Intro
Discover the 10c Thunderbolt II review, featuring lightning-fast data transfer, high-speed connectivity, and advanced peripherals, with in-depth analysis of its performance, compatibility, and innovative technology.
The technology world is constantly evolving, and one of the most significant advancements in recent years is the development of high-speed connectivity options. Among these, Thunderbolt technology has emerged as a game-changer, offering unprecedented speeds and versatility. The latest iteration, Thunderbolt 4, builds upon the successes of its predecessors, but for those looking for a balance between performance and compatibility, the Thunderbolt 3, also known as Thunderbolt II in some contexts, remains a highly relevant and sought-after technology. This article delves into the Thunderbolt II review, exploring its features, benefits, and why it remains a crucial component in many modern computing setups.
The importance of high-speed data transfer and connectivity cannot be overstated, especially in professional environments where time is of the essence. Thunderbolt II, with its capability to deliver speeds of up to 20 Gbps, has been a favorite among content creators, gamers, and businesses that require fast and reliable data transfer. Its ability to daisy-chain multiple devices, support for two 4K displays, and power delivery of up to 100W make it a versatile and powerful tool. Whether you're a professional looking to enhance your workflow or an enthusiast seeking to upgrade your computing experience, understanding the capabilities and limitations of Thunderbolt II is essential.
As we explore the Thunderbolt II review, it's clear that this technology has been designed with the future in mind. Its backward compatibility with previous Thunderbolt devices, albeit with some limitations, ensures that users can integrate it into their existing setups without significant hassle. Moreover, the Thunderbolt II's support for USB-C, with its compact and reversible design, has made it easier than ever to connect and disconnect devices, reducing wear and tear on ports and cables. This blend of innovation and practicality has made Thunderbolt II a staple in many industries, from video production and graphic design to gaming and virtual reality.
Introduction to Thunderbolt II

The Thunderbolt II, as an evolution of the original Thunderbolt technology, was designed to address the growing need for faster data transfer speeds and more versatile connectivity options. Developed by Intel in collaboration with Apple, Thunderbolt II was first introduced in 2013, offering a significant boost in performance compared to its predecessor. With the ability to deliver speeds of up to 20 Gbps, it more than doubled the bandwidth of the original Thunderbolt, making it an attractive option for professionals and consumers alike.
Key Features of Thunderbolt II
The key features of Thunderbolt II include its high-speed data transfer capability, support for multiple displays, daisy-chaining of devices, and power delivery. These features make it an ideal solution for a variety of applications, from professional content creation to gaming and general computing. Here are some of the key benefits and features: - High-Speed Data Transfer: Up to 20 Gbps, ideal for transferring large files such as videos and high-resolution images. - Display Support: Can support up to two 4K displays, making it perfect for professionals who need multiple monitors for their work. - Daisy-Chaining: Allows for the connection of up to six devices, including hard drives, monitors, and other peripherals, from a single Thunderbolt port. - Power Delivery: Can deliver up to 100W of power, sufficient for charging laptops and powering other devices.Benefits of Using Thunderbolt II
The benefits of using Thunderbolt II are multifaceted, catering to both professional and personal computing needs. For professionals, the high-speed data transfer and support for multiple high-resolution displays are invaluable. It enhances productivity by allowing for faster workflow, whether it's editing videos, designing graphics, or developing software. Additionally, its ability to connect multiple devices from a single port simplifies desk setups, reducing clutter and making it easier to manage peripherals.
For personal use, Thunderbolt II offers a significant upgrade in terms of connectivity and data transfer speeds. Gamers can enjoy faster loading times and smoother performance, while general users can transfer files between devices more quickly. The versatility of Thunderbolt II, combined with its backward compatibility and support for the latest devices, makes it a future-proof investment for anyone looking to enhance their computing experience.
Thunderbolt II vs. Thunderbolt 3 and Thunderbolt 4
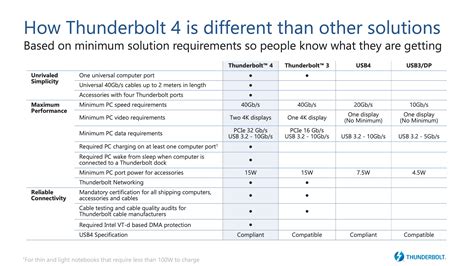
When considering Thunderbolt II, it's natural to wonder how it compares to the newer Thunderbolt 3 and Thunderbolt 4 technologies. Thunderbolt 3, for instance, offers speeds of up to 40 Gbps, doubling that of Thunderbolt II, and introduces USB-C as the standard connector, enhancing compatibility and convenience. Thunderbolt 4, the latest iteration, further improves upon this with enhanced security features, better USB4 compatibility, and the ability to support two 4K displays or one 8K display.However, the choice between these technologies depends on specific needs and budget considerations. For many users, the performance and features of Thunderbolt II remain more than sufficient, especially considering the cost savings compared to adopting the very latest technology. Moreover, the ecosystem of Thunderbolt II devices and accessories is well-established, making it easier to find compatible products.
Real-World Applications of Thunderbolt II

