Intro
The world of wireless networking has witnessed significant advancements in recent years, with various technologies emerging to cater to the growing demand for faster and more reliable internet connectivity. Two such technologies that have gained considerable attention are Wi-Fi 6 (Fi6) and Wi-Fi 10 (A10), also known as Wi-Fi 6E. In this article, we will delve into the details of these two technologies, exploring their features, benefits, and differences to help you make an informed decision about which one is best suited for your needs.
The importance of wireless networking cannot be overstated, as it has become an essential aspect of our daily lives. With the proliferation of smart devices, online gaming, and streaming services, the demand for high-speed and low-latency internet connectivity has never been higher. Wi-Fi 6 and Wi-Fi 10 are designed to address these demands, offering improved performance, capacity, and efficiency compared to their predecessors. As we explore the features and benefits of these technologies, you will gain a deeper understanding of how they can enhance your online experience.
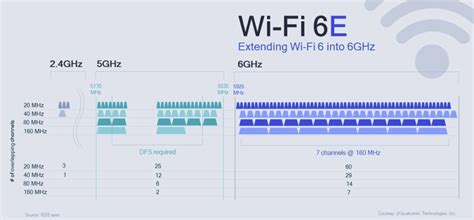
The evolution of wireless networking has been marked by significant milestones, with each new generation of Wi-Fi technology offering substantial improvements over the previous one. Wi-Fi 6, for instance, introduced several key features such as orthogonal frequency-division multiple access (OFDMA), multi-user multiple input multiple output (MU-MIMO), and 1024 quadrature amplitude modulation (1024-QAM). These features enabled Wi-Fi 6 to offer faster data transfer rates, improved capacity, and better performance in dense environments. Wi-Fi 10, on the other hand, builds upon the foundation laid by Wi-Fi 6, introducing new features and enhancements that further improve performance and capacity.
Introduction to Wi-Fi 6 (Fi6)
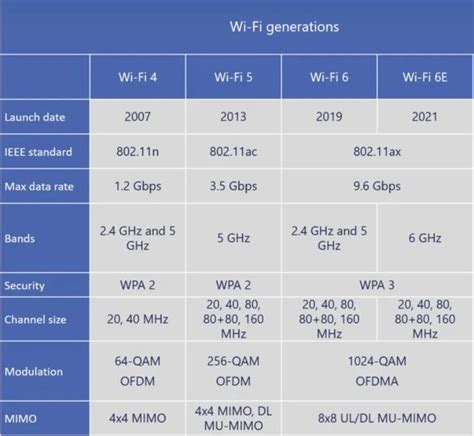
Introduction to Wi-Fi 10 (A10)

Key Features of Wi-Fi 6 (Fi6)

