reserve pay?
+The main difference between active duty and reserve pay is the basic pay rate, with active duty personnel receiving a higher rate than reservists.
What benefits are available to active duty personnel that are not available to reservists?
+Active duty personnel are eligible for a wider range of allowances and special pays, as well as benefits such as health insurance and retirement pay.
Can reservists receive education assistance and retirement pay?
+Yes, reservists may be eligible for education assistance and retirement pay, but at a lower level than active duty personnel.
How do I decide between active duty and reserve service?
+The decision to join the military as active duty or reserve should be based on an individual's needs and priorities, including lifestyle, career goals, and financial security.
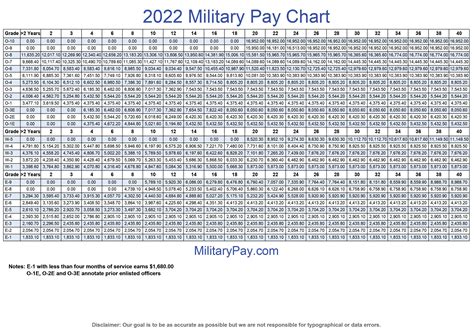
What is the pay scale for active duty personnel?
+The pay scale for active duty personnel is based on rank and time in service, with higher ranks and more time in service resulting in higher pay rates.
In conclusion, the decision to join the military as active duty or reserve is a significant one, with various factors to consider, including pay, benefits, and lifestyle. By understanding the differences between active duty and reserve pay, individuals can make informed decisions about their military service. Whether you are considering a career in the military or are already serving, it is essential to understand the pay structures and benefits available to you. We hope this article has provided you with the information you need to make an informed decision about your military service. If you have any further questions or would like to share your experiences, please comment below.