Thunderbolt II has a wide range of real-world applications that showcase its versatility and performance. In professional video production, for example, Thunderbolt II enables the quick transfer of high-resolution video files, making the editing process more efficient. Graphic designers can connect multiple high-resolution displays, enhancing their workspace and productivity. Gamers benefit from faster data transfer and the ability to connect high-performance peripherals.
In addition to these applications, Thunderbolt II is also used in data centers for high-speed data transfer, in research institutions for transferring large datasets, and in homes for enhancing entertainment systems. Its ability to support a variety of devices and applications makes it a valuable technology for anyone seeking to improve their computing experience.
Challenges and Limitations
Despite its many benefits, Thunderbolt II also comes with some challenges and limitations. One of the main limitations is its speed, which, while fast, is surpassed by newer technologies like Thunderbolt 3 and Thunderbolt 4. Additionally, the adoption of USB-C as a standard has made some older Thunderbolt II devices less compatible with newer systems without adapters.Moreover, the cost of Thunderbolt II devices and accessories can be higher than those using other connectivity standards, which may deter some potential users. However, for those who require its specific features and performance, Thunderbolt II remains a worthwhile investment.
Future of Thunderbolt Technology

As technology continues to evolve, the future of Thunderbolt looks promising. With each new iteration, we see significant improvements in speed, compatibility, and features. Thunderbolt 4, for example, not only offers faster speeds but also enhanced security and better support for the latest display technologies.
The development of USB4, which shares many similarities with Thunderbolt 3 and Thunderbolt 4 in terms of speed and versatility, also points to a future where high-speed connectivity becomes the norm. As more devices adopt these standards, we can expect to see a seamless and high-performance computing experience become more accessible to everyone.
Conclusion and Recommendations
In conclusion, Thunderbolt II remains a powerful and relevant technology for both professionals and consumers. Its high-speed data transfer, support for multiple displays, and versatility in connecting a variety of devices make it an excellent choice for enhancing productivity and computing experiences. While newer technologies like Thunderbolt 3 and Thunderbolt 4 offer improved performance, Thunderbolt II's established ecosystem and cost-effectiveness make it a viable option for many users.For those considering adopting Thunderbolt II, it's essential to weigh the benefits against the need for the latest and greatest technology. Professionals who require high-speed data transfer and support for multiple high-resolution displays may find Thunderbolt II to be more than sufficient for their needs. Consumers looking to upgrade their computing experience with faster data transfer and enhanced connectivity options will also find Thunderbolt II to be a valuable investment.
Thunderbolt II Image Gallery
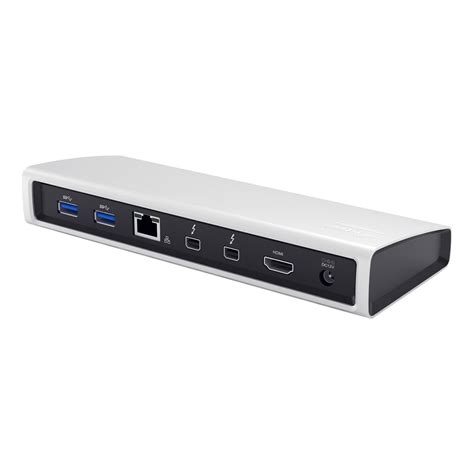
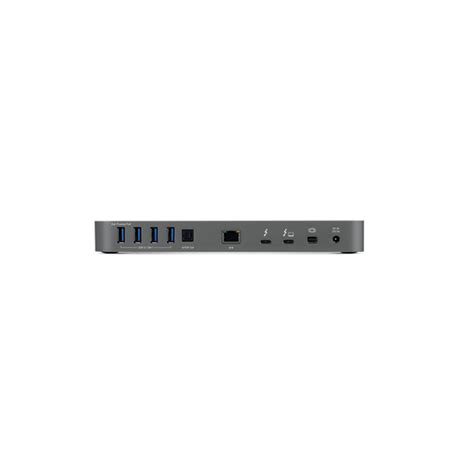










What is Thunderbolt II, and how does it work?
+Thunderbolt II is a high-speed connectivity technology developed by Intel in collaboration with Apple. It offers speeds of up to 20 Gbps, supporting the connection of multiple devices, including displays, hard drives, and peripherals, from a single port.
How does Thunderbolt II compare to Thunderbolt 3 and Thunderbolt 4?
+Thunderbolt II offers speeds of up to 20 Gbps, while Thunderbolt 3 and Thunderbolt 4 offer speeds of up to 40 Gbps. The newer technologies also introduce improvements in compatibility, security, and display support. However, Thunderbolt II remains a viable option for those who do not require the absolute latest in technology.
What are the real-world applications of Thunderbolt II?
+Thunderbolt II has a wide range of applications, including professional video production, graphic design, gaming, and general computing. It enhances productivity, allows for faster data transfer, and supports multiple high-resolution displays, making it a valuable technology for both professionals and consumers.
Is Thunderbolt II compatible with the latest devices and operating systems?
+Thunderbolt II is compatible with a variety of devices and operating systems, including macOS and Windows. However, some newer devices may require adapters for full compatibility, and the adoption of USB-C has made some older Thunderbolt II devices less compatible without adapters.
What is the future of Thunderbolt technology, and how will it evolve?
+The future of Thunderbolt technology looks promising, with each new iteration offering significant improvements in speed, compatibility, and features. The development of Thunderbolt 4 and the upcoming technologies points to a future where high-speed connectivity becomes the norm, enhancing computing experiences for professionals and consumers alike.
As we conclude our exploration of Thunderbolt II, it's clear that this technology has played a significant role in shaping the computing landscape. Whether you're a professional seeking to enhance your workflow or a consumer looking to upgrade your computing experience, understanding the benefits and limitations of Thunderbolt II is essential. We invite you to share your thoughts and experiences with Thunderbolt II, and to explore how this technology can meet your specific needs. By embracing high-speed connectivity, we open the door to new possibilities in productivity, entertainment, and innovation, paving the way for a future where technology seamlessly integrates into our daily lives.