Key Features of Wi-Fi 10 (A10)
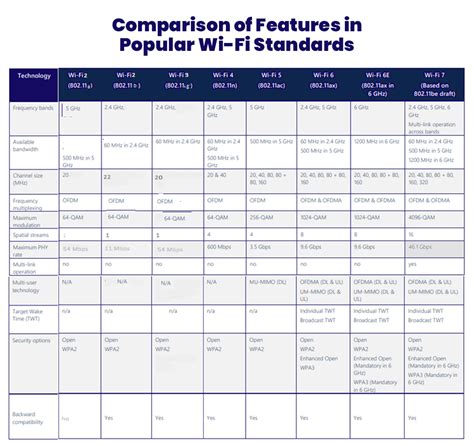
Comparison of Wi-Fi 6 (Fi6) and Wi-Fi 10 (A10)
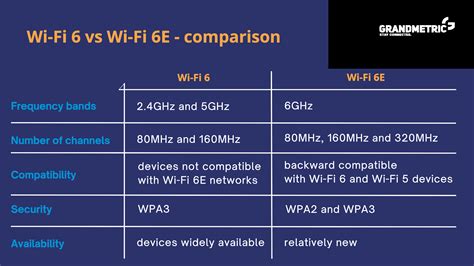
In terms of data transfer rates, Wi-Fi 10 offers faster speeds, with a maximum throughput of 9.6 Gbps. Wi-Fi 6, on the other hand, has a maximum throughput of 9.4 Gbps. However, it's worth noting that these speeds are theoretical and may vary depending on the specific implementation and environment.
Benefits of Wi-Fi 6 (Fi6) and Wi-Fi 10 (A10)
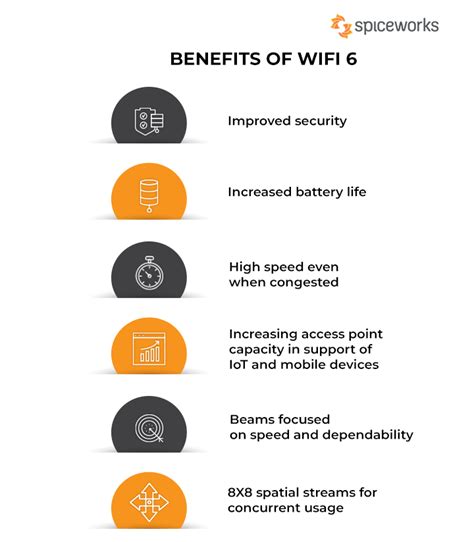
Real-World Applications of Wi-Fi 6 (Fi6) and Wi-Fi 10 (A10)
Gallery of Wi-Fi 6 and Wi-Fi 10
Wi-Fi 6 and Wi-Fi 10 Image Gallery






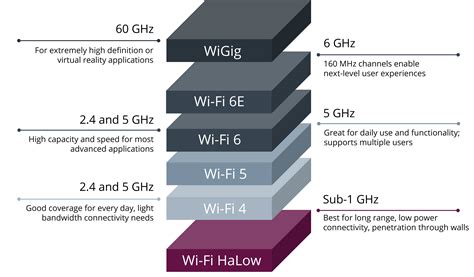
What is the main difference between Wi-Fi 6 and Wi-Fi 10?
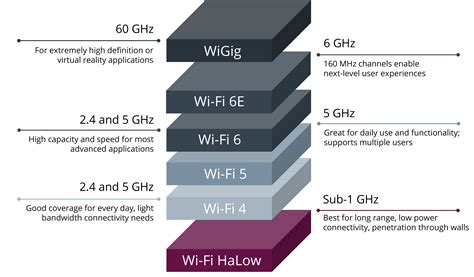
+The main difference between Wi-Fi 6 and Wi-Fi 10 is the introduction of a new 6 GHz frequency band in Wi-Fi 10, which provides a cleaner and less congested spectrum.
Which technology offers faster data transfer rates, Wi-Fi 6 or Wi-Fi 10?
+Wi-Fi 10 offers faster data transfer rates, with a maximum throughput of 9.6 Gbps.
What are some of the real-world applications of Wi-Fi 6 and Wi-Fi 10?
+Some of the real-world applications of Wi-Fi 6 and Wi-Fi 10 include smart homes, online gaming, streaming services, and enterprise environments.
Do Wi-Fi 6 and Wi-Fi 10 offer improved security features?
+Yes, both Wi-Fi 6 and Wi-Fi 10 introduce new security features, including improved encryption and authentication protocols.
Can Wi-Fi 6 and Wi-Fi 10 devices be used interchangeably?
+No, Wi-Fi 6 and Wi-Fi 10 devices are not interchangeable, as they operate on different frequency bands and have different technical specifications.
In conclusion, Wi-Fi 6 and Wi-Fi 10 are both powerful technologies that offer improved performance, capacity, and security compared to their predecessors. While Wi-Fi 10 offers a new 6 GHz frequency band and faster data transfer rates, Wi-Fi 6 is still a viable option for many applications. As the demand for high-speed and low-latency internet connectivity continues to grow, it's essential to understand the differences between these technologies and choose the one that best suits your needs. We invite you to share your thoughts and experiences with Wi-Fi 6 and Wi-Fi 10 in the comments below, and to explore our other articles on wireless networking and related topics.
